מאמרים

Agriculture, irrigation and drought induced international migration: Evidence from Mexico
There is now substantial empirical evidence that climatic variability increases international migration, but relatively little is known about the mechanism driving the association and about adaptations that may reduce it. We use detailed data on migrants from Mexico to the U.S. to provide evidence in support of the hypothesis that drought induced migration from Mexico to the U.S. is mediated by agricultural income shocks.
מידע נוסף

Beating the urban heat: Situation, background, impacts and the way forward in China
This paper reviews urban heat (UrHT) challenges following the SBAR (situation, background, assessment and recommendation) framework. The results indicate that heatwaves become more frequent, lasting and intense, especially after 1990s. Above 1960s level, heatwaves across China doubled in both magnitude and frequency by 2018.
מידע נוסף

Climate change increases risk of extreme rainfall following wildfire in the western United States
Post-wildfire extreme rainfall events can have destructive impacts in the western United States. Using two climate model large ensembles, we assess the future risk of extreme fire weather events being followed by extreme rainfall in this region. By mid-21st century, in a high warming scenario (RCP8.5), we report large increases in the number of extreme fire weather events followed within 1 year by at least one extreme rainfall event.
מידע נוסף

GAR Special Report on Drought
The GAR Special Report on Drought 2021 explores the systemic nature of drought and its impacts on achievement of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction, the SDGs and human and ecosystems health and wellbeing. Droughts have deep, widespread and underestimated impacts on societies, ecosystems, and economies.
מידע נוסף

IPCC Sixth Assessment Report - Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change
The IPCC has finalized the third part of the Sixth Assessment Report, Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change, the Working Group III contribution. It was finalized on 4 April during the 14th Session of Working Group III and 56th Session of the IPCC.
מידע נוסף

Impacts of Climate Change on Water Management. Stocktaking, scope for action and strategic fields of action
In December 2020, the German Working Group on Water Issues of the Federal States and the Federal Government (LAWA) prepared a comprehensive report on the concerns, potential responses and strategic fields of action in water resources management, updating the previous work released in 2017.
מידע נוסף

Policy Brief: Gender-Responsive Disaster Risk Reduction
This policy brief explores challenges faced in gender-responsive disaster risk reduction. Gender inequality, coupled with climate and environment crises, is the greatest sustainable development challenge of the present time.
מידע נוסף

Plan of approach for exceptional low water events in the Meuse basin
The Meuse International River Basin District faced several consecutive years of the summer drought between 2017 and 2020. In order to be able to adapt to these events, which are likely to occur more often because of climate change, the International Meuse Commission has drafted a plan of approach to deal with exceptional low water events, published at the end of 2020.
The document aims to answer three questions:
What is an exceptional low-water event in the Meuse basin?
What are their con
מידע נוסף
The document aims to answer three questions:
What is an exceptional low-water event in the Meuse basin?
What are their con

IPCC Sixth Assessment Report - Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability
The IPCC has finalized the second part of the Sixth Assessment Report, Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability, the Working Group II contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report. It was finalized on 27 February 2022 during the 12th Session of Working Group II and 55th Session of the IPCC.
מידע נוסף

Nature-based solutions and global climate protection: Assessment of their global mitigation potential and recommendations for international climate policy
Nature-based Solutions (NbS) build synergies between biodiversity conservation and societal challenges such as climate change. This paper derives a working definition of NbS based on an evaluation of existing definitions. It assesses the global mitigation and adaptation potential of NbS in relevant studies for forests, croplands, grasslands, terrestrial and coastal wetlands as well as settlements. Recommendations for international climate policy are derived.
מידע נוסף

UK Climate Change Risk Assessment 2022
As required by the Climate Change Act 2008, the UK government has undertaken the third five-year assessment of the risks of climate change on the UK. This is based on the Independent Assessment of UK Climate Risk, the statutory advice provided by the Climate Change Committee (CCC), commissioned by the UK government and devolved administrations.
מידע נוסף

Assessment Frameworks of Nature-based Solutions for Climate Change Adaptation and Disaster Risk Reduction
Nature-based solutions (NBS) play an important and increasing role in both adaptation and disaster risk management. This is also recognized within several global and European agreements and policies (e.g., UN’s SFDRR, EU Green Deal, the EU Adaptation Strategy) which embed NBS as a means to address climate change adaptation (CCA) and disaster risk reduction (DRR) as well as other societal challenges (e.g., biodiversity loss, climate mitigation). This calls for fit-for-purpose assessments, which c
מידע נוסף

Beating the Heat: A Sustainable Cooling Handbook for Cities
Beating the Heat: A Sustainable Cooling Handbook for Cities, states that by the end of this century, many cities could warm as much as 4 °C if GHG emissions continue at high levels. Even at 1.5°C of warming, 2.3 billion people could be vulnerable to severe heat waves. The new guide offers planners an encyclopedia of proven options to help cool cities.
מידע נוסף

The way forward: Supporting climate adaptation in coastal towns and small cities
This article summarizes and reflects upon the work presented in ‘The Unusual Suspects in Climate Change Adaptation – Small Coastal Cities and Towns’ special issue. Across the special issue the challenge of adapting coastal towns and small cities to the impacts of climate change was clearly evident. In order to address some of the challenges, an initial way forward is outlined here to act as a pathway for future research. The areas requiring particular focus include: building a network of coastal
מידע נוסף

IPCC Sixth Assessment Report - AR6 Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis
The Working Group I contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report addresses the most up-to-date physical understanding of the climate system and climate change, bringing together the latest advances in climate science, and combining multiple lines of evidence from paleoclimate, observations, process understanding, and global and regional climate simulations.
מידע נוסף

Rethinking resilient agriculture: From Climate-Smart Agriculture to Vulnerable-Smart Agriculture
Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA) is seeking to overcome the food security problem and develop rural livelihoods while minimizing negative impacts on the environment. However, when such synergies exist, the situation of small-scale farmers is often overlooked, and they are unable to implement new practices and technologies. Therefore, the main aim of this study is to improve CSA by adding the neglected but very important element “small-scale farmer”, and introduce Vulnerable-Smart Agriculture (VSA
מידע נוסף

Index for climate change adaptation in China and its application
With the increasing awareness of the risks and impacts of climate change, scholars tend to pay more attention to the applications of indicators, which access the effectiveness of climate change adaptation. This study aims to evaluate the overall progress of climate change adaptation in China during 2010‒2018 in a quantitative manner. The Index for Climate Change Adaptation in China (ICCAC) has been thus developed by adopting the analytic hierarchy process weighting and expert scoring method. Nam
מידע נוסף

The impact of climate change on mental health and emotional wellbeing: current evidence and implications for policy and practice
Climate change and mental health are two of the most significant and pressing challenges facing societies across the world. Yet, growing awareness of these global issues has not been met with sufficient action to mitigate their impacts. Mental illness – or the disabling effects of distress – already affects around a billion people globally, while the effects of climate change are increasingly apparent. Both of these issues are projected to increase and stand to affect many more people without su
מידע נוסף

The impact of climate change on mental health and emotional wellbeing: current evidence and implications for policy and practice
Climate change and mental health are two of the most significant and pressing challenges facing societies across the world. Yet, growing awareness of these global issues has not been met with sufficient action to mitigate their impacts. Mental illness – or the disabling effects of distress – already affects around a billion people globally, while the effects of climate change are increasingly apparent. Both of these issues are projected to increase and stand to affect many more people without su
מידע נוסף

Independent Assessment of UK Climate Risk-Advice to Government For the UK's third Climate Change Risk Assessment
The Adaptation Committee’s Independent Assessment of UK Climate Risk sets out the priority climate change risks and opportunities for the UK. The report draws on an extensive programme of analysis, consultation and consideration by the Committee involving over 450 people, 130 organisations and more than 1,500 pages of evidence and analysis
מידע נוסף

Business-as-usual will lead to super and ultra-extreme heatwaves in the Middle East and North Africa
Global climate projections suggest a significant intensification of summer heat extremes in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA). To assess regional impacts, and underpin mitigation and adaptation measures, robust information is required from climate downscaling studies, which has been lacking for the region. Here, we project future hot spells by using the Heat Wave Magnitude Index and a comprehensive ensemble of regional climate projections for MENA. Our results, for a business-as-usual path
מידע נוסף

Changing Lengths of the Four Seasons by Global Warming
How long will the four seasons be by 2100? Increasing evidence suggests that the length of a single season or in regional scales has changed under global warming, but a hemispherical-scale response of the four seasons in the past and future remains unknown. We find that summer in the Northern Hemisphere midlatitudes has lengthened, whereas winter has shortened, owing to shifts in their onsets and withdrawals, accompanied by shorter spring and autumn. Such changes in lengths and onsets can be mai
מידע נוסף

Climate and Environmental Change in the Mediterranean Basin Current Situation and Risks for the Future - 1st Mediterranean Assessment Report
The First Mediterranean Assessment Report (MAR1) prepared by the independent network of Mediterranean Experts on Climate and environmental Change (MedECC) founded in 2015 is now finished.
MedECC assesses the best available scientific knowledge on climate and environmental change and associated risks in the Mediterranean Basin in order to render it accessible to policymakers, stakeholders and citizens. The report includes a Summary for Policymakers (SPM), which comprises the key messages of the
מידע נוסף
MedECC assesses the best available scientific knowledge on climate and environmental change and associated risks in the Mediterranean Basin in order to render it accessible to policymakers, stakeholders and citizens. The report includes a Summary for Policymakers (SPM), which comprises the key messages of the

Climate change strategic narratives in the United Kingdom: Emergency, Extinction, Effectiveness
Achieving policy, business and behaviour change necessary to mitigate climate change is one of the most formidable challenges of the twenty-first century. Increasingly, researchers have argued that communicating purposively designed stories – ‘strategic narratives’ – may be effective in building support for the policy measures necessary to limit anthropogenic warming to 2˚C above pre-industrial levels
מידע נוסף

United Nations Climate Change Annual Report 2019
Greater efforts are required to adapt to the impacts of climate change and to
protect people and the planet. The UNFCCC interacts with governments and
partners in searching for ways to increase developing countries’ capacity to adapt.
This year in adaptation was marked by the secretariat’s provision of support to
countries for developing their national adaptation plans, the work of the
Adaptation Committee on climate finance, the enhancement of partnerships
under the Nairobi work programme
מידע נוסף
protect people and the planet. The UNFCCC interacts with governments and
partners in searching for ways to increase developing countries’ capacity to adapt.
This year in adaptation was marked by the secretariat’s provision of support to
countries for developing their national adaptation plans, the work of the
Adaptation Committee on climate finance, the enhancement of partnerships
under the Nairobi work programme

מגמות השינוי בטמפרטורה בישראל, תחזיות עד 2100
בדו"ח "שינויי אקלים בישראל מגמות עבר ומגמות חזויות במשטר הטמפרטורות והמשקעים"
דו"ח מחקר מס' 0000075-2019-0804-4000 ,נובמבר 2019 ,השירות המטאורולוגי( אותו פרסמנו
בסוף שנה שעברה, מוצגת השתנות הטמפרטורה עבור שני תרחישים, (האחד מתון 5.RCP4 והשני
קיצוני יותר 5.RCP8 )בו האנושות אינה נוקטת בשום פעולה לצמצום גזי החממה. השתנות
הטמפרטורה הוצגה לשני תרחישים אלו עד שנת 2050.
בעבודה הנוכחית אנו מרחיבים את חישוב מגמות השינוי החזויות, לאותם שני תרחישים, עד שנת
2100.
מידע נוסף
דו"ח מחקר מס' 0000075-2019-0804-4000 ,נובמבר 2019 ,השירות המטאורולוגי( אותו פרסמנו
בסוף שנה שעברה, מוצגת השתנות הטמפרטורה עבור שני תרחישים, (האחד מתון 5.RCP4 והשני
קיצוני יותר 5.RCP8 )בו האנושות אינה נוקטת בשום פעולה לצמצום גזי החממה. השתנות
הטמפרטורה הוצגה לשני תרחישים אלו עד שנת 2050.
בעבודה הנוכחית אנו מרחיבים את חישוב מגמות השינוי החזויות, לאותם שני תרחישים, עד שנת
2100.

תכנית פעולה היערכות לשינויי אקלים - תל אביב יפו - 2020
התכנית ממפה את שינויי האקלים הצפויים ואת השפעתם על העיר, על האוכלוסייה ועל מערך השירותים והסביבה הפיזית.
מתוך ניתוח התחזיות והתרחישים, זיהינו שתי משימות מפתח לעשור הקרוב: קירור העיר וניהול המים.
לצורך מימושן, קבענו מגוון כלים ופעולות, כדי להבטיח את המשך איכות החיים בעיר, למרות שינויי האקלים.
מידע נוסף
מתוך ניתוח התחזיות והתרחישים, זיהינו שתי משימות מפתח לעשור הקרוב: קירור העיר וניהול המים.
לצורך מימושן, קבענו מגוון כלים ופעולות, כדי להבטיח את המשך איכות החיים בעיר, למרות שינויי האקלים.

Collaboratively Developing Tools for Climate Change Adaptation-Lessons for Research and Policy
Climate change is causing extreme weather events to increase in frequency and intensity, putting cities, home to most of Europe’s population, at rapidly increasing risk
מידע נוסף

Collaboratively Developing Tools for Climate Change Adaptation-Lessons for Research and Policy
Climate change is causing extreme weather events to increase in frequency and intensity, putting cities, home to most of Europe’s population, at rapidly increasing risk
מידע נוסף

What is ecosystem-based adaptation
Healthy ecosystems can reduce the negative impacts of climate change. For instance, coastal habitats like mangroves provide natural flood defences, well-protected lakes retain water sources during droughts, and healthy forests reduce the risk of devastating wildfires. Ecosystem-based adaptation (EbA) is an approach that uses these ecosystem services as part of a holistic adaptation strategy. Often through win-win outcomes, EbA protects vulnerable communities from extreme weather while simultaneo
מידע נוסף

Accelerating invasion potential of disease vector Aedes aegypti under climate change
Vector-borne diseases remain a major contributor to the global burden of disease, while climatechange is expected to exacerbate their risk. Characterising vector development rate and its spatio-temporal variation under climate change is central to assessing the changing basis of human disease risk. We develop a mechanistic phenology model and apply it to Aedes aegypti, an invasive mosquito vector for arboviruses (e.g. dengue, zika and yellow fever).
מידע נוסף

Shifting to climate change aware cities to facilitate the city resilience implementation
Climate change (CC) is one of the most urgent threats to modern societies, having direct and indirect consequences on the rapid growth of urban areas. Cities are attempting to both reduce their impact on the environment and build resilience to be able to face the irreversible effects of CC through plans and strategies
מידע נוסף

The Dasgupta Review – Independent Review on the Economics of Biodiversity- Interim Report
The independent Review will explore the sustainability of our engagements with Nature – what we take from it; how we transform what we take from it and return to it; why we have disrupted Nature’s processes; and what we must urgently do differently to enhance our collective wealth and well-being, and that of our descendants
מידע נוסף

-Common Ground Between the Paris Agreement and the Sendai Framework - Climate Change Adaptation and Disaster Risk Reduction
Countries are faced with the growing challenge of managing increasing risks from climate change and climate variability, putting development and the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals at risk. The adoption in 2015 of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction and the Paris Agreement on climate change provides a clear mandate for increased coherence in countries’ approaches to climate and disaster risk reduction
מידע נוסף

Common Ground Between the Paris Agreement and the Sendai Framework-Climate Change Adaptation and Disaster Risk Reduction
Countries are faced with the growing challenge of managing increasing risks from climate change and climate variability, putting development and the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals at risk. The adoption in 2015 of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction and the Paris Agreement on climate change provides a clear mandate for increased coherence in countries’ approaches to climate and disaster risk reduction
מידע נוסף

The projected timing of abrupt ecological disruption from climate change
As anthropogenic climate change continues the risks to biodiversity will increase over time, with future projections indicating that a potentially catastrophic loss of global biodiversity is on the horizon1,2,3. However, our understanding of when and how abruptly this climate-driven disruption of biodiversity will occur is limited because biodiversity forecasts typically focus on individual snapshots of the future. Here we use annual projections (from 1850 to 2100) of temperature and precipitati
מידע נוסף

How our responses to climate change and the coronavirus are linked
The coronavirus pandemic may lead to a deeper understanding of the ties that bind us on a global scale
מידע נוסף

UNDRR Annual Report 2019
Annual report for the United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction 2019
מידע נוסף

The Global Risks Report 2020
The Global Risks Report 2020 presents the major risks the world will be facing in the coming year. The global economy is facing an increased risk of stagnation, climate change is striking harder and more rapidly than expected
מידע נוסף

Climate risk and response: Physical hazards and socioeconomic impacts
In this report, we look at the physical effects of our changing climate. We explore risks today
and over the next three decades and examine cases to understand the mechanisms through
which physical climate change leads to increased socioeconomic risk
מידע נוסף
and over the next three decades and examine cases to understand the mechanisms through
which physical climate change leads to increased socioeconomic risk

Building urban resilience with nature-based solutions: How can urban planning contribute?
Cities face increasing environmental, social and economic challenges that together threaten the resilience of urban areas and the residents who live and work there. These challenges include chronic stresses and acute shocks, amplified by climate change impacts. Nature-based solutions have emerged as a concept for integrating ecosystem-based approaches to address a range of societal challenges
מידע נוסף

Climate Finance and Sustainable Cities
The theme of the 2019 SCF Forum was “Climate finance and sustainable cities”. The objective of the Forum was to enhance understanding of how to accelerate the mobilization and delivery of climate finance for the development of sustainable cities
מידע נוסף

Yearbook of global climate Action 2019
The Yearbook identifies opportunities and challenges for mitigation and resilience in the seven thematic areas of the Marrakech Partnership (land use, oceans and coastal zones, water, human settlements, transport, energy and industry) and the cross-cutting area of finance
מידע נוסף

Meeting the looming policy challenge of sea-level change and human migration
Minimizing the adverse consequences of sea-level change presents a key societal challenge. New modelling is necessary to examine the implications of global policy decisions that determine future greenhouse gas emissions and local policies around coastal risk that influence where and how we live
מידע נוסף

2019 - IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate
The latest Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Special Report
highlights the urgency of prioritizing timely, ambitious and coordinated action to address
.unprecedented and enduring changes in the ocean and cryosphere
מידע נוסף
highlights the urgency of prioritizing timely, ambitious and coordinated action to address
.unprecedented and enduring changes in the ocean and cryosphere

The Role of Green Infrastructures in Urban Planning for Climate Change Adaptation
The population that lives in cities has surpassed the one that lives in the countryside. Cities are recognized as apriority source of pollution. The degradation of air quality and the phenomenon of Urban Heat Island (UHI) are some of the most well-known consequences of urban development. The adaptation of the cities is emerging as one of the greatest challenges that urban planners will face in this century. Urban Green Infrastructures (GIs) could help cities adapt to climate change
מידע נוסף

UN 2019 sixth Global Environment Outlook: GEO-6 - Summary for Policymakers
UN Environment’s sixth Global Environment Outlook (2019) calls on decision makers to take immediate action to address pressing environmental issues to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals as well as other Internationally Agreed Environment Goals, such as the Paris Agreement
מידע נוסף

Accelerating Climate Action
This report builds on the OECD Well-being Framework and applies a new perspective that analyses synergies and trade-offs between climate change mitigation and broader goals such as health, education, jobs, as well as wider environmental quality and the resources needed to sustain our livelihoods through time
מידע נוסף

Business Climate Resilience: Thriving Through the Transformation
WBCSD’s report brings together important global developments and latest thinking on climate adaptation and resilience, with particular focus on private sector climate resilience. It builds on the need for businesses to prepare for both the physical risks that are associated with climate change, as well as the associated transitional risks on the path towards a net-zero economy
מידע נוסף

The Global Risks Report 2019
The Global Risks Report 2019 is published against a backdrop of worrying geopolitical and geo-economic tensions. If unresolved, these tensions will hinder the world’s ability to deal with a growing range of collective challenges
מידע נוסף

The Global Climate in 2015–2019
Compared to the previous five-year assessment period 2011–2015, the current five-year period 2015–2019 has seen a continued increase in carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions
and an accelerated increase in the atmospheric concentration of major greenhouse
gases (GHGs), with growth rates nearly 20% higher
מידע נוסף
and an accelerated increase in the atmospheric concentration of major greenhouse
gases (GHGs), with growth rates nearly 20% higher

Challenges to natural and human communities from surprising ocean temperatures
Based on historical and lived experience, people expect certain conditions to prevail in the ecosystems they depend upon. Climate change is now introducing strong trends that push conditions beyond historic levels. Using ocean ecosystems as a case study, we show that the frequency of surprising temperatures is increasing faster than expected. We then use these events as motivation to develop a theory for how temperature trends and events will impact natural and human communities
מידע נוסף

A Land Without Water
Climate change, waves of refugees and poor planning are draining water supplies
in Jordan
מידע נוסף
in Jordan

Changing climate both increases and decreases European river floods
Climate change has led to concerns about increasing river floods resulting from the greater water-holding capacity of a warmer atmosphere. These concerns are reinforced by evidence of increasing economic losses associated with flooding in many parts of the world, including Europe
מידע נוסף

Valuing the Global Mortality Consequences of Climate Change Accounting for Adaptation Costs and Benefits
We develop empirically-grounded estimates of willingness-to-pay to avoid excess mortality risks caused by climate change. Using 40 countries' subnational data, we estimate a mortality-temperature relationship that enables global extrapolation to countries without data and projection of its future evolution, accounting for adaptation benefits. Further, we develop a revealed preference approach to recover unobserved adaptation costs
מידע נוסף

Tens of thousands additional deaths annually in cities of China between 1.5 °C and 2.0 °C warming
The increase in surface air temperature in China has been faster than the global rate, and more high temperature spells are expected to occur in future. Here we assess the annual heat-related mortality in densely populated cities of China at 1.5 °C and 2.0 °C global warming
מידע נוסף

Adaptive responses of animals to climate change are most likely insufficient
Biological responses to climate change have been widely documented across taxa and regions, but it remains unclear whether species are maintaining a good match between phenotype and environment, i.e. whether observed trait changes are adaptive. Here we reviewed 10,090 abstracts and extracted data from 71 studies reported in 58 relevant publications, to assess quantitatively whether phenotypic trait changes associated with climate change are adaptive in animals
מידע נוסף

The imperative of climate action to protect human health in Europe
The report focuses on the consequences of climate change for human health in Europe and the benefits of acting now to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in order to stabilise the climate
מידע נוסף

Microbiologists' Warning to Humanity: microorganisms and climate change
This Consensus Statement documents the central role and global importance of microorganisms In climate change biology
מידע נוסף

Managed retreat as a strategy for climate change adaptation in small communities: public health implications
In coming decades, sea level rise associated with climate change will make some communities uninhabitable. Managed retreat, or planned relocation, is a proactive response prior to catastrophic necessity. Managed retreat has disruptive health, sociocultural, and economic impacts on communities that relocate. Health impacts include mental health, social capital, food security, water supply, sanitation, infectious diseases, injury, and health care access
מידע נוסף

Monitoring and Evaluation Indicators for Climate Change-Related Health Impacts, Risks, Adaptation, and Resilience
Climate change poses a range of current and future health risks that health professionals need to understand, track, and manage. However, conventional monitoring and evaluation (M&E) as practiced in the health sector, including the use of indicators, does not adequately serve this purpose. Improved indicators are needed in three broad categories: (1) vulnerability and exposure to climate-related hazards; (2) current impacts and projected risks; and (3) adaptation processes and health system resi
מידע נוסף

Climate Change, Impacts and Vulnerability in Europe 2016 - An Indicator-based Report
This report is an indicator-based assessment of past and projected climate change and its impacts on ecosystems and society. It also looks at society’s vulnerability to these impacts and at the development of adaptation policies and the underlying knowledge base.
מידע נוסף

Communicating Climate Change Adaptation and Resilience
Communicating the impacts of climate change and possible adaptive responses is a relatively recent branch of the larger endeavor of climate change communication. This recent emergence, in large part, is driven by the fact that the impacts and policy/planning/practice responses have only recently emerged in more widespread public consciousness and discourse, and thus in scholarly treatment
מידע נוסף

Climate Change Adaptation in Pacific Countries: Fostering Resilience Through Gender Equality
Women and girls are disproportionately affected by the impacts of climate change in the Pacific due to prevailing gender inequalities. Meanwhile, the participation and leadership of women in climate change adaptation has been identified globally as critical for fostering resilience in families, communities and nations
מידע נוסף

Adapting to Climate Change: The Remarkable Decline in the US Temperature-Mortality Relationship over the Twentieth Century
This paper examines the temperature-mortality relationship over the course of the twentieth-century United States both for its own interest and to identify potentially useful adaptations for coming decades. There are three primary findings. First, the mortality impact of days with mean temperature exceeding 80°F declined by 75 percent. Almost the entire decline occurred after 1960. Second, the diffusion of residential air conditioning explains essentially the entire decline in hot day–related fa
מידע נוסף

Climate Change Legislation in Israel
Israel faces a number of challenges that require clear and robust energy and climate policies – including an average population growth rate of 1.8% per year (2000-2010), soaring energy demand and high emissions per capita (despite negligible total emissions). It is also an arid, coastal country exposed to climate-related risks, mainly water shortages and sea level rise. Regulatory developments in the last few years have been informed by both international and domestic processes, including the pr
מידע נוסף

Adapting to climate change: 2013 strategy for exercising the adaptation reporting power
he adaptation reporting power under the Climate Change Act 2008 aims to ensure that climate change risk management is systematically undertaken by reporting authorities. This aims to help ensure that public service and infrastructure are resilient to climate change, and to monitor the level of preparedness of key sectors to climate change.
The 2013 strategy for the adaptation reporting power has been developed after discussions with stakeholders and consideration of consultation responses. Th
מידע נוסף
The 2013 strategy for the adaptation reporting power has been developed after discussions with stakeholders and consideration of consultation responses. Th

Climate adaptation reporting second round: UK Power Networks
Progress report by UK Power Networks on their climate change adaptations. This report sets out their progress in adapting to the current and future predicted effects of climate change on their organisation.
This report was invited by Defra under the adaptation reporting power under the Climate Change Act 2008.

The Economic Consequences of Climate Change
This report provides a new detailed quantitative assessment of the consequences of climate change on economic growth through to 2060 and beyond. It focuses on how climate change affects different drivers of growth, including labour productivity and capital supply, in different sectors across the world. The sectoral and regional analysis shows that while the impacts of climate change spread across all sectors and all regions, the largest negative consequences are projected to be found in the heal
מידע נוסף

Overview of challenges and achievements in the climate adaptation of cities and in the Climate Proof Cities program
Despite all international, national and local initiatives to mitigate climate change, a certain degree of climate change is unavoidable. Urban environments in particular seem vulnerable to the consequences of climate change. How can cities, which are dynamic systems where most people live and work, prepare for such changes in climate? In the Netherlands, the Climate Proof Cities (CPC) research program (2010–2014) was established, aimed at: “strengthening the adaptive capacity and reducing the vu
מידע נוסף

Impacts of Climate Change on Vector Borne Diseases in the Mediterranean Basin — Implications for Preparedness and Adaptation Policy
The Mediterranean region is vulnerable to climatic changes. A warming trend exists in the basin with changes in rainfall patterns. It is expected that vector-borne diseases (VBD) in the region will be influenced by climate change since weather conditions influence their emergence. For some diseases (i.e., West Nile virus) the linkage between emergence andclimate change was recently proved; for others (such as dengue) the risk for local transmission is real. Consequently, adaptation and preparati
מידע נוסף

French National Climate Change Impact Adaptation Plan
The first French National Adaptation Plan aims to plan adaptation actions, prevent inappropriate adaptation and ensure consistency across public policy measures relating to adaptation. It aims to present measures designed to help France prepare for and exploit new climatic conditions in France for the next five years, covering the period 2011-2015.
מידע נוסף

Systematic review approaches for climate change adaptation research
Recent controversy has led to calls for increased standardization and transparency in the methods used to synthesize climate change research. Though these debates have focused largely on the biophysical dimensions of climate change, human dimensions research is equally in need of improved methodological approaches for research synthesis. Systematic review approaches, and more recently realist review methods, have been used within the health sciences for decades to guide research synthesis. Despi
מידע נוסף

ENERGY DARWINISM II- Why a Low Carbon Future Doesn’t Have to Cost the Earth
Up to $44 trillion could be going up in smoke if the world does not act on climate change, according to the latest piece of research from U.S. banking giant Citigroup. The report – Energy Darwinism II: Why a Low Carbon Future Doesn't Have to Cost the Earth -- has forecast that spending on energy will hit around $200 trillion in the next 25 years. The study then examines two scenarios: one that Citi describe as an "'inaction' on climate change scenario", and another that looks at what could happen if a low carbon, "different energy mix" is pursued.
מידע נוסף

Climate Change Risks and Adaptation: Linking Policy and Economics
Climate change is giving rise to diverse risks, ranging from changing incidences of tropical diseases to increased risks of drought, varying widely in their potential severity, frequency and predictability. Governments must integrate the management of these climate risks into policy making if they are to successfully adapt to a changing climate. Economic analysis has a vital role to play in supporting these efforts, by identifying costs and benefits and supporting decision-making for an uncertain future. However, this analysis needs to be adapted to the institutions, policies and climate risks in a given country. Building on the experience of OECD countries, this report sets out how the latest economic evidence and tools can enable better policy making for adaptation.
מידע נוסף

The Role of the 2015 Agreement in Enhancing Adaptation to Climate Change
Adaptation responses are needed to address the existing levels of climate variability and to prepare for future climate impacts. There is wide agreement that adaptation is an important issue and would benefit from being enhanced through more effective action and better planning. The prominence of adaptation in the UNFCCC negotiations has increased, in part as the scientific evidence has become clearer that climate change is occurring and its impacts are projected to grow in future. Efforts to enhance adaptation actions and increase resilience are thus expected to play a key role in the post-2020 climate agreement to be agreed at COP21 in December 2015. This paper explores how the 2015 agreement can help to foster enhanced policies and co-ordinate planning for greater resilience and adaptation capabilities at the national level. The paper considers the technical advantages and disadvantages of selected adaptation-related concepts that have been put forward in the negotiations. These include proposals for global or national goals; developing or improving adaptation institutions or planning; enhancing information availability; and facilitating or enhancing adaptation finance. Many of these proposals have the potential to improve sub-national, national and international planning about and responses to climate adaptation. However, the actual impact of these proposals is likely to vary significantly depending on how they are implemented on the ground.
מידע נוסף

OECD, IEA Provide Overview of First 29 INDCs
September 2015: The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and International Energy Agency (IEA) have published a report, titled 'Overview of INDCs Submitted by 31 August 2015,' which summarizes the key information communicated in countries' intended nationally determined contributions (INDCs) submitted under the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). The report examines the mitigation components of INDCs that had been submitted by 31 August 2015, analyzing their clarity and transparency as well as the likely aggregate impact on greenhouse (GHG) emissions. The report was authored by Christina Hood (IEA), Liwayway Adkins (IEA)and Ellina Levina (IEA). On the transparency and clarity of the INDCs, the report assesses the nature of the goals, whether absolute emission reduction targets or relative to a baseline; and whether economy-wide or sectoral. It also looks at the conditions attached to some of the INDCs, particularly relating to the availability of international support.The report also analyzes the mitigation ambition of the INDCs, using four studies that have undertaken assessments of the INDCs.
מידע נוסף

The GLOBE climate legislation study: a review of climate change legislation in 66 countries
This document is the product of an ongoing co-operation between GLOBE
International and the Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the
Environment at the London School of Economics. It was financially supported by
(the United Kingdom’s Foreign & Commonwealth Office (FCO).
מידע נוסף
International and the Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the
Environment at the London School of Economics. It was financially supported by
(the United Kingdom’s Foreign & Commonwealth Office (FCO).

Climate Adaptation: Seizing the Challenge
The World Economic Forum’s Global Agenda Council on Climate Change’s report, Climate Adaptation: Seizing the Challenge, captures some of the latest thinking in the field of climate adaptation and financing, with the goal of assisting decision-makers in the public and private sectors gain a better understanding of the issue
מידע נוסף

Climate change adaptation and water resourc emanagement: A review of the literature
This paper considers the extent and usefulness of the existing empirical literature on water supply, demand, and adaptation to climate change for incorporation into integrated assessment modeling efforts. We review the existing literature on the likely economic impacts of climate change, acting through water supply and demand effects in specific river basins, and the ability of adaptation to mitigate those impacts. Since adaptive responses will be implemented largely by local, regional, and nati
מידע נוסף

Adaptive climate change governance for urban resilience
Climate change poses new challenges to cities and new flexible forms of governance are required that are able to take into account the uncertainty and abruptness of changes. The purpose of this paper is to discuss adaptive climate change governance for urban resilience. This paper identifies and reviews three traditions of literature on the idea of transitions and transformations, and assesses to what extent the transitions encompass elements of adaptive governance. This paper uses the open sour
מידע נוסף

Building Resilience against Climate Effects—A Novel Framework to Facilitate Climate Readiness in Public Health Agencies
Climate change is anticipated to have several adverse health impacts. Managing these risks to public health requires an iterative approach. As with many risk management strategies related to climate change, using modeling to project impacts, engaging a wide range of stakeholders, and regularly updating models and risk management plans with new information—hallmarks of adaptive management—are considered central tenets of effective public health adaptation. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has developed a framework, entitled Building Resilience Against Climate Effects, or BRACE, to facilitate this process for public health agencies. Its five steps are laid out here. Following the steps laid out in BRACE will enable an agency to use the best available science to project likely climate change health impacts in a given jurisdiction and prioritize interventions. Adopting BRACE will also reinforce public health’s established commitment to evidence-based practice and institutional learning, both of which will be central to successfully engaging the significant new challenges that climate change presents.
מידע נוסף

USACE Climate Preparedness and Resilience Policy Statement
The Policy Statement says that "Mainstreaming climate change adaptation means that it will be considered at every step in the project life cycle for all USACE projects, both existing and planned… to reduce vulnerabilities and enhance the resilience of our water-resource infrastructure."The Policy Statement establishes the Assistant Secretary of the Army (Civil Works) as the agency official responsible for ensuring implementation of all aspects of this policy. Through this policy, USACE establishes the USACE Committee on Climate Preparedness an Resilience to oversee and coordinate agency-wide climate change adaptation planning and implementation. The Committee is chaired by the Chief, Engineering and Construction.
מידע נוסף

Protecting Health from Climate Change in the WHO European Region
“How far are we in the WHO European Region in implementing action to counter the health impacts of climate change?” This was the question posed to representatives of Member States in the WHO European Region of in the WHO working group on health in climate change (HIC). Twenty-two Member States provided answers to a comprehensive 2012 questionnaire that focused on eight thematic areas (governance; vulnerability, impact and adaptation (health) assessments (VIA); adaptation strategies and action plans; climate change mitigation; strengthening health systems; raising awareness and building capacity; greening health services; and sharing best practices). Strong development has been in climate change vulnerability and impact assessments, as well as strengthening health systems and awareness raising. Areas where implementation would benefit from further action are the development of national health adaptation plans, greening health systems, sharing best practices and reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in other sectors. At the Fifth Ministerial Conference on Environment and Health in Parma, Itatly in 2010, the European Commitment to Act on climate change and health and the European Regional Framework for Action to protect health from climate change were endorsed by the fifty-three European Member States. The results of this questionnaire present the most comprehensive assessment so far of progress made by European Member States to protect public health from climate change since the Parma Conference agreements.
מידע נוסף

FY 2015 National Water Program Guidance
The National Water Program released the final FY 2015 National Water Program Guidance Addendum (published 4/2014). The entire NWPG can be viewed as one document on the EPA's Office of the Chief Financial Officer's website.
מידע נוסף

United Kingdom national adaptation programme: Making the country resilient to a changing climate
This report outlines the steps government, businesses and communities are already taking to address the most severe and urgent threats of climate change, as identified by Defra last year in its Climate Change Risk Assessment
מידע נוסף

Climate Change And President Obama's Action Plan
The United States is leading global efforts to address the threat of climate change. President Obama is taking the biggest step yet to combat climate change by finalizing America’s Clean Power Plan, which sets the first-ever carbon pollution standards for power plants.
מידע נוסף

Flood risk in Europe: the long-term outlook
Floods, storms and other hydro-meteorological events account for around two thirds of the damage costs of natural disasters, and these costs have increased since 1980, according to a recent EEA assessment of climate change impacts in Europe.The observed increase in damage costs from extreme weather events is mainly due to land use change, increases in population, economic wealth and human activities in hazard-prone areas and to better reporting. To confirm the exact role played by climate change in flooding trends in past decades, it would be necessary to have more reliable, long-time series data for rivers with a natural flow regime.
מידע נוסף

Rural Households in a Changing Climate
This paper argues that climate change poses two distinct, if related, sets of chenges for poor rural households: chenges related to the increasing frequency and severity of weather shocks and chenges related to long-term shifts in temperature, rainf patterns, water availability, and other environmental factors Within this framework, the paper examines evidence from existing empirical literature to compose an initial picture of household-level strategies for adapting to climate change in rural settings The authors find that although households possess numerous strategies for managing climate shocks and shifts, their adaptive capacity is insufficient for the task of maintaining—let alone improving—household welfare They describe the role of public policy in fortifying the ability of rural households to adapt to a changing climate
מידע נוסף

On Welfare Frameworks and Catastrophic Climate Risks
Recent theoretical work in the economics of climate change has suggested that climate policy is highly sensitive to ‘fat-tailed’ risks of catastrophic outcomes (Weitzman, 2009) [68]. Such risks are suggested to be an inevitable consequence of scientific uncertainty about the effects of increased greenhouse gas concentrations on climate. Criticisms of this controversial result fall into three categories: The first suggests that it may be irrelevant to cost benefit analysis of climate policy, the second challenges the fat-tails assumption, and the third questions the behavior of the utility function assumed in the result. This paper analyses these critiques and suggests that those in the first two categories have formal validity, but that they apply only to the restricted setup of the original result, which may be extended to address their concerns. They are thus ultimately unconvincing. Critiques in the third category are shown to be robust however they open up new ethical and empirical challenges for climate economics that have thus far been neglected—how should we ‘value’ catastrophes as a society? I demonstrate that applying results from social choice to this problem can lead to counterintuitive results, in which society values catastrophes as infinitely bad, even though each individual's utility function is bounded. Finally, I suggest that the welfare functions traditionally used in climate economics are ill-equipped to deal with climate catastrophes in which population size changes. Drawing on recent work in population ethics I propose an alternative welfare framework with normatively desirable properties, which has the effect of dampening the contribution of catastrophes to welfare.
מידע נוסף

Climate Change Risk Assessment for the Agriculture Sector
UK agriculture could be significantly affected by climate change Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns, changes in sunshine levels and in concentrations of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2), and increasing frequency of weather events currently considered extreme would all have an impact on operations, productivity and the range of products offered by
the sector
מידע נוסף
the sector

A Structural Land-Use Analysis of Agricultural Adaptation to Climate Change: A Proactive Approach
This article proposes a proactive approach for analyzing agricultural adaptation to climate change wherein agricultural production technologies are regarded as potential targets of research and development (R&D) efforts. We develop a structural land-use model wherein farmers maximize profit by allocating their land among crop-technology bundles. Proactive R&D directions are derived by identifying the technological attributes through which climate change reduces overall agricultural profitability
מידע נוסף

Interactions between climate and habitat loss effects on biodiversity: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Climate change and habitat loss are both key threatening processes driving the global loss in biodiversity. Yet little is known about their synergistic effects on biological populations due to the complexity underlying both processes. If the combined effects of habitat loss and climate change are greater than the effects of each threat individually, current conservation management strategies may be inefficient and at worst ineffective. Therefore, there is a pressing need to identify whether inte
מידע נוסף

Cambridge City Council Carbon Management Plan 2011 - 2016
This updates our first Strategy and Action Plan, which covered the period from 2008-2012. The revised strategy sets out the framework for action by the City Council to manage the risks associated with climate change and contribute towards the global effort to avert future dangerous climate change by reducing carbon dioxide emissions. Key actions contained within this strategy include:
Improving the energy efficiency of council-owned homes
Through development of the Cambridge Local Plan, ensure that new developments meet recognized sustainability standards, ie Level 4 of the Code for Sustainable Homes for residential developments
Working with the County Council to improvement cycling facilities and infrastructure in Cambridge, including cycling parking and new routes
מידע נוסף

Helsinki Metropolitan Area Climate Change Adaptation Strategy
The Helsinki Metropolitan Area Climate Change Adapta
-
tion Strategy has been prepared in close cooperation with
the four cities of the metropolitan area (Helsinki, Espoo,
Vantaa and Kauniainen), the Helsinki Region Environmen
-
tal Services Authority HSY and other municipal, regional
and state level organisations. In the strategy, strategic
starting points and policies with which the metropolitan
area prepares for the consequences of climate change,
are compiled.
מידע נוסף

The Mediterranean City: A Conference on Climate Change Adaptation
The Mediterranean City: A Conference on Climate Change Adaptation will initiate an ongoing collaboration of cities working together to share ideas, needs and strategies to adapt to the current and future impacts of climate change as they similarly affect the five Mediterranean-climate regions of the world. The conference will bring together an international network of experts from the academic, policy, business, public health and government worlds. Mediterranean-climate regions largely occur along the western edges of continents between the 30 degree and 40 degree parallels in both northern and southern hemispheres. The Mediterranean climate, moderated by cold ocean currents offshore, is characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, rainy winters. While these ecosystems cover just under three percent of the earth's land area, they contain about 20 percent of its plant biodiversity, including over 26, 000 endemic species.
מידע נוסף

Integrating Climate Change Adaptation into the Town of Ajax Official Plan
This case study offers insight into how climate change adaptation str
ategies can be main
-
streamed into official documents. It provides background information on how climate
change is expected to affect the Town of Ajax and describes the importance of
mainstreaming climate change initiatives and planning.
The case study con
cludes with lessons learned that may assist other Ontario communities
to adopt action
-
oriented policies to move toward adapting to climate change.
מידע נוסף

International Exchange Governance of Climate Change Adaptation: National Strategies and their Implementation
Climate change
adaptation is becoming more and more relevant in climate
change
governance
.
Certain geographical regions are particular
ly
vulnerable to a changing climate, notably t
he Alpine
space
.
F
or
the
first time
representatives of
seven
Alpine countries
met in
Ittigen
(Switzerland)
on
May 9
,
2012
.
These were
26
p
articipants from Austria, France
,
Germany, Italy, Liechtenstein,
Slovenia and
Switzerland
.
The international exchange was initiated
in the frame of the
ETC Alpine
Space
project C3
-
Alps (Capitalising Climate Change Knowledge for Adaptation in the Alpine Space)
by the Swiss Federal Office for the Environment
,
supported by
the
Environment Agency Austria.
מידע נוסף

Turn Down the Heat: Why a 4°C Warmer World Must Be Avoided
This report, produced for the World Bank by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and Climate Analytics, attempts to describe what climate change impacts are likely to be felt in a ‘4°C world', i.e. a world where global average temperatures have risen four degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. In doing so, it hopes to motivate actors and insert urgency into climate change mitigation and adaptation efforts.
מידע נוסף

Conceptualizing Urban Adaptation to Climate Change: Findings from an Applied Adaptation Assessment Framework
Urban areas have particular sensitivities to climate change, and therefore adaptation to a warming planet represents a challenging new issue for urban policy makers in both the developed and developing world. Further to climate mitigation strategies implemented in various cities over the past 20 years, more recent efforts of urban management have also included actions taken to adapt to increasing temperatures, sea level and extreme events. Through the examination and comparison of seven cities, this paper identifies the various levels of administrative adaptation planning, the tools and information used in making policy choices, and the roles of governance and finance in urban adaptation to climate change. Lessons learned from these seven cases are presented to better inform the next generation of cities adapting to climate change.
מידע נוסף

UK climate change risk assessment: government report
The Government published the UK Climate Change Risk Assessment (CCRA) on 25 January 2012, the first assessment of its kind for the UK and the first in a 5 year cycle. It sets out the main priorities for adaptation in the UK under 5 key themes identified in the CCRA 2012 Evidence Report - Agriculture and Forestry; Business, industries and Services; Health and Wellbeing; Natural Environment and Buildings and Infrastructure - and describes the policy context, and action already in place to tackle
מידע נוסף

Simulation of temperature and precipitation climatology for the Central Asia CORDEX domain using RegCM 4.0
The Coordinated Regional Climate Downscaling Experiment (CORDEX) is a framework designed to coordinate international efforts on regional climate simulations. CORDEX domains encompass the majority of land areas of the world. Region 8 of the CORDEX basically covers Central Asia, with the corners of the domain at 54.76 degrees N, 11.05 degrees E; 56.48 degrees N, 139.13 degrees E; 18.34 degrees N, 42.41 degrees E; and 19.39 degrees N, 108.44 degrees E and with a horizontal resolution of 50 km. In the present study, the results of an experiment with the ICTP regional climate RegCM 4.0 model that was run for seasonal mean air temperature and precipitation total series are presented. The experiment consists of one simulation from 1989 to 2010 using ERA-Interim reanalysis data as the boundary condition, another simulation for the period 1970-2000 using the global climate model ECHAM5 A1B scenario data for forcing, and finally a simulation for the period 2070-2100 using the ECHAM5 A1B scenario projection data for forcing. Between these 3 simulations we determined the temperature and precipitation climatology obtained from RegCM 4.0 downscaling for Region 8 of the CORDEX framework. In spite of the diverse topography of the region, the temperature and precipitation climatology obtained by RegCM 4.0 from hindcast data captures the general characteristics of the climate of Central Asia. In winter, the warm temperature bias of the forcing data is slightly decreased by regional downscaling. The influences of the Indian monsoon system are well represented, as this region covers a large area towards the southern boundary of Region 8, even though the focus of this work was to capture the general characteristics of the whole region.
מידע נוסף

Climate change impacts on international seaports: knowledge, perceptions, and planning efforts among port administrators
Seaports are located in vulnerable areas to climate change impacts: on coasts susceptible to sea-level rise and storms or at mouths of rivers susceptible to flooding. They serve a vital function within the local, regional, and global economy. Their locations in the heart of sensitive estuarine environments make it an imperative to minimize the impacts of natural hazards. Climate impacts, like a projected SLR of .6 m to 2 m and doubling of Category 4 and 5 hurricanes by 2100, will result in more extreme events at many seaports. To assess the current state of knowledge on this issue, we surveyed port authorities from around the world about how administrators felt climate change might impact their operations, what sea-level change would create operational problems, and how they planned to adapt to new environmental conditions. The planned rapid expansion of ports reported by the survey respondents indicates that adaptation measures should be considered as ports construct new infrastructure that may still be in use at the end of the century. Respondents agreed that the ports community needs to address this issue and most felt relatively uninformed about potential climate impacts. Although most ports felt that SLR would not be an issue at their port this century, sea-level rise was nevertheless an issue of great concern. Our results suggest opportunities for the scientific community to engage with port practitioners to prepare proactively for climate change impacts on this sector.
מידע נוסף

Technologies for Climate Change Adaptation – The Water Sector
This guidebook aims to provide expert information on the technologies most relevant for climate change adaptation in the water sector in developing countries.It is meant to be a practical tool for use by a broad range of stakeholders, including those in governmental agencies, water utilities, community water boards, non-governmental organizations, and private sector companies.The guidebook first reviews the projected impacts of climate change on the water sector. It then addresses the role of adaptation in the water sector and six typologies under which available strategies are categorized.Eleven technologies and practices are given detailed treatment in this guidebook and four others are covered briefly. While these do not constitute all of the adaptation technologies available in the water sector, they do represent many of the most important adaptation technologies for developing countries
מידע נוסף

Adapting to Climate Change: Cities and the Urban Poor
Global climate change will have enormous impacts on urban areas in the developing world. The known and growing effects of climate change –increased temperatures, rising seas, and increased incidence of severe storms –will be especially significant for cities due to the location of many along the coast ,the population and capital assets at risk, and the important role of port cities in national economies. This paper explores some of the emerging issues that cities in the developing world confront as they begin to develop plans and strategies to adapt to the effects of global climate change. The emphasis is on low-income populations, both those now settled in cities and those still to migrate from rural areas. In some instances, this migration is due to reduced agricultural productivity, itself a product of global climate change. The urban poor are vulnerable because of where they live and the condition of their shelter. Yet their low incomes, poor access to information, and lack of market alternatives limit their ability to move to safer environments.
מידע נוסף

The Value of Green Infrastructure for Urban Climate Adaptation
In this paper the Center for Clean Air Policy (CCAP) provides information on the costs and benefits of “green” infrastructure solutions for bolstering local adaptation to climate change. The report provides examples of a variety of approaches to incorporating green practices as well as the benefits to urban communities, such as improvements in land value, quality of life, public health, hazard mitigation, and regulatory compliance. A selection of green infrastructure solutions are evaluated for their performance and benefits, discerning their value for climate adaptation. Eco-roofs, green alleys and streets, and urban forestry techniques are examined in detail along with their respective economic cost and benefits. In addition, the report describes managerial, institutional, and market-based approaches to climate resilience, in which local governments can use incentives to lower climate risks and encourage adaptive behavior. Select examples of green infrastructure costs, performance, and benefits from pioneering cities are provided in detail as well.
מידע נוסף

Managing risks and increasing resilience: the Mayor’s climate change adaptation strategy
Managing risks and increasing resilience is the Mayor’s climate change adaptation strategy for London. It details his strategic approach to managing the climate risks we face now and in the future in order to maintain London as one of the best big cities in the world.Our climate is changing and further changes are expected. Together, we need to prepare for warmer, wetter winters, hotter, drier summers and more frequent extreme weather. Timely action will bring positive benefits, including jobs, investment, economic security and an improved quality of life. If we don’t act, we are likely to face an increasing risk of floods, droughts and heat waves.Managing risks and increasing resilience looks at who and what is vulnerable to extreme weather today, considers how climate change will affect the existing climate risks, or create new risks or opportunities in the future and provides a framework for action.
מידע נוסף

Federal, State, and Local Tax Policies for Climate Change: Coordination or Cross-Purpose?
Although the United States has not yet enacted comprehensive climate change legislation at the Federal level, federal tax laws affecting energy have significant climate change effects. At the regional level, several groups of States have joined together in climate change legislation. Most States and many localities have tax laws affecting energy. State and local governments often enact legislation in response to federal actions, or to fill gaps in federal legislation. When national, state, and local governments all attempt to influence energy use through tax legislation, without coordination, inefficiencies and conflicts are bound to arise. In the absence of Federal leadership on climate change, a second best alternative is coordination between Federal, State and local efforts to encourage energy-wise behavior. This essay explores alternatives for coordination and potential challenges.
מידע נוסף

Protecting the Coast
In this draft book chapter, the authors – one a former political appointee at EPA in the Obama administration, the other a senior climate change adaption adviser at EPA – discuss the law and policy of adapting to climate change in coastal areas of the United States. The most dramatic effects of climate change will occur on the coast. That’s where the twin threats of rising seas and stronger storms are already mounting the beaches. And that is where most Americans, along with billions of dollars in cultural and commercial assets, currently reside. Cities like Miami, New York, New Orleans, and Washington, D.C., are in the crosshairs. Adapting to climate change on the coast will require a plan based on a tough defense, smart adjustment, and managed retreat. This Chapter addresses the legal framework of the first two elements. Part I of this Chapter divides adaptation into helpful categories and sets out some guiding principles that we think all adaptation strategies should follow. Part II focuses on strategies geared toward resisting storm surge or floodwaters. These include “hard armoring” strategies, like dikes and levees and “soft armoring strategies,” like coastal restoration. Part III focuses on strategies of adjustment, in which use patterns or consumption patterns are modified to take into consideration climate impacts. We illustrate this type of adaptation with the example of adapting to saltwater intrusion. In Part IV, we offer concluding remarks.
מידע נוסף

Total Costs and Budgetary Effects of Adaptation to Climate Change: An Assessment for the European Union
Adaptation to climate change is gaining increasing relevance in the public debate of climate policy. However, detailed and regionalised cost estimates as a basis for cost-benefit-analyses are rare. We compose available cost estimates for adaptation in Europe, and in particular Germany, Finland and Italy. Furthermore, a systematic overview on fiscal aspects of adaptation is provided, with focus on budgetary effects of adaptation in the different impact sectors. Combining cost estimates, considerations on fiscal aspects and governmental interventions in adaptation processes, we present data-based guesses of public adaptation costs in the EU, divided by impact sectors. The findings show an expectedly large public burden in the adaptation of transport infrastructure and coastal protection, while high adaptation costs in the agriculture sector are predominantly private. The change in energy demand may well lead to a significant decrease in public expenditure. Considering the regional heterogeneity of adaptation measures and the high uncertainty of quantitative adaptation analyses, further research in the form of bottom-up-studies is needed.
מידע נוסף

Future hydrology and climate in the River Nile basin: a review
A critical discussion of recent studies that analysed the effects of climate change on the water resources of the River Nile Basin (RNB) is presented. First, current water-related issues on the RNB showing the particular vulnerability to environmental changes of this large territory are described. Second, observed trends in hydrological data (such as temperature, precipitation, river discharge) as described in the recent literature are presented. Third, recent modelling exercises to quantify the effects of climate changes on the RNB are critically analysed. The many sources of uncertainty affecting the entire modelling chain, including climate modelling, spatial and temporal downscaling, hydrological modelling and impact assessment are also discussed. In particular, two contrasting issues are discussed: the need to better recognize and characterize the uncertainty of climate change impacts on the hydrology of the RNB, and the necessity to effectively support decision-makers and propose suitable adaptation strategies and measures. The principles of a code of good practice in climate change impact studies based on the explicit handling of various sources of uncertainty are outlined.
מידע נוסף

Thinking through the climate change challenge
In October 2010, a group of leading thinkers on environmental policy met at the Sustainable Consumption Institute at the University of Manchester for a conference in honour of Nobel Laureate Tom Schelling. This column presents a 10-point guideline for climate change policy co-authored by 26 attendees that focuses on designing policies that are credible, easily monitored, and easily enforced.
מידע נוסף

Extreme precipitation in Europe: statistical threshold selection based on climatological criteria
In the present study, both parametric (peak over threshold: mean residual life, dispersion index, threshold choice) and non-parametric (percentiles indices 95% and 99%) statistical techniques are employed, aiming at the identification of rainfall thresholds above which a precipitation event can be characterized as extreme. The analysis is based on 45 years (1960–2004) rain gauge daily records from 65 meteorological stations over the European region. According to two climatologically based criteria that were introduced in the study, it was found that a combined peak over threshold methodology has been shown to yield higher threshold values above which extreme precipitation events occur, in comparison to the 95th percentile indices. Overall, concerning northern Europe, it was found that in the majority of the stations, the threshold values vary from 20 to 30 mm, while the results concerning the Mediterranean region are less coherent and the selection of extreme precipitation thresholds differs from region to region. Stations over eastern Mediterranean appear to have thresholds higher than 30 mm, while stations located over the main cyclone trajectories and the cyclogenesis zone of Mediterranean are those with the higher extreme precipitation thresholds (higher than 45 mm).
מידע נוסף

To know what we cannot know: Global mapping of minimal detectable absolute trends in annual precipitation
Fresh water resources, human societies, and ecosystems are expected to be strongly impacted by climate change, with precipitation trends being one of the most important elements that will be closely monitored. However, the natural variability of precipitation data can often mask existing trends such that the results appear as statistically insignificant. Information on the limitations of trend detection is important for risk assessment and for decision making related to adaption strategies under inherent uncertainties. This paper reports on an effort to quantify and map minimal detectable absolute trends in annual precipitation data series on a global scale. Monte Carlo simulations were conducted to generate realizations of trended precipitation data for different precipitation means and coefficients of variance, and the Mann–Kendall method was applied for detecting the trend significance. Global Precipitation Climatology Centre (GPCC) VASClimO data was used to compute the mean and coefficient of variance of annual precipitation over land and to map minimal detectable absolute trends. It was found that relatively high magnitude trends (positive or negative) have a low chance of being detected as a result of high natural variance of the precipitation data. The largest undetectable trends were found for the tropics. Arid and semiarid regions also present high relative values in terms of percent change from the mean annual precipitation. Although the present analysis is based on several simplified assumptions, the goal was to point out an inherent problem of potentially undetectable high absolute trends that must be considered in analyzing precipitation data series and assessing risks in adaption strategies to climate change.
מידע נוסף

Recent changes in precipitation, ITCZ convection and northern tropical circulation over North Africa (1979–2007)
This article focuses on some recent changes observed in the Tropics with special emphasis on the African monsoon region using high-resolution gridded precipitation from the Climatic Research Unit (period 1979–2002), outgoing longwave radiation at the top of the atmosphere from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and atmospheric reanalyses from the Climate Prediction Center (NCEP-DOE2, period 1979–2007). The results show a rainfall increase in North Africa since the mid-90s with significant northward migrations of rainfall amounts, i.e. + 1.5° for the 400 mm July to September isohyets, whereas deep convection has significantly increased and shifted northward. The subsidence branch of the northern meridional overturning has also been reinforced and shifted by 1° latitude northward in winter. At larger scale, an unambiguous reorganisation of the circulation with increasing subsidence in high troposphere over the Mediterranean and increasing ascendance in the African Intertropical Convergence Zone in northern summer has been noticed in the meridional cell overturning. After 1993–1994, the migration of the Saharan heat low towards northwest has been more marked (+1° to + 2° in latitude; − 1° to − 2° in longitude), whereas its centre intensified at the peak of the tropical rainy season (+10 gpm thickness in the 700–925 hPa layer). These changes are associated with significant reinforcements of the southwesterly low-level winds and Tropical Easterly jet and with a northward shift of the African Easterly jet. Analyses of Global Circulation Model outputs issued from Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (A1B scenario and from forced experiments on the ARPEGE-climat (Action de Recherche Petite Echelle Grande Echelle) and Atmospheric Global Circulation Model show that at least part of these changes could be due to the recent warming observed in the Mediterranean/Saharan region.
מידע נוסף

Changes in precipitation with climate change
There is a direct influence of global warming on precipitation. Increased heating leads to greater evaporation and thus surface drying, thereby increasing the intensity and duration of drought. However, the water holding capacity of air increases by about 7% per 1°C warming, which leads to increased water vapor in the atmosphere. Hence, storms, whether individual thunderstorms, extratropical rain or snow storms, or tropical cyclones, supplied with increased moisture, produce more intense precipitation events. Such events are observed to be widely occurring, even where total precipitation is decreasing: ‘it never rains but it pours!’ This increases the risk of flooding. The atmospheric and surface energy budget plays a critical role in the hydrological cycle, and also in the slower rate of change that occurs in total precipitation than total column water vapor. With modest changes in winds, patterns of precipitation do not change much, but result in dry areas becoming drier (generally throughout the subtropics) and wet areas becoming wetter, especially in the mid- to high latitudes: the ‘rich get richer and the poor get poorer’. This pattern is simulated by climate models and is projected to continue into the future. Because, with warming, more precipitation occurs as rain instead of snow and snow melts earlier, there is increased runoff and risk of flooding in early spring, but increased risk of drought in summer, especially over continental areas. However, with more precipitation per unit of upward motion in the atmosphere, i.e. ‘more bang for the buck’, atmospheric circulation weakens, causing monsoons to falter. In the tropics and subtropics, precipitation patterns are dominated by shifts as sea surface temperatures change, with El Niño a good example. The volcanic eruption of Mount Pinatubo in 1991 led to an unprecedented drop in land precipitation and runoff, and to widespread drought, as precipitation shifted from land to oceans and evaporation faltered, providing lessons for possible geoengineering. Most models simulate precipitation that occurs prematurely and too often, and with insufficient intensity, resulting in recycling that is too large and a lifetime of moisture in the atmosphere that is too short, which affects runoff and soil moisture.
מידע נוסף

The FLASH Project: using lightning data to better understand and predict flash floods
The FLASH project was implemented from 2006 to 2010 under the EU FP6 framework. The project focused on using lightning observations to better understand and predict convective storms that result in flash floods. As part of the project 23 case studies of flash floods in the Mediterranean region were examined. For the analysis of these storms lightning data from the ZEUS network were used together with satellite derived rainfall estimates in order to understand the storm development and electrification. In addition, these case studies were simulated using mesoscale meteorological models to better understand the meteorological and synoptic conditions leading up to these intense storms. As part of this project tools for short term predictions (nowcasts) of intense convection across the Mediterranean and Europe, and long term forecasts (a few days) of the likelihood of intense convection were developed. The project also focused on educational outreach through our website http://flashproject.org supplying real time lightning observations, real time experimental nowcasts, forecasts and educational materials. While flash floods and intense thunderstorms cannot be prevented as the climate changes, long-range regional lightning networks can supply valuable data, in real time, for warning end-users and stakeholders of imminent intense rainfall and possible flash floods.
מידע נוסף

Economics of Adaptation to Climate Change: Learning from Impact and Vulnerability Literature
In the international arena, two broad policy responses have emerged to deal with negative impact of climate change, i.e. 'mitigation' and 'adaptation'. Though adaptation is required to reduce unmitigated climatic impact, the ongoing international climate conventions and scholarly studies have given less emphasis to it in comparison to mitigation. In climate change economics literature, the notion adaptation has been used in two discourses: 'impact' and 'vulnerability', and both are different in the context of not only addressing research question but also assessing adaptive capacity. Assuming adaptation as 'static or end-point' approach, the impact studies have estimated potential impact cost, which involves both adaptation and residual or un-mitigated impact cost, based on projected emission scenarios now and forever. The vulnerability studies, in contrast, have presumed adaptation as 'starting-point' approach, and assessed risk of an entity within the broader social, economic, political and environmental context. In the context of adaptation, the former (impact) assumes clairvoyant farmer hypothesis, and hence, suggests climate specific adaptations. The later (vulnerability), on the other hand, views adaptation as the current ability of a person to cope with risk and secure livelihoods, which in particular assessing vulnerability, who adapts and his/her risk attitude behaviour, and process of occurring adaptations. Though the purpose of both is to reduce negative impact through adaptation, the present study surveys both the sets of studies based on two questions: how the notion of adaptation is being articulated and to what extent their findings are useful for implementing and facilitating adaptations.
מידע נוסף

Market mechanisms for adaptation to climate change - lessons from mitigation and a pathway to implementation
Such instruments should be as efficient as possible, and in other policy fields market-based mechanisms have been used to maximize efficiency. So far however, there is almost no experience with adaptation taxes, tradable project-based offsets or tradable allowances, whereas climate change mitigation has been a field where such instruments have been widely applied during the last two decades. While generally, market-based instruments for mitigation can be seen as successful, several key lessons have been learned. (1) Pilot phases are important to test an instrument and to correct design flaws.(2) Distortions by lobbies can lead to adverse distributional effects. Regulatory uncertainty reduces the efficiency gains. (3) Transaction costs can form a significant barrier. (4) Monitoring and independent verification are key to prevent fraud. These lessons should be taken into account in the design of market mechanisms for adaptation, and we derive requirements for that. Finally, we discuss a concrete pathway to establishing market mechanisms for adaptation and define priorities for further research and possible pilot implementation, differentiating by types of adaptation.
מידע נוסף

Climate Trends and Global Crop Production Since 1980
Efforts to anticipate how climate change will affect future food availability can benefit from understanding the impacts of changes to date. We found that in the cropping regions and growing seasons of most countries, with the important exception of the United States, temperature trends from 1980 to 2008 exceeded one standard deviation of historic year-to-year variability. Models that link yields of the four largest commodity crops to weather indicate that global maize and wheat production decli
מידע נוסף

Adapting urban water systems to climate change
ICLEI, UNESCO-IHE and IWA have authored, as part of the ‘SWITCH – Managing Water for the City of the Future’ project, a handbook on adapting urban water systems to climate change. The handbook aims to fill a gap in the adaptation field: while a lot of information is available about various adaptation topics, there is a lack of guidance for decision makers at the local level working on urban water who wish to proactively prepare for and adapt to climate change. The handbook first examines some of the key areas of vulnerability to climate change within urban water systems. The handbook also proposes flexible and future-oriented urban water planning as a means to address climate change and implement adaptation actions. Finally, the handbook presents case studies of cities throughout the world that have already planned for adaptation or implemented specific actions aiming at increasing their resilience to climate change.
מידע נוסף

The Landscape of Climate Finance: A CPI Report
Climate finance has been a key topic in recent international climate negotiations, resulting in a commitment to increase the flow of climate finance from developed to developing countries to USD 100 billion per year by 2020. Building a comprehensive picture of climate finance flows is essential to this effort. Understanding how much and what type of support is being made available to advance action on low-carbon, climate-resilient development, how these types of support correspond to countries’ needs, and whether financial resources are being spent productively is critical to building trust among countries and ensuring the effective use of the available financial resources.In this paper, CPI assesses the current status of the climate finance landscape, mapping its magnitude and nature along the life cycle of finance flows, i.e. the sources of finance, intermediaries involved in distribution, financial instruments, and final uses. After presenting estimates of current flows based on available data, describing the methodology, and discussing the sources of data, we offer recommendations to improve further data-gathering efforts.
מידע נוסף

Future hydrology and climate in the River Nile basin: a review
A critical discussion of recent studies that analysed the effects of climate change on the water resources of the River Nile Basin (RNB) is presented. First, current water-related issues on the RNB showing the particular vulnerability to environmental changes of this large territory are described. Second, observed trends in hydrological data (such as temperature, precipitation, river discharge) as described in the recent literature are presented. Third, recent modelling exercises to quantify the effects of climate changes on the RNB are critically analysed. The many sources of uncertainty affecting the entire modelling chain, including climate modelling, spatial and temporal downscaling, hydrological modelling and impact assessment are also discussed. In particular, two contrasting issues are discussed: the need to better recognize and characterize the uncertainty of climate change impacts on the hydrology of the RNB, and the necessity to effectively support decision-makers and propose suitable adaptation strategies and measures. The principles of a code of good practice in climate change impact studies based on the explicit handling of various sources of uncertainty are outlined.
מידע נוסף

Assessing the costs and benefits of adaptation options: an overview of approaches
This paper outlines three methods for assessing the costs and benefits of different adaptation options. The paper aims to elaborate on the role and purpose of assessment and to explain the most commonly used assessment approaches. The paper is comprised of four sections: (i) the first section introduces the purpose of the assessment and the assessment criteria; (ii) the second section provides an overview of methodological issues and explains the three main methods of assessment; (iii) the third section gives examples of best practices and lists some lessons learned by previous assessment teams; and (v) the fifth section concludes the paper, emphasizing the need for continued assessments even after the climate change adaptation plan is in place. This publication has been developed under the Nairobi work programme on impacts, vulnerability and adaptation to climate change.
מידע נוסף

Lessons Learned on Local Climate Adaptation from the Urban Leaders Adaptation Initiative
This report summarizes the main findings of the Center for Clean Air Policy (CCAP)'s Urban Leaders Adaptation Initiative. In partnership with government leaders from ten large counties and cities, CCAP launched the Initiative to foster local climate adaptation efforts and to develop and implement climate resilient strategies. This report provides an assessment of general lessons learned over the course of the project and thoughts about future directions for local climate adaptation.
מידע נוסף

Climate Change and Migration: Rethinking Policies for Adaptation and Disaster Risk Reduction
Climate change due to greenhouse gas emissions is now, at some level, a fact. IPCC and other scientific bodies have modeled a number of future scenarios estimating changes in weather patterns, ocean currents, and (more recently) ecosystems. Average atmospheric temperatures are increasing and with this increase scientists expect (and in some cases may already be observing) more rapid melting of the earth’s ice sheets, sea level rise, and greater seasonal variability in rainfall. They are documenting more frequent storms and intense flooding in some areas, and severe and prolonged droughts in others, predicting further water scarcity, diminished food production, and unemployment. With the increase in natural disasters, vulnerable communities (those with weak support systems, governance, and capacity to respond) are most at risk. Many may be displaced or increase their reliance on migration as a coping strategy for survival. The rise in humanitarian crises presents enormous challenges for poorer countries and the international organizations called on for assistance. These challenges are exacerbated by the lack of consistent policies, standards, and practices in disaster planning related to human displacement and migration. As the findings of the Academy and case studies presented in this volume reveal, human mobility is not always adverse to community development but in some circumstances may help build resilience. Better understanding the opportunities and impacts of migration, and how to protect those displaced by disaster, can help governments to improve their climate adaptation strategies. So, too can improving cooperation among neighboring states with shared natural resources and among countries of migration origin and destination. To do this effectively, governments will need to rethink existing disaster planning, migration policy, and institutional frameworks. The findings and recommendations in this introductory chapter are the result of the 2010 Summer Academy on Social Vulnerability organized by UNU-EHS and MRF from July 25-31, 2010 in Hohenkammer, Germany. They provide a foundation for further consideration of how governments can better manage displacement and migration related to climate disasters. The papers that follow this introductory chapter in Sections 1 and 2 below are the selected work of Academy participants who undertook specific case studies as part of their graduate or post-graduate work and in preparation for the program. In some circumstances they refined their analysis to incorporate their learning experience. The compilation of works is not meant to represent a comprehensive study of all issues relevant to climate-related migration. Rather, the individual studies provide a unique, in-depth focus on various aspects of the issue and on multiple regions where climate change impacts may be significant. They suggest new avenues for research, policy, and law that may be relevant to decision makers in affected regions, and bring a greater depth to the issues discussed by the Academy.
מידע נוסף

Climate change: present and future risks to health – and necessary responses
Recent observed changes in Earth's climate, to which humans have contributed substantially, are affecting various health outcomes. These include altered distributions of some infectious disease vectors (ticks at high latitudes, malaria mosquitoes at high altitudes), and an uptrend in extreme weather events and associated deaths, injuries and other health outcomes. Future climate change, if unchecked, will have increasing, mostly adverse, health impacts - both direct and indirect. Climate change will amplify health problems in vulnerable regions, influence infectious disease emergence, affect food yields and nutrition, increase risks of climate-related disasters and impair mental health. The health sector should assist society understand the risks to health and the needed responses.
מידע נוסף

Climate Change, Natural Disasters and Migration: An Empirical Analysis
The aim of this paper is to assess the relationship between natural disasters caused by climate change and migration by examining migration rates and levels of education in developing countries. Many studies such as the Stern review (2007) or the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC, 2007) predict an intensification of climate change for future years. Thus climate change has taken an essential place in world governance. The relationship between climate change, natural disasters and migration is crucial; developed countries need to manage the increasingly complicated issues of additional incoming migratory flows caused by environmental degradation. We investigate this relationship by using panel data from developing countries in order to see the effect of natural disasters on migration rates and how that varies according to the level of education. Estimations are made with a country fixed effects estimator through an accurate econometric model. The results confirm previous studies, namely that natural disasters are positively associated with emigration rates. But beyond this result, the main contribution of this paper is to show that natural disasters due to climate change exacerbate the brain drain in developing countries characterized by the migration of highly skilled people just when those countries are at their most vulnerable and need greater support from skilled workers to deal with the damage associated with natural disasters. The paper also shows that this effect varies depending on geographical location.
מידע נוסף

Climate Change Adaptation and Real Option Evaluation: A Case Study in Campeche, Mexico
This report illustrates the application of a (relatively) new method to guide decision making under high (and unknowable) levels of uncertainty. The approach allows for the identification of robust policy options that are economically beneficial under different scenarios and varying levels uncertainty. Option value techniques are commonly employed in the finance literature to identify investment decisions that are resilient across a spectrum of outcomes. The methods are technically advanced
מידע נוסף

INTERNATIONAL ENVIRONMENTAL AGREEMENTS IN THE PRESENCE OF ADAPTATION
We show that adaptive measures undertaken by countries in the face of climate change, apart from directly reducing the damage caused by climate change, may also indirectly mitigate greenhouse gas emissions by increasing the stable size of international agreements on emission reductions. Moreover, we show that the more e¤ective the adaptive measure in terms of reducing the marginal damage from emissions, the larger the stable size of the international environmental agreement. In addition, we show
מידע נוסף

Climate change and children’s health
Through many pathways, and in particular via placing additional stress upon the availability of food, clean air, and clean water and by potentially expanding the burden of disease from certain vector-borne diseases, climate change represents a major threat to child health. Pediatricians have already seen and will increasingly see the adverse health effects of climate change in their practices. Because of this, and many other reasons, pediatricians have a unique capacity to help resolve the climate change problem.
מידע נוסף

Climate change and farmers' mental health: risks and responses
Climate change is exacerbating climate variability, evident in more frequent and severe weather-related disasters, such as droughts, fires, and floods. Most of what is known about the possible effects of climate change on rural mental health relates to prolonged drought. But though drought is known to be a disproportionate and general stressor, evidence is mixed and inconclusive. Over time, like drought other weather-related disasters may erode the social and economic bases on which farming communities depend. Rural vulnerability to mental health problems is greatly increased by socioeconomic disadvantage. Related factors may compound this, such as reduced access to health services as communities decline and a "stoical" culture that inhibits help-seeking. Australia has the world's most variable climate and is a major global agricultural producer. Yet despite Australia's (and, especially, rural communities') dependence on farmers' well-being and success, there is very little-and inconclusive-quantitative evidence about farmers' mental health. The aim of this review is to consider, with a view to informing other countries, how climate change and related factors may affect farmers' mental health in Australia. That information is a prerequisite to identifying, selecting, and evaluating adaptive strategies, to lessen the risks of adverse mental health outcomes. The authors identify the need for a systematic epidemiology of the mental health of farmers facing increasing climate change- related weather adversity.
מידע נוסף

Ethics and the Economist: What Climate Change Demands of Us
Climate change is changing not only our physical world, but also our intellectual, social, and moral worlds. We are realizing that our situation is profoundly unsafe, interdependent, and uncertain. What, then, does climate change demand of us, as human beings and as economists? A discipline of economics based on Enlightenment notions of mechanism and disembodied rationality is not suited to present problems. This essay suggests three major requirements: first, that we take action; second, that we work together; and third, that we focus on avoiding the worst, rather than obtaining the optimal. The essay concludes with suggestions of specific steps that economists can take as researchers, teachers, and in our other roles.
מידע נוסף

Mitigation + Adaptation: What is the optimal climate change policy mix?
In dealing with climate change, how much should governments focus their effort on mitigation (emission reduction to prevent climate change) and on adaptation (coping with a changed climate)? Very little research has gone into pinning down which strategy is dynamically optimal under what kind of conditions. This paper contributes to this debate by developing a parsimonious optimal control model that focuses on the non-linearity of climate change and the presence of multiple countries. Calibrated simulation results are provided to characterize the model. The results show that the optimal policy mix – or the adoption decision for mitigation and adaptation – is determined by two key parameters: an adjusted mitigation/adaptation cost ratio and the climate change damage elasticity. The latter depends crucially on the non-linearity (suddenness) of climate change. Country heterogeneity influences the policy choice strongly in favour of adaptation.
מידע נוסף

Adaptation to Climate Change and Economic Growth in Developing Countries
The global climate is changing, and will continue to do so even if greenhouse gas emissions are dramatically curbed. Economies are therefore faced with the challenge of adapting to climate change. This challenge is particularly important in developing countries, which, due to a combination of unfortunate geography and high sensitivity, are most vulnerable to climate change. From a macro-economic point of view, there remains much to learn about the characteristics of optimal adaptation. In partic
מידע נוסף

Plan or React? Analysis of Adaptation Costs and Benefits Using Integrated Assessment Models
The present work seeks to examine adaptation and mitigation interaction and to assess dynamically the regional costs and benefits of adaptation. This is done by developing a framework to incorporate adaptation as a policy variable in an Integrated Assessment framework in three Integrated Assessment Models (IAMs): the Dynamic Integrated model of Climate and the Economy (DICE), the Regional Integrated model of Climate and the Economy (RICE), and the World Induced Technical Change Hybrid (WITCH) model. The modified models – AD-DICE, AD-RICE and AD-WITCH – are calibrated and used in policy simulations to examine the regional distribution of adaptation costs, the optimal policy mix between different types of adaptation, and the interactions between adaptation and mitigation. The AD-WITCH model also includes investments in “adaptive capacityâ€, such as social protection programmes, which can enhance the effectiveness of adaptation actions, though not directly reducing damages. By using different IAMs, this paper presents the first inter-model comparison of results on adaptation costs. Results show that the total costs of climate change are the lowest when both mitigation and adaptation are undertaken in conjunction. Any least-cost policy response to climate change will need to involve substantial amounts of mitigation efforts, investments in adaptation stock and reactive adaptation measures to limit the remaining damages.
מידע נוסף

Distributional Consequences of Climate Change Impacts on the Power Sector: Who Gains and Who Loses?
Climate change tends to negatively affect the power sector, inter alia, by causing cooling problems in power plants and impairing the water supply required for hydro-power generation. In future, when global warming is expected to increase, autonomous adaptation to climate change via international electricity markets inducing reallocations of power generation may not be sufficient to prevent supply disruptions. Furthermore, the consequent changes of supply patterns and electricity prices might cause an undesirable redistribution of wealth both between individual power suppliers and between suppliers and consumers. This study ascertains changes in European power supply patterns and electricity prices caused by ongoing global warming as well as related redistribution of wealth for different climate change scenarios. Our results confirm that autonomous adaptation in the power sector should be complemented by planned public adaptation in order to preserve energy security and to prevent undesired distributional effects.
מידע נוסף

ADAPTING TO CLIMATE CHANGE Cost Benefits and Modelling Approaches
As part of the research carried out under the Gemina Work Package 6.2.10, this paper provides a summary and a critical survey of the methodologies and results of the literature on the economics of adaptation.
We divide the literature into two broad areas of research. First, we examine the studies that analyse adaptation from a bottom-up perspective. Second, we introduce the studies that examine adaptation using a top-down approach. The first group of studies investigates cost and benefits of sectoral adaptation strategies with a geographical detail that varies from country-level to global-level. The second group gathers two different streams of literature that share macro approaches, as opposed to the micro ones of the former group. It includes both theoretical works as well as the contributions based on Integrated Assessment Models (IAMs).
IAMs have originally been created to study policies aimed at limiting global warming. Recently they have also been extended to include adaptation as an alternative policy option to mitigation. This latter development has raised new issues that represent new challenges for the research community. In particular, how to make use of the vast amount of information provided by the bottom-up literature and how to integrate it into global models is paramount. Important research gaps to be filled include the improvement of the quantitative assessment of cost and benefit of adaptation needs, especially in some sectors and in developing countries and the clarification of the aggregation procedure used for scaling up bottom-up data. In addition, uncertainty and irreversibility are very marginally tackled by adaptation studies. Finally, the role of adaptation in international climate change negotiations, which is presently growing in importance, remains largely unexplored.
מידע נוסף

Making Adaptation Count Concepts and Options for Monitoring and Evaluation of Climate Change Adaptation
This report aims to provide adaptation and development practitioners with a practical framework for developing monitoring and evaluation systems that can track the success and failure of adaptation initiatives in the development context.
מידע נוסף

Climate Change Adaptation for Building Designers: An Introduction
Adapting building designs for climate change is about managing the unavoidable. While there is debate around what level of adaptation is needed, there is growing awareness that design practices need to take into account predictions of increased risk and intensity of extreme events. This paper examines potential climate change effects on buildings, highlights the potential for capacity building through education, and presents examples of adaptive strategies for building design.
מידע נוסף

Israel's Second National Communication on Climate Change
The report relates to Israel's special circumstances, its national inventory of greenhouse gas emissions, national policy on mitigation and adaptation, and more. It looks at developments in the field of climate change since the submission of Israel's first national report to the United Nations exactly ten years ago, in November 2000. Israel's Second National Communication will be distributed at the Climate Change Conference which convenes in Cancun, Mexico from November 29 to December 10, 2010. The report was prepared as part of Israel's commitment under the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change.
מידע נוסף

International environmental agreements in the presence of adaptation
We show that adaptive measures undertaken by countries in the face of climate change, apart from directly reducing the damage caused by climate change, may also indirectly mitigate greenhouse gas emissions by increasing the stable size of international agreements on emission reductions. Moreover, we show that the more effective the adaptive measure in terms of reducing the marginal damage from emissions, the larger the stable size of the international environmental agreement. In addition, we show that larger coalitions, in the presence of adaptation, may lead to lower global emission levels and higher welfare.
מידע נוסף

Financing Adaptation to Climate Change with Climate Derivatives
Natural hazard events in 2010 and 2011 such as the eruption of the volcano Eyjafjallajokull on Iceland, the heatwave in Russia, the extreme floods in northeastern Australia, and more recently the earthquake followed by a tsunami at Fukushima in Japan demonstrated the vulnerability of the networked global economy, where interruptions in supplies of important goods to industrial firms or to the food industry meant that gradually more and more sectors of the economy were affected. Further, interest in attributing the risk of damaging weather-related events to anthropogenic climate change is increasing. Hence, as climate change progresses over the coming decades, a widening range of sectors will experience both direct and indirect climate change related damages. The 2001 IPCC report stated that if greenhouse gas (GHG) concentrations were stabilised, sea level would nonetheless continue to rise for hundreds of years. However, according to the latest estimates from the International Energy Agency (IEA), in 2010 GHG emissions increased by a record amount, indicating that emissions are now close to being back on a business as usual path. Therefore, adaptation is inevitable and one has to build uncertainty into the planning process resulting from the effects of the emissions that have already occurred and will still occur in the coming decades. We propose to use climate derivatives to make climate investible in order to finance mitigation and adaptation to climate change. We give a detailed explanation of the mechanism used to provide higher yield than market to long-term investors, and describe as an example two structured products designed to finance adaptation via the real options approach and the context-first approach.
מידע נוסף

International Cooperation on Climate Change Adaptation from an Economic Perspective
This paper investigates the economic incentives of countries to cooperate on international adaptation financing. Adaptation is generally implicitly incorporated in the climate change damage functions as used in Integrated Assessment Models. We replace the implicit decision on adaptation with explicit adaptation in a multi-regional setting by using an adjusted RICE model. We show that making adaptation explicit will not affect the optimal mitigation path when adaptation is set at its optimal level. Sub-optimal adaptation will, however, change the optimal mitigation path. Furthermore this paper studies for different forms of cooperation what effects international adaptation transfers will have on (i) domestic adaptation and (ii) the optimal mitigation path. Adaptation transfers will fully crowd out domestic adaptation in a first best setting. Transfers will decrease overall mitigation in our numerical simulations. An analytical framework is used to analyse the most important mechanisms and a numerical model is used to assess the magnitude of effects.
מידע נוסף

Plan or React? Analysis of Adaptation Costs and Benefits Using Integrated Assessment Models
Financing for adaptation is a core element in the ongoing international negotiations on climate change. This has motivated a number of recent global estimates of adaptation costs. While important from an agenda setting perspective, many of these estimates nevertheless have a number of limitations. They are typically static (i.e. estimated for one specific year), do not differentiate between investments in various types of adaptation or quantify the resulting benefits, and are delinked from policies and investments in greenhouse gas mitigation.
מידע נוסף

Comparative analysis of algal communities in the rivers of northern and southern Israel as bearing on ecological consequences of climate change
Climatic impact on algal communities is analyzed by comparing two unpolluted river ecosystems, the Oren River of Mediterranean zone, Northern Israel and Zin River of the Central Negev Desert, Southern Israel. Bio-indication method was used for assessment of ecologically significant variations in the composition of algal communities in both rivers. Our analysis highlighted the distinctions in taxonomic diversity and abundances of both salinity tolerant (halobic) and alkaliphilic groups of algae.
מידע נוסף

Mainstreaming climate change adaptation in Indian cities
If climate change is perceived as a global threat, this can mean that too little attention is paid to the ways in which it affects local populations and settlements. This also means too little attention to the importance of locally driven adaptation, both to reduce risks and to be better prepared to cope with consequences. This paper reviews the many initiatives underway in India that respond to climate change, and discusses what else is needed to mainstream effective adaptation, as well as identifying what currently constrains this. It also discusses how adaptation has to be mainstreamed within urban development and urban governance. Most municipal authorities in India are already grappling with large deficits in infrastructure and services and do not see climate change adaptation as a priority or as their responsibility. However, their attention may be engaged if they can see the co-benefits between adaptation and measures to address development and environmental health concerns.
מידע נוסף

Adapting to Climate Change: An Introduction for Canadian Municipalities
This book is an update and expansion of the document
published in 2006 by the Canadian Climate Impacts and
Adaptation Research Network (Mehdi, 2006) under the
same title. It provides municipal decision-makers and staff
with information to help them understand the need for
climate change adaptation and how to put adaptation
measures in place. The book also refers to other guides
that can help municipalities identify and address risks
and opportunities, and to case studies that illustrate how
municipalities of varying sizes from across the country
are taking action now.
מידע נוסף

Adapting to Climate Change: A Risk-based Guide for Local Governments
Using the Canadian national standard framework for risk management, this guide is intended to assist local and regional governments (as well as health officials, emergency managers and businesses) in understanding the risks related to climate change and how to manage predicted impacts. The guide provides an overview of climate trends and projections in BC and the local government planning context. The document focuses primarily on the steps in the risk management process. Briefly summarized, the steps are: getting started; preliminary analysis; risk estimation; risk evaluation; risk controls and adaptation decisions; and implementing and monitoring. The guide stresses the importance of communication and documentation throughout all steps.
מידע נוסף

Climate change, food stress, and security in Russia
Farming in higher latitudes is generally believed to benefit from a warmer climate due to extended growing season, reduced risk of frost, availability of more productive cultivars, and an opening potential of farming in northern locations. We analyzed the impact of climate change on production of cereals in Russia and found that this general perception of beneficiary effect of a warmer climate is unlikely to hold, primarily due to increasing risk of droughts in the most important agricultural ar
מידע נוסף

Climate Protection Commitment Heidelberg
This is the result of cooperation. On the one hand, the city provides not only a hotline to answer any questions residents may have concerning cleanliness or garbage, but also a comprehensive and reliable garbage disposal and city cleaning service with comparatively low charges. On the other hand, the residents demonstrate the strength of their commitment in community action events, such as the spring clean and by carefully separating their garbage. This, in turn, contributes to sustainable recycling: Heidelberg's organic waste is turned into high-quality compost.
מידע נוסף

Modeling the effects of weather and climate change on malaria transmission
BACKGROUND: In recent years, the impact of climate change on human health has attracted considerable attention; the effects on malaria have been of particular interest because of its disease burden and its transmission sensitivity to environmental conditions.OBJECTIVES: We investigated and illustrated the role that dynamic process-based mathematical models can play in providing strategic insights into the effects of climate change on malaria transmission.METHODS: We evaluated a relatively simple model that permitted valuable and novel insights into the simultaneous effects of rainfall and temperature on mosquito population dynamics, malaria invasion, persistence and local seasonal extinction, and the impact of seasonality on transmission. We illustrated how large-scale climate simulations and infectious disease systems may be modeled and analyzed and how these methods may be applied to predicting changes in the basic reproduction number of malaria across Tanzania.RESULTS: We found extinction to be more strongly dependent on rainfall than on temperature and identified a temperature window of around 32-33 degrees C where endemic transmission and the rate of spread in disease-free regions is optimized. This window was the same for Plasmodium falciparum and P. vivax, but mosquito density played a stronger role in driving the rate of malaria spread than did the Plasmodium species. The results improved our understanding of how temperature shifts affect the global distribution of at-risk regions, as well as how rapidly malaria outbreaks take off within vulnerable populations.CONCLUSIONS: Disease emergence, extinction, and transmission all depend strongly on climate. Mathematical models offer powerful tools for understanding geographic shifts in incidence as climate changes. Nonlinear dependences of transmission on climate necessitates consideration of both changing climate trends and variability across time scales of interest.
מידע נוסף

Urban Forests: A Climate Adaptation Guide
This guide has been prepared to help communities in British Columbia (B.C.) identify and prepare for some of the impacts of climate change. It provides information on how communities can use urban forests to manage some of the impacts of changing climates and how to adapt these urban forests so that they survive and thrive in future climates. This is a high-level overview that is targeting at the staff and elected officials in B.C."s communities--small and large, rural and urban--including those who do not have professional arborists or urban foresters on staff.
מידע נוסף

Arab Climate Resilience Initiative Climate Change: Economic challenges and Opportunities in the Arab Regions
This working paper aims to suggest a strategic and action oriented recommendations for developing a potential win-win inter-Arab corporations in some specific sectors related to Climate Change (Urban planning, Energy efficiency, Renewable energy, Clean technology transfer, Financial mechanisms, Research and development and knowledge development and management) involving the key actors. To secure early political ownership, the paper has deeply explored policy recommendations included in the Arab policy declarations, and strategies adopted by the governments of the region such as the sustainable development initiative in the Arab region, the Arab strategy for sustainable consumption and production, and the Arab strategy on climate change. The paper was meant to trigger a regional debate on relevant priorities for UNDP interventions as well as opportunities for inter-Arab cooperation.
מידע נוסף

Mapping of Climate Change Threats and Human Development Impacts in the Arab Region
The aim of this report is to present a comprehensive desk review and mapping exercise for an overview of the impact of climate change on the Arab region. The report is based on existing literature from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), technical papers and expert reports about the impact of climate change on Arab countries. Information and analysis are presented by sub-region, and in order to facilitate analysis, countries were grouped into: The Middle East and North Africa (MENA), namely, Algeria, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, Libyan Arab Jamahiriya, Mauritania, Morocco, the Occupied Palestinian Territory, Tunisia, Syria, and Yemen; the States of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), namely, Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates; and the Sub-Saharan countries, namely, Comoros, Djibouti, Somalia and Sudan.
מידע נוסף

Climate change, food stress, and security in Russia
Farming in higher latitudes is generally believed to benefit from a warmer climate due to extended growing season, reduced risk of frost, availability of more productive cultivars, and an opening potential of farming in northern locations. We analyzed the impact of climate change on production of cereals in Russia and found that this general perception of beneficiary effect of a warmer climate is unlikely to hold, primarily due to increasing risk of droughts in the most important agricultural areas of the country. Past impacts of droughts on food security throughout the twentieth century suggest that a number of adaptation options are available to mitigate the increasing risks of crop failure. We analyze the effectiveness of these measures in connection with a set of climate change projections, under two contrasting scenarios of interregional grain trade: “Fortress Market” and “Open Market.”
מידע נוסף

Preparing for a changing climate: The Chicago climate action plan's adaptation strategy
The Chicago Climate Action Plan (CCAP), Chicago’s roadmap for reducing climate change impacts and adapting to the changes already occurring, relied on rigorous analysis to formulate policy decisions through stakeholder coordination and public engagement. Three key pieces of analysis contributed to Chicago’s adaptation strategy: an evaluation of Chicago’s higher and lower greenhouse gas emissions scenarios; an assessment of Chicago’s economic risk under both emissions scenarios; and a prioritization of potential impacts using a scoring system that included likelihood of occurrence and local consequences of occurrence.Potential adaptation tactics were categorized according to their expected benefits and costs and led to the creation of working groups to develop action plans that will include primary actors, timelines, budgets, and performance measures that the City will monitor. While not essential for all cities, the impacts analysis was of high value to the adaptation strategy. However, a strategy for stakeholder engagement is crucial in ensuring that the implications of climate impacts are properly understood.
מידע נוסף

Uncertainties associated with quantifying climate change impacts on human health: a case study for diarrhea
Background Climate change is expected to have large impacts on health at low latitudes where droughts and malnutrition, diarrhea, and malaria are projected to increase.Objectives The main objective of this study was to indicate a method to assess a range of plausible health impacts of climate change while handling uncertainties in a unambiguous manner. We illustrate this method by quantifying the impacts of projected regional warming on diarrhea in this century.Methods We combined a range of linear regression coefficients to compute projections of future climate change-induced increases in diarrhea using the results from five empirical studies and a 19-member climate model ensemble for which future greenhouse gas emissions were prescribed. Six geographical regions were analyzed.Results The model ensemble projected temperature increases of up to 4°C over land in the tropics and subtropics by the end of this century. The associated mean projected increases of relative risk of diarrhea in the six study regions were 8–11% (with SDs of 3–5%) by 2010–2039 and 22–29% (SDs of 9–12%) by 2070–2099.Conclusions Even our most conservative estimates indicate substantial impacts from climate change on the incidence of diarrhea. Nevertheless, our main conclusion is that large uncertainties are associated with future projections of diarrhea and climate change. We believe that these uncertainties can be attributed primarily to the sparsity of empirical climate–health data. Our results therefore highlight the need for empirical data in the cross section between climate and human health.
מידע נוסף

The vulnerability of beach tourism to climate change – an index approach
The attractiveness of a region for touristic activities depends strongly on the local weather and climate. This paper analyses the vulnerability of the beach tourism sector towards climate change by means of an index approach on a country level. A vulnerability framework for the tourism sector is developed and on its basis, indicators are defined for exposure, sensitivity and adaptive capacity. A transparent index approach, including a robustness analysis with multiple transformation methods and weighting sets, yields an assessment of the overall relative vulnerability of the beach tourism sector in 51 countries. Aggregate results on an annual level are presented as a starting point for a more detailed comparison of countries based on the individual indicators. The important limitations regarding the availability of accurate indicators as well as the concept of vulnerability itself are discussed. Despite these limitations, the present study contributes to integrating the numerous direct as well as indirect effects climate change may have on beach tourism.
מידע נוסף

The gender perspective in climate change and global health
Population health is a primary goal of sustainable development. United Nations international conferences like the Beijing Platform for Action have highlighted the key role of women in ensuring sustainable development. In the context of climate change, women are affected the most while they display knowledge and skills to orient themselves toward climate adaptation activities within their societies. To investigate how the gender perspective is addressed as an issue in research and policy-making concerning climate change and global health. A broad literature search was undertaken using the databases Pubmed and Web of Science to explore the terms ‘climate change,’ ‘health,’ ‘gender,’ and ‘policy.’ Climate change and health-related policy documents of the World Health Organization (WHO) and National Communications and National Adaptation Programs of Action reports submitted to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change of selected countries were studied. Assessment guidelines to review these reports were developed from this study's viewpoint. The database search results showed almost no articles when the four terms were searched together. The WHO documents lacked a gender perspective in their approach and future recommendations on climate policies. The reviewed UN reports were also neutral to gender perspective except one of the studied documents. Despite recognizing the differential effects of climate change on health of women and men as a consequence of complex social contexts and adaptive capacities, the study finds gender to be an underrepresented or non-existing variable both in research and studied policy documents in the field of climate change and health.
מידע נוסף

Non-heat related impacts of climate change on working populations
Environmental and social changes associated with climate change are likely to have impacts on the well-being, health, and productivity of many working populations across the globe. The ramifications of climate change for working populations are not restricted to increases in heat exposure. Other significant risks to worker health (including physical hazards from extreme weather events, infectious diseases, under-nutrition, and mental stresses) may be amplified by future climate change, and these may have substantial impacts at all scales of economic activity. Some of these risks are difficult to quantify, but pose a substantial threat to the viability and sustainability of some working populations. These impacts may occur in both developed and developing countries, although the latter category is likely to bear the heaviest burden.This paper explores some of the likely, non-heat-related health issues that climate change will have on working populations around the globe, now and in the future. These include exposures to various infectious diseases (vector-borne, zoonotic, and person-to-person), extreme weather events, stress and mental health issues, and malnutrition.
מידע נוסף

Evolvability of between-year seed dormancy in populations along an aridity gradient
Under global climate change, adaptation to new conditions is crucial for plant species persistence. This requires the ability to evolve in traits that are correlated with changing climatic variables. We studied between-year seed dormancy, which correlates with environmental variability, and tested for clinal trends in its evolvability along an aridity gradient in Israel. We conducted a germination experiment under five irrigation levels with two dryland winter annuals (Biscutella didyma, Bromus fasciculatus) from four sites along the gradient. Species differed in means and evolvability of dormancy. Biscutella had high dormancy, which significantly increased with aridity but decreased with higher irrigation. In Bromus, dormancy was low, similar among populations, and only marginally affected by irrigation. Evolvability in Biscutella was high and varied among populations, without a clinal trend along the gradient. Conversely, in Bromus, trait evolvability was low and declined with increasing aridity. We argue that changes in evolvability along climatic gradients depend on the relative intensity of stabilizing selection. This may be high in Bromus and not only depends on environmental stress, but also on variability. Our findings point to the importance of measuring evolvability of climate-related traits across different natural and artificial environments and for many coexisting species.
מידע נוסף

Water for an integrative climate paradigm
By the logic of the New Water Paradigm (NWP), it is deforestation, industrial agriculture, and urbanisation that determine climate by draining land, so that more solar energy re-enters the atmosphere as sensible heat, rather than latent heat of evaporation. Human-made 'hot plates' lead to irregular precipitation and other climate destabilisation effects, but these can be mitigated through rainwater conservation and re-vegetation. This integrative paradigm combines the management of climate, water, biodiversity, and land, with implications for agriculture, forestry, engineering, urban design and regional planning.
מידע נוסף

Invasive species and climate change: Conyza canadensis (L.) Cronquist as a tool for assessing the invasibility of natural plant communities along an aridity gradient
The predicted reduction in precipitation in the eastern Mediterranean due to climate change may expose the natural plant communities to invasive species. We assessed whether natural plant communities along an aridity gradient in Israel were resistant to invasion by considering differences in abiotic conditions and community characteristics in these regions. We considered Conyza canadensis as a model plant as it is a common invader in the region. We examined the mechanisms and functional traits of both the plant communities and C. canadensis that promote or discourage invasion. Study sites represented a rainfall gradient with four ecosystem types: mesic Mediterranean, Mediterranean, semiarid and arid. Our results showed that the mechanisms of community invasion resistance varied along the aridity gradient. At the arid and semiarid sites, water deficiency impaired the establishment of C. canadensis. At the mesic Mediterranean site, plant competition had a negative effect on C. canadensis performance, thus greatly reducing the likelihood of its establishment. We conclude that a decrease in regional precipitation due to climate change may not affect intrinsic resistance characteristics of natural plant communities to invasion in the area.
מידע נוסף

Climate Change and Health Research in the Eastern Mediterranean Region
Anthropologically induced climate change, caused by an increased concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, is an emerging threat to human health. Consequences of climate change may affect the prevalence of various diseases and environmental and social maladies that affect population health. In this article, we reviewed the literature on climate change and health in the Eastern Mediterranean Region. This region already faces numerous humanitarian crises, from conflicts to natural hazards and a high burden of disease. Climate change is likely to aggravate these emergencies, necessitating a strengthening of health systems and capacities in the region. However, the existing literature on climate change from the region is sparse and informational gaps stand in the way of regional preparedness and adaptation. Further research is needed to assess climatic changes and related health impacts in the Eastern Mediterranean Region. Such knowledge will allow countries to identify preparedness vulnerabilities, evaluate capacity to adapt to climate change, and develop adaptation strategies to allay the health impacts of climate change.
מידע נוסף

Climate change impacts on working people (the HOTHAPS initiative): findings of the South African pilot study.
It is now widely accepted that climate change is occurring as a result of the accumulation of greenhouse gases (GHG) in the atmosphere. With the prospect of a warmer world, increased attention is being devoted to the implications for worker well-being and work performance. The ‘high occupational temperature health and productivity suppression’ (HOTHAPS) programme is a multi-centre health research and prevention programme aimed at characterising and quantifying the extent to which working people are affected by, or adapt to, heat exposure while working. The main aim of the current South African pilot study was to look at the perceptions of outdoor workers regarding their work environment in hot weather and how this affected their health and productivity levels. A qualitative study utilising focus group discussions was employed in two sites, Johannesburg (which has a temperate climate) and Upington (located in the hottest part of South Africa). This pilot study has demonstrated that people working in sun-exposed conditions in hot parts of South Africa currently experience heat-related health effects, with implications for their well-being and ability to work and that further research is warranted. In this regard, the pilot study has proved valuable in informing the design, site, sample selection, and logistical planning for a proposed main study on the health and performance aspects of work in hot weather in South Africa.
מידע נוסף

Observed and projected changes in drought conditions of Turkey
Drought has become a recurring phenomenon in Turkey in the past few decades. Analyzing the historical occurrence and future projections of drought characteristics such as frequency, intensity and duration provide a better understanding of the range of climate futures for one particular country. Hence, this study aimed at analyzing the likely changes of drought characteristics in the future. The Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) has been used to assess the drought characteristics. Rainfall datasets for the period 1960-1990 were acquired from 52 stations throughout Turkey. The future rainfall series for the years 2070-2100 were simulated using a regional climate model (RegCM3). The validated RegCM3 was used for simulating future climatic data, and the simulated rainfall series were used for calculation of drought indices. To asses the likely changes in future drought characteristics, each simulated future rainfall series was compared with the average rainfall amount derived from the reference period in SPI calculations. The maps were drawn to determine the spatial changes of droughts. The results showed that drought conditions are diverse in the country, and also increasing trends for intensity, frequency and duration were detected. The Eastern part of Marmara, the Black Sea and north-east part of the East Anatolia Region are characterized by wetter conditions.
מידע נוסף

Trends in CO2 emissions in Israel—an international perspective
As a Party to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, Israel conducts a periodical inventory of greenhouse gases emissions. These data allowed the generation of time series of CO2 emissions per capita and per GDP for the period 1990–2004. It was found that CO2 emissions per capita increased dramatically from 1990 to 2000, reflecting the rapid economic growth that was initiated by the massive immigration wave at the beginning of the nineties. These emissions remained stable between 2000 and 2004, reflecting the economic stagnation caused by the uprising in the Palestinian Territories, as well as stagnation in the global economy. CO2 emissions per GDP (CO2 intensity) remained stable along the whole reviewed period. This stability can be explained by a shift in electricity consumption from the industrial sector towards the commercial and the residential sectors, corresponding to an increase in the standard of living in the same period. A comparison was held with countries considered as developed for many years represented by the five largest economies (G-5) and recently developed countries (RDCs). Although Israel exhibits emission levels within the range of the G-5 countries, it does not fit the patterns demonstrated by these countries. Trends observed in Israel resemble these observed in other RDCs, such as Spain or Greece, confirming the classification of Israel in this category.
מידע נוסף

Change in pan evaporation over the past 50 years in the arid region of China
Pan evaporation, as a surrogate of potential evaporation, is reported to have decreased in different regions of the world since the 1950s. There is much literature to explain the decrease in pan evaporation using the so-called evaporation complimentary relationship hypothesis and it is argued that pan evaporation can be understood as a sign of global warming and indication of an accelerating hydrologic cycle. On the other hand, some scientists insist that the pan evaporation trends may be caused by a global dimming, which effectively reduces the solar radiation to the ground surface. However, few reports are available about the changes in pan evaporation and their implications to water balance in arid regions. In the present study, we investigate the trends in pan evaporation in arid regions of China over the past 50 years and attempt to characterize the changes in water balance in these areas. It is found that pan evaporation in these areas has portrayed a statistically significant decreasing trend, which may be attributed mainly to decreases in wind speed and diurnal temperature range and increase in precipitation. The trends in some major meteorological factors such as pan evaporation, precipitation, temperature, wind speed and others imply an enhanced hydrological cycle in the study area.
מידע נוסף

First projection of climatological mean river discharges in the Magdalena River basin, Colombia, in a changimg climate during the 21st century
This study projects the river discharge in the Magdalena River basin, Colombia, considering projected climate conditions for the 21st century, by using a 20-km-mesh atmospheric global climate model and a 0.5°-mesh global river routing model under a greenhouse gas emission scenario. The climatological annual mean river discharges along the main stream of the Magdalena River do not change significantly, however precipitation, evaporation, and total runoff into the river show statistically significantly changes over most of the Magdalena River basin. By the end of the 21st century, the projected climatological monthly mean river discharge at Puerto Berrio decreases statistically significantly in April, October, and November (P < 0.05), compared to current values, whereas it shows a distinct increase for June through August, thereby reducing the present bimodality of its seasonal variation. Minimum climatological monthly mean river discharge in February could be lower at the end of the 21st century than in the current condition. These results should help increase the awareness of the changing river discharge in the Magdalena River basin, and prepare adaptation strategies to face these challenges.
מידע נוסף

Climate change adaptation: the pivotal role of water
The document advocates for significant investments and policy shifts to be done, guided by the following principles: (i) Mainstream adaptations within the broader development context; (ii) Strengthen governance and improve water management; (iii) Improve and share knowledge and information on climate and adaptation measures, and invest in data collection; (iv) Build long-term resilience through stronger institutions, and invest in infrastructure and in well functioning ecosystems; (v) Invest in cost-effective and adaptive water management as well as technology transfer; and (vi) Leverage additional funds through both increased national budgetary allocations and innovative funding mechanisms for adaptation in water management.
מידע נוסף

Future changes in Central Europe heat waves expected to mostly follow summer mean warming
Daily output from the PRUDENCE ensemble of regional climate simulations for the end of the twentieth and twenty-first centuries over Europe is used to show that the increasing intensity of the most damaging summer heat waves over Central Europe is mostly due to higher base summer temperatures. In this context, base temperature is defined as the mean of the seasonal cycle component for those calendar days when regional heat waves occur and is close, albeit not identical, to the mean temperature for July–August. Although 36–47% of future Central Europe July and August days at the end of the twenty-first century are projected to be extreme according to the present day climatology, specific changes in deseasonalized heat wave anomalies are projected to be relatively small. Instead, changes in summer base temperatures appear much larger, clearly identifiable and of the same order of magnitude as changes in the whole magnitude of heat waves. Our results bear important consequences for the predictability of central European heat wave intensity under global warming conditions.
מידע נוסף

Cross-comparison of climate change adaptation strategies across large river basins in Europe, Africa and Asia
A cross-comparison of climate change adaptation strategies across regions was performed, considering six large river basins as case study areas. Three of the basins, namely the Elbe, Guadiana, and Rhine, are located in Europe, the Nile Equatorial Lakes region and the Orange basin are in Africa, and the Amudarya basin is in Central Asia. The evaluation was based mainly on the opinions of policy makers and water management experts in the river basins. The adaptation strategies were evaluated considering the following issues: expected climate change, expected climate change impacts, drivers for development of adaptation strategy, barriers for adaptation, state of the implementation of a range of water management measures, and status of adaptation strategy implementation. The analysis of responses and cross-comparison were performed with rating the responses where possible. According to the expert opinions, there is an understanding in all six regions that climate change is happening. Different climate change impacts are expected in the basins, whereas decreasing annual water availability, and increasing frequency and intensity of droughts (and to a lesser extent floods) are expected in all of them. According to the responses, the two most important drivers for development of adaptation strategy are: climate-related disasters, and national and international policies. The following most important barriers for adaptation to climate change were identified by responders: spatial and temporal uncertainties in climate projections, lack of adequate financial resources, and lack of horizontal cooperation. The evaluated water resources management measures are on a relatively high level in the Elbe and Rhine basins, followed by the Orange and Guadiana. It is lower in the Amudarya basin, and the lowest in the NEL region, where many measures are only at the planning stage. Regarding the level of adaptation strategy implementation, it can be concluded that the adaptation to climate change has started in all basins, but progresses rather slowly.
מידע נוסף

Europe adapts to climate change: Comparing national adaptation strategies
For the last two decades, European climate policy has focused almost exclusively on mitigation of climate change. It was only well after the turn of the century, with impacts of climate change increasingly being observed, that adaptation was added to the policy agenda and EU Member States started to develop National Adaptation Strategies (NASs). This paper reviews seven National Adaptation Strategies that were either formally adopted or under development by Member States at the end of 2008. The strategies are analysed under the following six themes. Firstly, the factors motivating and facilitating the development of a national adaptation strategy. Secondly, the scientific and technical support needed for the development and implementation of such a strategy. Thirdly, the role of the strategy in information, communication and awareness-raising of the adaptation issue. Fourthly, new or existing forms of multi-level governance to implement the proposed actions. Fifthly, how the strategy addresses integration and coordination with other policy domains. Finally, how the strategy suggests the implementation and how the strategy is evaluated. The paper notes that the role of National Adaptation Strategies in the wider governance of adaptation differs between countries but clearly benchmarks a new political commitment to adaptation at national policy levels. However, we also find that in most cases approaches for implementing and evaluating the strategies are yet to be defined. The paper concludes that even though the strategies show great resemblance in terms of topics, methods and approaches, there are many institutional challenges, including multi-level governance and policy integration issues, which can act as considerable barriers in future policy implementation.
מידע נוסף

Recent changes in the Mediterranean water cycle: A pathway toward long-term regional hydroclimatic change?
An observational analysis of Mediterranean Sea water cycle variability based on recently available datasets provides new insights on the long-term changes that affected the region since the 1960s. Results indicate an overall increase in evaporation during 1958–2006, with a decrease up until the mid-1970s and an increase thereafter. Precipitation variability is characterized by substantial interdecadal variations and a negative long-term trend. Evaporation increase, primarily driven by SST variability, together with precipitation decrease resulted in a substantial increase in the loss of freshwater from the Mediterranean Sea toward the overlying atmosphere. An increase in the freshwater deficit is consistent with observed Mediterranean Sea salinity tendencies and has broad implications for the Mediterranean water cycle and connected systems.These observational results are in qualitative agreement with simulated Mediterranean Sea water cycle behavior from a large ensemble of models from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 3 (CMIP3). However, simulated anomalies are about one order of magnitude smaller than those observed. This inconsistency and the large uncertainties associated with the observational rates of change highlight the need for more research to better characterize and understand Mediterranean water cycle variations in recent decades, and to better simulate the crucial underlying processes in global models.
מידע נוסף

Water access, water scarcity, and climate change
This article investigates the approaches of the various discourses operating in the water sector and how they address the issues of scarcity and equitable access under projected climate change impacts. Little synergy exists between the different approaches dealing with these issues. Whilst being a sustainable development and water resources management issue, a holistic view of access, scarcity and the projected impacts of climate change is not prevalent in these discourses. The climate change discourse too does not adequately bridge the gap between these issues. The projected impacts of climate change are likely to exacerbate the problems of scarcity and equitable access unless appropriate adaptation strategies are adopted and resilience is built. The successful delivery of accessible water services under projected climate change impacts therefore lies with an extension of the adaptive water management approach to include equitable access as a key driver.
מידע נוסף

Urban greening to cool towns and cities: A systematic review of the empirical
‘Urban greening’ has been proposed as one approach to mitigate the human health consequences of increased temperatures resulting from climate change. We used systematic review methodology to evaluate available evidence on whether greening interventions, such as tree planting or the creation of parks or green roofs, affect the air temperature of an urban area. Most studies investigated the air temperature within parks and beneath trees and are broadly supportive that green sites can be cooler than non-green sites. Meta-analysis was used to synthesize data on the cooling effect of parks and results show that, on average, a park was 0.94 °C cooler in the day. Studies on multiple parks suggest that larger parks and those with trees could be cooler during the day. However, evidence for the cooling effect of green space is mostly based on observational studies of small numbers of green sites. The impact of specific greening interventions on the wider urban area, and whether the effects are due to greening alone, has yet to be demonstrated. The current evidence base does not allow specific recommendations to be made on how best to incorporate greening into an urban area. Further empirical research is necessary in order to efficiently guide the design and planning of urban green space, and specifically to investigate the importance of the abundance, distribution and type of greening. Any urban greening programme implemented would need to be appropriately designed and monitored to continue to evaluate benefit to human health through reducing temperature.
מידע נוסף

Climate change and the global malaria recession
The current and potential future impact of climate change on malaria is of major public health interest1, 2. The proposed effects of rising global temperatures on the future spread and intensification of the disease3, 4, 5, and on existing malaria morbidity and mortality rates3, substantively influence global health policy6, 7. The contemporary spatial limits of Plasmodium falciparum malaria and its endemicity within this range8, when compared with comparable historical maps, offer unique insights into the changing global epidemiology of malaria over the last century. It has long been known that the range of malaria has contracted through a century of economic development and disease control9. Here, for the first time, we quantify this contraction and the global decreases in malaria endemicity since approximately 1900. We compare the magnitude of these changes to the size of effects on malaria endemicity proposed under future climate scenarios and associated with widely used public health interventions. Our findings have two key and often ignored implications with respect to climate change and malaria. First, widespread claims that rising mean temperatures have already led to increases in worldwide malaria morbidity and mortality are largely at odds with observed decreasing global trends in both its endemicity and geographic extent. Second, the proposed future effects of rising temperatures on endemicity are at least one order of magnitude smaller than changes observed since about 1900 and up to two orders of magnitude smaller than those that can be achieved by the effective scale-up of key control measures. Predictions of an intensification of malaria in a warmer world, based on extrapolated empirical relationships or biological mechanisms, must be set against a context of a century of warming that has seen marked global declines in the disease and a substantial weakening of the global correlation between malaria endemicity and climate.
מידע נוסף

Climate change impacts on working people: how to develop prevention policies
The evidence on negative consequences from climate change on human health and well-being is growing (1–5). The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) described climate change as a threat to the climate system that sets the basis for life and human health conditions (6). The changing climate is expected to affect basic requirements needed to support and sustain human health such as good food, clean water, and unpolluted air, with negative effects that are expected to be unequally distributed.Climate change has several direct adverse effects on working people such as heat exhaustion and heat stroke (7), as well as indirect effects including increased risks for infectious diseases, changing distribution and transmission patterns of vector-borne diseases, malnutrition, water and sanitation problems, and injuries due to extreme weather events (5). The poorest countries and the most vulnerable and marginalized individuals in all countries will experience the worst consequences from climate change (5, 8, 9). Regardless of the wealth of any nation, those who are poor, sick, very young or old, and those working intensely in high heat exposure are most at risk (10). In this special issue of Global Health Action a collection of papers are published in connection with COP 16 (Cancun, Mexico, December 2010) focusing on the impact of the current climate and climate change on working people. Most of the papers deal with conditions related to heat exposure and some relate to other occupational health problems linked to climate change. The impact of a changing climate on health, well-being, and productivity of working people is an area with consequences at all levels of society: family, community, region, country (7). There are also economic consequences for individual workers and their families, employers, and countries that deserve special attention.
מידע נוסף

Influence of climate on malaria transmission depends on daily temperature variation
Malaria transmission is strongly influenced by environmental temperature, but the biological drivers remain poorly quantified. Most studies analyzing malaria–temperature relations, including those investigating malaria risk and the possible impacts of climate change, are based solely on mean temperatures and extrapolate from functions determined under unrealistic laboratory conditions. Here, we present empirical evidence to show that, in addition to mean temperatures, daily fluctuations in temperature affect parasite infection, the rate of parasite development, and the essential elements of mosquito biology that combine to determine malaria transmission intensity. In general, we find that, compared with rates at equivalent constant mean temperatures, temperature fluctuation around low mean temperatures acts to speed up rate processes, whereas fluctuation around high mean temperatures acts to slow processes down. At the extremes (conditions representative of the fringes of malaria transmission, where range expansions or contractions will occur), fluctuation makes transmission possible at lower mean temperatures than currently predicted and can potentially block transmission at higher mean temperatures. If we are to optimize control efforts and develop appropriate adaptation or mitigation strategies for future climates, we need to incorporate into predictive models the effects of daily temperature variation and how that variation is altered by climate change.
מידע נוסף

Public perceptions of climate change as a human health risk: surveys of the United States, Canada and Malta
We used data from nationally representative surveys conducted in the United States, Canada and Malta between 2008 and 2009 to answer three questions: Does the public believe that climate change poses human health risks, and if so, are they seen as current or future risks? Whose health does the public think will be harmed? In what specific ways does the public believe climate change will harm human health? When asked directly about the potential impacts of climate change on health and well-being, a majority of people in all three nations said that it poses significant risks; moreover, about one third of Americans, one half of Canadians, and two-thirds of Maltese said that people are already being harmed. About a third or more of people in the United States and Canada saw themselves (United States, 32%; Canada, 67%), their family (United States, 35%; Canada, 46%), and people in their community (United States, 39%; Canada, 76%) as being vulnerable to at least moderate harm from climate change. About one third of Maltese (31%) said they were most concerned about the risk to themselves and their families. Many Canadians said that the elderly (45%) and children (33%) are at heightened risk of harm, while Americans were more likely to see people in developing countries as being at risk than people in their own nation. When prompted, large numbers of Canadians and Maltese said that climate change can cause respiratory problems (78–91%), heat-related problems (75–84%), cancer (61–90%), and infectious diseases (49–62%). Canadians also named sunburn (79%) and injuries from extreme weather events (73%), and Maltese cited allergies (84%). However, climate change appears to lack salience as a health issue in all three countries: relatively few people answered open-ended questions in a manner that indicated clear top-of-mind associations between climate change and human health risks. We recommend mounting public health communication initiatives that increase the salience of the human health consequences associated with climate change.
מידע נוסף

The health impacts of heat waves in five regions of New South Wales, Australia: a case-only analysis
To determine and characterise the health impacts of extreme heat events on the population in five regions of New South Wales (NSW). Such data provide evidence necessary for the development of policy and programme initiatives designed to reduce the burden of disease due to the impact of climate change. A case-only approach was used to analyse 1,497,655 emergency hospital admissions in Sydney East and West, Illawarra, Gosford-Wyong and Newcastle. The distribution of daily minimum and maximum temperatures in each region was used to define extreme heat (≥99th percentile). We investigated the susceptibility of the main causes of emergency hospital admission to extreme heat. We also examined the presence of underlying conditions as a risk modifier of emergency hospital admission on extreme heat. Logistic regression model was used to estimate the effect modifications. Main causes: On days of extreme heat, the risk of emergency hospital admission due to heat-related injuries, dehydration and other disorders of fluid, electrolyte and acid–base balance increased more than the risk of admission from other causes. Underlying conditions: Those with underlying mental and behavioural disorders, diseases of nervous and circulatory system, especially cardiac, diseases of respiratory system, especially asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, neoplasms and renal disease, especially renal failure, were more susceptible to an extreme heat event. In this study, we identified several main diagnoses and underlying conditions for emergency hospital admission that are particularly susceptible to extreme heat events. This knowledge can contribute directly to establishing health programmes that would effectively target those with higher relative risk of emergency hospital admission due to extreme heat.
מידע נוסף

Impact of rainfall manipulations and biotic controls on soil respiration in Mediterranean and desert ecosystems along an aridity gradient
Spatially heterogeneous ecosystems form a majority of land types in the vast drylands of the globe. To evaluate climate-change effects on CO2 fluxes in such ecosystems, it is critical to understand the relative responses of each ecosystem component (microsite). We investigated soil respiration (Rs) at four sites along an aridity gradient (90–780 mm mean annual precipitation, MAP) during almost 2 years. In addition, Rs was measured in rainfall manipulations plots at the two central sites where ∼30% droughting and ∼30% water supplementation treatments were used over 5 years. Annual Rs was higher by 23% under shrub canopies compared with herbaceous gaps between shrubs, but Rs at both microsites responded similarly to rainfall reduction. Decreasing precipitation and soil water content along the aridity gradient and across rainfall manipulations resulted in a progressive decline in Rs at both microsites, i.e. the drier the conditions, the larger was the effect of reduction in water availability on Rs. Annual Rs on the ecosystem scale decreased at a slope of 256/MAP g C m−2 yr−1 mm−1 (r2=0.97). The reduction in Rs amounted to 77% along the aridity gradient and to 16% across rainfall manipulations. Soil organic carbon (SOC) decreased with declining precipitation, and variation in SOC stocks explained 77% of the variation in annual Rs across sites, rainfall manipulations and microsites. This study shows that rainfall manipulations over several years are a useful tool for experimentally predicting climate-change effects on CO2 fluxes for time scales (such as approximated by aridity gradients) that are beyond common research periods. Rainfall reduction decreases rates of Rs not only by lowering biological activity, but also by drastically reducing shrub cover. We postulate that future climate change in heterogeneous ecosystems, such as Mediterranean and deserts shrublands will have a major impact on Rs by feedbacks through changes in vegetation structure.
מידע נוסף

Adaptation to climate change in Sweden: knowledge, policy and practice
Our research explores how science can help Swedish stakeholders to assess adaptation needs and options. In our research, meetings between scientists and stakeholders revealed a positive attitude to using scientific knowledge in adaptation decision-making. The study suggests that, to support decision-making, there is a need for scientific results (notably climate change and impact scenarios) to be presented in a more user-friendly fashion, as well as for greater informal interaction between scientists, practitioners and policymakers.In particular, there is a need for results to show shorter time horizons, provide clear graphics, and offer more locally relevant information.
מידע נוסף

Climate change and its impacts on the coastal zone of the Nile Delta, Egypt
The main objectives of the current work are (1) to determine historic pattern of shoreline changes (erosion and accretion) along the north coast of the Nile Delta, (2) to present a future view on what to be expected regarding climate change impacts, sea-level rise (SLR) scenarios, expected land losses and alteration of some soil characteristics (3) to recognize negative impacts of SLR on the Nile Delta coast and (4) to assess and suggest protection measures. The current investigation was conducted using the advanced techniques of remote sensing and geographic information system. The investigated area with 394 measured locations is located along the northern coast of the Nile Delta between Alexandria and ElTina plain in Sinai peninsula exactly between 29°20′ and 32°40′ E and 29°54′ and 31°35′ N with the minimum erosion values of 1.11 m2, maximum of 6,044,951.64 m2 and total of 16.02 km2. On the other hand, 177 sites showed minimum accretion values of 0.05 m2, maximum of 2,876,855.86 m2 and total of 13.19 km2. SLR was determined by applying the quadrant equation for 10-year intervals using 1990 as the base year. Mediterranean SLR along the Nile Delta coast could be estimated considering three different scenarios (low 0.20 m, medium 0.50 m, and high 0.90 m). Impacts of SLR are divided into (1) primary and (2) secondary impacts. Over the coming decades, the Nile Delta will face greater threat due to SLR and land subsidence as well. Regarding climate change and its impacts on soil characteristics, rapid increase in salinity values during the former three decades were found. This increase may be due to the intrusion of salty water of the Mediterranean. On the other hand, organic matter content decreased due to higher temperature, especially during the summer season. Some protection measures were assessed and suggested to combat or tackle SLR.
מידע נוסף

On Modeling and Interpreting the Economics of Catastrophic Climate Change
With climate change as prototype example, this paper analyzes the implications of structural uncertainty for the economics of low probability, high-impact catastrophes
מידע נוסף

Spain, Water and Climate Change in COP 15 and Beyond: Aligning Mitigation and Adaptation through Innovation (WP)
The water/energy nexus opens a range of opportunities to align mitigation and adaptation framed by human security, which prioritises human development. In this context, Spain has an opportunity to play a leading role in realising this potential by pursuing a coherent multilevel strategy specifically designed for water and climate variability and change. Spain has a clear opportunity and, for practical policy reasons, a very clear self-interest in placing the water/energy nexus and the alignment of mitigation and adaptation high on the political agenda. The aim at COP-15 should be first for a global agreement and, as second best, a small multilateral group with Mediterranean and Latin American countries on the need to link water and climate change and variability. The second act will be the EU Presidency, where Spain can leave a legacy.
מידע נוסף

Effect of extreme rainfall events on the water resources of the Jordan River
As a response to climate change, shifting rainfall trends including increased multi-year droughts and an escalation in extreme rainfall events are expected in the Middle East. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the potential impact of these shifting trends on stream flow in the Jordan River and its tributaries. We use a non-homogeneous hidden Markov model to generate artificial daily rainfall simulations which capture independently shifting trends of increased droughts and escalated extreme. These simulations are then used as input into a hydrological model calibrated for the upper catchments of the Jordan River to compare the impact on stream flow and water resources between the different rainfall scenarios. We compare the predicted baseflow and surface flow components of the tested watersheds, and find that while an increase in extreme rainfall events increases the intensity and frequency of surface flow, the over all flow to the Jordan River, and the characteristics of the baseflow in the Jordan River system is not largely impacted. In addition, though it has been suggested that in the case of a multi-year drought the karstic nature of the aquifer might lead to more intense, non-linear reductions in stream flow, here we quantify and show the conditions when annual stream flow reduce linearly with rainfall, and when these relations will become non-linear.
מידע נוסף

Seattle Climate Protection Initiative: Progress Report 2009
The 2009 Climate Protection Initiative Progress Report details Seattle's numerous environmental and smart growth programs such as bicycle and pedestrian improvements, new transit options, electric car infrastructure, conservation efforts and green building programs. In addition to reducing the city's contribution to global warming, Seattle will also prepare for climate change by ensuring that its infrastructure, facilities, and services are ready to adapt to the projected impacts of climate change. The report's page on adaptation reviews efforts to conserve water in anticipation of a reduction in snow pack, and highlights the creation of sea-level rise maps for use by city officials in future planning.
מידע נוסף

Climate change and health: impacts, vulnerability, adaptation and mitigation
Global climate change is progressing and health impacts have been observed in a number of countries, including Australia. The main health impacts will be due to direct heat exposure, extreme weather, air pollution, reduced local food production, food- and vectorborne infectious diseases and mental stress. The issue is one of major public health importance. Adaptation to reduce the effects of climate change involves many different sectors to minimise negative health outcomes. Wide-scale mitigation is also required, in order to reduce the effects of climate change. In addition, future urban design must be modified to mitigate and adapt to the effects of climate change. Strategies for mitigation and adaptation can create co-benefits for both individual and community health, by reducing non-climate-related health hazard exposures and by encouraging health promoting behaviours and lifestyles
מידע נוסף

Biodiversity and Climate Change in the European Union
If the loss of biodiversity continues – or
accelerates – it will compromise the achieve
-
ment of the climate change goals. Urgent
action now to halt the further biodiversity
loss and degradation will help to maintain
provision of ecosystem services and future
options for reducing the extent of climate
change and managing its impacts. Healthy
ecosystems are a
precondition for stabilising
the climate system. Therefore maintenance
and restoration of biodiversity and healthy
ecosystems represent our life insurance for
the future.
מידע נוסף

Convenient Solutions to an inconvenient Truth, Ecosystem-based Approaches to Climate Change
The World Bank's Environment Department has published a report titled “Convenient Solutions to an Inconvenient Truth: Ecosystem-based Approaches to Climate Change,” which sets out an argument for including ecosystem-based approaches to mitigation and adaptation as a third and essential pillar in national strategies to address climate change.
Such ecosystem-based strategies can offer cost-effective, proven and sustainable solutions contributing to, and complementing, other national and regional adaptation strategies. The report notes that three of the world's greatest challenges over the coming decades will be biodiversity loss, climate change and water shortages. It underscores that promoting further integration of ecosystem-based approaches into climate change responses and national adaptation strategies will require access to greater sources of funding, including capitalizing on opportunities to protect natural ecosystems as part of major energy and infrastructure projects. The report reviews the Bank's experience in promoting market-based financing mechanisms and instruments to expand the reach of the carbon market. New initiatives and investment funds, such as the Forest Carbon Partnership Facility, the Forest Investment Program and the Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, are highlighted as new opportunities to better protect natural capital, benefit communities and use cost-effective green technology to address the challenges of climate change.
מידע נוסף

Towards a Strategy on Climate Change, Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity A discussion paper prepared by the EU Ad Hoc Expert Working Group on Biodiversity and Climate Change
Biodiversity and ecosystem services are not just
the victims of our mismanagement, but are
our ally in dealing with the problems of
global environmental change. Ecosystem-based
approaches contribute to tack
ling the causes and consequences of climate change, provide
multiple benefits across society and protect the vital natural functions on which human well-
being depends. An increasing number of recen
t reviews, policy documents and reports e.g.
"The Natural Fix? – the role of ecosystems in climate mitigation" by UNEP
7
and "Convenient
Solutions to an Inconvenient Truth: Ecosyste
m-based Approaches to Climate Change" by the
Environment Department of The World Bank
8
emphasise the two-way link between
biodiversity and climate change and demonstrat
e an increasing awareness of the important
role of ecosystems in the climate system as well
as of the value of protecting biodiversity as a
route to moderating climate change. Without
healthy and resilient ecosystems it will not be
possible to stabilise the climat
e system or to adapt to the
unavoidable impacts of climate
change. Therefore urgent action is needed
to halt the further lo
ss and degradation of
biodiversity and ecosystem services, if we are to
retain the ability to reduce the extent of
climate change and manage its impacts.
מידע נוסף

Ecosystem-based Adaptation (EbA) Fifth session of the UNFCCC Ad Hoc Working Group on Long-Term Cooperative Action under the Convention (AWG-LCA)
Ecosystem-based Adaptation (EbA) includes a range of local and landscape scale
strategies that enable both people and nature to adapt in the face of climate change. An
ecosystem-based approach to adaptation is compatible and supportive of a wide range
of local and national development objectives, as
well as with ongoing adaptation efforts
at community level, and with existing priorities identified in many of the most vulnerable
countries.
מידע נוסף

California Climate Change Adaptation
The State of California addresses adaptation to climate change through its California Climate Adaptation Strategy which summarizes climate change impacts and recommends adaptation strategies.
The State is also developing an Adaptation Planning Guide (APG) to provide a decision-making framework intended for use by local and regional stakeholders to aid in the interpretation of climate science and to develop a systematic rationale for reducing risks caused, or exacerbated, by climate change.
The State's third major assessment on climate change explores local and statewide vulnerabilities to climate change, highlighting opportunities for taking concrete actions to reduce climate-change impacts. See the Reports on the Third Assessment.
The California Natural Resources Agency and the California Energy Commission have released Cal-Adapt, a web-based tool which enables city and county planners, government agencies, and the public to identify potential climate change risks in specific areas throughout California.
מידע נוסף

Adapting Buildings and Cities for Climate Change
We have been told by the science that we only have a few years to reduce our carbon emissions to levels that will prevent climate chaos, to effectively mitigate. We believe that in the face of rapid and catastrophic change the more pressing challenge is to develop the processes by which we can adapt to at least three degrees of climate change in the coming handful of decades. All around us now is evidence that many are not taking the scale of task ahead seriously. There is no doubt that much can be achieved with new approaches to design, and technological fixes, but it is ultimately only with a fundamental re-ordering of our priorities, our aspirations and our societies that we will create a social, economic and physical environment in which Homo sapiens can hope to survive, en masse, safely, through to the end of this century.
מידע נוסף

Adapting to Climate Change Towards a European framework for action
This White Paper sets out a framework to reduce the EU’s vulnerability to the impact of
climate change. It builds on the wide-rangi
ng consultation launched in 2007 by the Green
Paper on Adapting to Climate Change in Europe
1
and further research efforts that identified
action to be taken in the short-
term. The framework is designed to evolve as further evidence
becomes available. It will complement
action by Member States and support wider
international efforts to adapt to
climate change, particularly in
developing countries. The EU
is working with other partner countries in the UNFCCC
2
towards a post-2012 climate
agreement which will address adaptation as well as mitigation. The Commission's proposals
in this context are set out in the Communicatio
n entitled “Towards a comprehensive climate
change agreement in Copenhagen
מידע נוסף

Assessing the impact of climate change on representative field crops in Israeli agriculture: a case study of wheat and cotton
Climate changes, associated with accumulation of greenhouse gases, are expected to have a profound influence on agricultural sustainability in Israel, a semi-arid area characterized by a cold wet winter and a dry warm summer. Accordingly this study explored economic aspects of agricultural production under projected climate-change scenarios by the “production function” approach, as applied to two representative crops: wheat, as the major crop grown in Israel’s dry southern region, and cotton, representing the more humid climate in the north. Adjusting outputs of the global climate model HadCM3 to the specific research locations, we generated projections for 2070–2100 temperatures and precipitations for two climate change scenarios. Results for wheat vary among climate scenarios; net revenues become negative under the severe scenario (change from −145 to −273%), but may increase under the moderate one (−43 to +35%), depending on nitrogen applied to the crop. Distribution of rain events was found to play a major role in determining yields. By contrast, under both scenarios cotton experiences a considerable decrease in yield with significant economic losses (−240 and −173% in A2 and B2 scenarios, respectively). Additional irrigation and nitrogen may reduce farming losses, unlike changes in seeding dates.
מידע נוסף

City of Madrid Plan for the Sustainable Use of Energy and Climate Change Prevention 2008
Madrid City Council is aware that climate change prevention
and energy efficiency are among the main challenges
facing the city of Madrid. In recent years, considerable
effort has been made in this respect, through measures
designed to address both objectives, such as the Local Air
Quality Strategy, energy diversification of the City Council
fleet or participation in European projects, among others.
The combination of these actions and their continuation
over time have led to a significant abatement of emissions.
מידע נוסף

Chicago Climate Action Plan - Strategy 5: Adaptation
Chicagoans have long prized the city’s spacious green parks and tree-shaded streets. In warmer months, when cooling breezes blow off the lake, people crowd the city’s ball fields, summer festivals and open-air concerts. Even the bracing change of seasons is a source of civic pride. Yet as many who have already dedicated themselves to climate issues know, our familiar cycle of weather my soon become a dim memory. The earth responds slowly to changes in atmospheric gases. For that reason, over the next few decades, we will continue to face the consequences of our heat-trapping gas emissions from decades past.
Aggressive action will reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the future. We must also take action by adapting to changes that are already happening and preparing for the changes ahead. The previous sections have outlined mitigation strategies – key elements of the plan to reduce the likelihood of adverse conditions. Adaptation, the courses of action detailed here, will help reduce the impact of the changes that can be expected even if we greatly reduce emissions.
מידע נוסף

Chicago Climate Action Plan
The Chicago Climate Action Plan was created to determine the challenges we face in Chicago as a result of climate change, outline achievable goals to reduce emissions and adapt to changes that currently impact the city of Chicago. The Chicago Climate Action Plan outlines five strategies: Energy Efficient Buildings; Clean and Renewable Energy Sources; Improved Transportation Options; Reduced Waste and Industrial Pollution, and Adaptation.
מידע נוסף

Adaptation to climate change in the European Union efficiency vs. equity considerations
EU climate policy is based on GHG emissions reduction (mitigation) coupled with measures aimed at responding efficiently to the unavoidable consequences of climate change (adaptation). However, as the European Commission recently stated in its Green Paper on adaptation in Europe, there is still a need to develop an overall EU adaptation strategy. Moreover, such a strategy should take into consideration both efficiency and equity concerns. In this article we propose a framework for EU adaptation policy that addresses both concerns and which enables a transparent decision-making process. In the proposed scheme universal weightings of the individual policy objectives have to be agreed upon prior to actual decision-making.
מידע נוסף

Cambridge Climate Change Strategy & Action Plan 2008-2012
The purpose of the Cambridge Climate Change Strategy & Action Plan is to establish the framework for action in Cambridge to tackle the causes and consequences of climate change. It describes the present situation, rationale, future intentions and actions for Cambridge City Council to take in order to achieve them.
מידע נוסף

Stern Review: the Economics of Climate Change
The Stern Review, released on October 30, 2006, provides the most thorough and rigorous analysis to date of the costs and risks of climate change and reducing emissions and convincingly argues that the benefits of strong, early global action to mitigate climate change will be far lower than the costs.
מידע נוסף

Assessing the robustness of adaptation decisions to climate change uncertainties: A case study on water resources management in the East of England
Projections of future climate change are plagued with uncertainties, causing difficulties for planners taking decisions on adaptation measures. This paper presents an assessment framework that allows the identification of adaptation strategies that are robust (i.e. insensitive) to climate change uncertainties. The framework is applied to a case study of water resources management in the East of England, more specifically to the Anglian Water Services’ 25 year Water Resource Plan (WRP). The paper presents a local sensitivity analysis (a ‘one-at-a-time’ experiment) of the various elements of the modelling framework (e.g., emissions of greenhouse gases, climate sensitivity and global climate models) in order to determine whether or not a decision to adapt to climate change is sensitive to uncertainty in those elements.
Water resources are found to be sensitive to uncertainties in regional climate response (from general circulation models and dynamical downscaling), in climate sensitivity and in climate impacts. Aerosol forcing and greenhouse gas emissions uncertainties are also important, whereas uncertainties from ocean mixing and the carbon cycle are not. Despite these large uncertainties, Anglian Water Services’ WRP remains robust to the climate change uncertainties sampled because of the adaptation options being considered (e.g. extension of water treatment works), because the climate model used for their planning (HadCM3) predicts drier conditions than other models, and because ‘one-at-a-time’ experiments do not sample the combination of different extremes in the uncertainty range of parameters. This research raises the question of how much certainty is required in climate change projections to justify investment in adaptation measures, and whether such certainty can be delivered.
מידע נוסף

Challenges to manage the risk of water scarcity and climate change in the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean region is undergoing rapid local and global social and environmental changes. All indicators point to an increase in environmental and water scarcity problems with negative implications towards current and future sustainability. Water management in Mediterranean countries is challenged these pressures and needs to evolve to reach the target of increasing population with reliable access to freshwater established by the Millennium Development Goals. This paper first reviews and evaluates current and future social and environmental pressures on water resources, including climate change. The results show that pressures are not homogeneous across the region and sectors of water use. Second the paper evaluates the adaptation strategies to cope with water scarcity, including technology, use of strategic groundwater, and management. Finally, the paper proposes a framework for managing the risk of water scarcity based on preparedness rather than a crisis approach. The importance of local management at the basin level is emphasized, but the potential benefits depend on the appropriate multi-institutional and multi-stakeholder coordination.
מידע נוסף

Developing a Municipal Adaptation Plan (MAP) for climate change: the city of Cape Town
Climate change increases the likelihood of extreme weather events such as droughts, floods and heat waves, as well as more gradual changes in temperature and precipitation. The city of Cape Town (South Africa) is at risk from projected climate-induced warming and changes in rainfall variability. This makes resource management and infrastructure planning more challenging and increases the urgency of the need to adapt city-level operations to both current climate variability and future climate change. To date, however, the main focus of adaptation planning has been at the nationallevel, and has not adequately addressed municipal-scale adaptation. This paper presents and discusses an overarching framework that would facilitate the development of a Municipal Adaptation Plan (MAP). The example of the city of Cape Town illustrates some of the sector-level assessments and potential climate threats, as well as resource mobilization issues that need to be addressed during the development and implementation of a MAP. In conclusion, a number of barriers to developing a MAP are discussed.
מידע נוסף

A Survey of Climate Change Adaptation Planning
The report is divided into two sections: (i) adaptation planning guidebooks and frameworks, and (ii) adaptation planning efforts that are currently underway. This introductory survey report is designed to provide a “road map” to some of this information. It makes no claim to be comprehensive or to represent best practices on adaptation. Rather, the goal in producing this survey is to help generate discussion and the sharing of ideas, efforts and lessons learned across the adaptation community.
מידע נוסף

Climate change adaptation by design: a guide for sustainable communities
Drawing on research just published as part of the Building Knowledge for a Changing Climate programme, the guide uniquely considers how adaptation options are influenced by geographical location and the scale of development. It considers the interrelated roles of the planning system, communities, other stakeholders and delivery bodies. It seeks to ensure a better understanding of climate risks while demonstrating effective adaptation strategies through case studies from around the world.
Case studies and guidance include: policy and legislative drivers for adaptation action both internationally and in the UK; a proposed framework for delivering adaptation action at the regional and local levels, together with some guidance on creating local adaptation strategies; a menu of adaptation options using practical examples, organized according to the main climate risks that communities in the UK face; technologies for climate risk management.
מידע נוסף

Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Water, Land-use and Economic Return in Agriculture
We develop a regional scale economic model for analyzing climate-change impacts on agriculture. Non-linear production functions describing yield responses to land allocation, water application and water salinity are integrated into a mathematical programming model. The responses to water quantity and quality are estimated by the use of scientific-based models simulating equilibrium in the root zone among plant's water uptake, soil salinity and soil's water content. Internalization of land allocation among crops is based on Howitt's PMP calibration approach (1995). The model, therefore, enables assessment of climate-change impacts on optimal agricultural management, where adaptation is considered endogenously with respect to both the extensive and intensive margins.
The model is applied to the case of Israel. We divide the country into 14 regions and estimate regional future precipitation levels by implementing a climate-change down-scaling procedure. Then the model computes optimal agricultural managements under these projected rainfall levels. The results indicate a reduction of about 20% in statewide annual agricultural net-revenues by the year 2100 in comparison to 2002. Land allocated to field crops is increased on the expense of forages and vegetables. The shares of field crops and forages in the agricultural irrigation-water allotment are increased, while that of vegetables declines.
מידע נוסף

Finland's national strategy for adaptation to climate change
The Parliament’s reply to the National Climate Strategy submitted to the Parliament in
March 2001 identifi ed the need to draft a programme for adaptation to climate change.
The preparation of the National Strategy for Adaptation to Climate Change was started
in the latter part of 2003. The work was coordinated by the Ministry of Agriculture
and Forestry and representatives from the Ministry of Traffi c and Communications,
Ministry of Trade and Industry, Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Ministry of the
Environment, Ministry for Foreign Affairs, Finnish Meteorological Institute and Finnish
Environment Institute took part in the preparation. Each Ministry was responsible for
assessing the impacts and identifying adaptation measures in its own sector.
מידע נוסף

Finland's national strategy for adaptation to climate change
The Parliament’s reply to the National Climate Strategy submitted to the Parliament in
March 2001 identifi ed the need to draft a programme for adaptation to climate change.
The preparation of the National Strategy for Adaptation to Climate Change was started
in the latter part of 2003. The work was coordinated by the Ministry of Agriculture
and Forestry and representatives from the Ministry of Traffi c and Communications,
Ministry of Trade and Industry, Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Ministry of the
Environment, Ministry for Foreign Affairs, Finnish Meteorological Institute and Finnish
Environment Institute took part in the preparation. Each Ministry was responsible for
assessing the impacts and identifying adaptation measures in its own sector.
מידע נוסף

Weather changes associated with hospitalizations for cardiovascular diseases and stroke in California, 1983-1998
Poisson regression models were used to evaluate associations between temperature, precipitation, days of extreme heat, and other weather changes (lagged 7 days), as well as El Niño events, with hospitalizations for acute myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, congestive heart failure, and stroke in three California regions. Temperature changes were defined as a 3 °C decrease in maximum temperature or a 3 °C increase in minimum temperature. Temperature and precipitation were analyzed separately for normal weather periods and El Niño events, and for both weather periods combined. Associations varied by region, age, and gender. In Los Angeles, temperature changes resulted in small changes in hospitalizations. Among San Francisco residents 70+ years of age, temperature changes increased hospitalizations for nearly all outcomes from 6% to 13%. Associations among Sacramento residents were similar to those in San Francisco: among men 70+ years of age, temperature changes increased hospitalizations by 6%–11% for acute myocardial infarction and congestive heart failure, and 10%–18% for stroke. El Niño events were consistently and significantly associated with hospitalizations only in San Francisco and Sacramento, and then only for angina pectoris (increasing hospitalizations during El Niño events). These exploratory analyses merit further confirmation to improve our understanding of how admissions to hospitals for cardiovascular disease and stroke change with changing weather. Such an understanding is useful for developing current public health responses, for evaluating population vulnerability, and for designing future adaptation measures.
מידע נוסף

Buying Time: A User’s Manual for Building Resistance and Resilience to Climate Change in Natural Systems
This publication is meant for Protected Areas Managers. It gives detailed information about assessing occurring and possible damage from climate change and fending off the damage - buying time for our protected areas while the world works out the only long-term solution - reducing CO2 emissions - See more at: http://wwf.panda.org/?8678/BUYING-TIME-A-Users-Manual-for-Building-Resistance-and-Resilience-to-Climate-Change-in-Natural-Systems#sthash.YLG2orEK.dpuf
מידע נוסף

Chapter 1 - Global climate change and health an old story writ large
Chapter 1 of the book "Climate Change and Human Health" is presented. It describes the context and process of global climate change and how human societies should respond. It anticipates that humankind's increasing emission of greenhouse gases will induce a long-term change in the world's climate. It details the findings of a report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
מידע נוסף

Background Paper to the Task Force on Climate Change, Adaptation and Vulnerable Communities
The sharpest impact of our changing climate on hum
an systems will be the rise in incidence and
severity of climate-related disasters. The two main disciplines concerned with human
vulnerability to climate extremes are disaster
management and climate change. While disaster
managers develop and implemen
t hands-on tools for reducing vu
lnerability to natural hazards,
they have yet to incorporate the implications of
climate change into their work. Climate change
researchers and policymakers are increasingly fo
cusing on adapting to a changing climate, but
have not yet spelled out how to do so with groun
d-level action. Working from different point of
departure, both disciplines have come to
a common conclusion, that natural resource
mismanagement contributes to the vulnerability of
human systems to these hazards, and enhanced
management can provide a tool for vulnerability reduction.
מידע נוסף

An Anatomy of Adaptation to Climate Change and Variability
Adaptation to climate variability and change is important both for impact assessment (to estimate adaptations which are likely to occur) and for policy development (to advise on or prescribe adaptations). This paper proposes an "anatomy of adaptation" to systematically specify and differentiate adaptations, based upon three questions: (i) adapt to what? (ii) who or what adapts? and (iii) how does adaptation occur? Climatic stimuli include changes in long-term mean conditions and variability about means, both current and future, and including extremes. Adaptation depends fundamentally on the characteristics of the system of interest, including its sensitivities and vulnerabilities. The nature of adaptation processes and forms can be distinguished by numerous attributes including timing, purposefulness, and effect. The paper notes the contribution of conceptual and numerical models and empirical studies to the understanding of adaptation, and outlines approaches to the normative evaluation of adaptation measures and strategies.
מידע נוסף

Anticipated public health consequences of global climate change
Human activities are placing enormous pressures on the biosphere. The introduction of new chemicals and the increasing ambient levels of existing chemicals have resulted in atmospheric degradation. This paper reviews some of the adverse effects of stratospheric ozone depletion and global warming. Because the atmospheric effects of ozone depletion are fairly well characterized, quantitative risk estimates have been developed. However, because the atmospheric effects of global warming are less understood, public health problems that could be intensified by climate change are assessed qualitatively. The interactive effects of these two phenomena are also discussed.
מידע נוסף

Guide to Climate Change Adaptation in Cities
This Guide is a practical resource on responding to the challenges of climate change adaptation in cities. The principal intended audience is city officials and practitioners in developing countries, who are beginning to consider the issues of climate change adaptation, and can find in this guide an introduction and comprehensive overview of this evolving topic.The Guide offers examples of good practices and successful experiences and describes other available resource materials and tools. It outlines practical perspectives, showing ways to link climate change to community priorities and other important city issues such as disaster risk reduction, economic development, public health, sustainability, food security and other priorities. In so doing, it can contribute to the development and implementation of adaptation plans in cities, strengthening capacities and helping to catalyze dialogue on adaptation among city managers and other stakeholders.
מידע נוסף
מאמרים ופרסומים אחרונים

תוכנית היערכות לאומית לשינוי אקלים
המשרד להגנת הסביבה מפרסם את השלב הראשון של התוכנית הלאומית להיערכות לשינוי אקלים.
מידע נוסף

משבר האקלים – קונצנסוס מדעי לנוכח התעלמות והכחשה
מדעני האקלים שבים ומתריעים כי פליטות גזי חממה שמקורן בפעילות האדם מביאות להשתנות האקלים, והשתנות זו משפיעה דרמטית על הסביבה, על המערכות האקולוגיות ועל מרבית ההיבטים של תנאי החיים על כדור הארץ
מידע נוסף

מפת סיכונים לאומית להיערכות לשינוי אקלים
במסגרת ההיערכות לשינוי אקלים, המשרד להגנת הסביבה עסק בשנה האחרונה בפיתוח כלי גאוגרפי תומך בקבלת החלטות מבוססות מדע וידע. הכלי יסייע למקבלי החלטות בכל הרמות לקבל החלטות ולקבוע סדרי עדיפויות מושכלות בתכנון וביישום של ההיערכות לשינוי אקלים.
מידע נוסף

שינויי הטמפרטורה בישראל – בראי שלושה אטלסים אקלימיים
עבודה זו בוחנת את מגמות השינוי בטמפרטורה בישראל בהתבסס על השוואת שלוש תקופות מיצוע
של 15 שנה מתוך האטלסים האקלימיים שפרסם השירות המטאורולוגי הישראלי: ,1979-1964
2009-1995 ו.2020-2006
מידע נוסף
של 15 שנה מתוך האטלסים האקלימיים שפרסם השירות המטאורולוגי הישראלי: ,1979-1964
2009-1995 ו.2020-2006

שינוי האקלים העולמי: אתגרים, השלכות ומדיניות בעולם ובישראל
מסמך זה נכתב לבקשת ועדת הפנים והגנת הסביבה. מטרתו להקיף סוגיות יסוד במגוון
תחומים הקשורים למדיניות האקלים, לקראת ועידת האקלים 28COP שמתקיימת בדובאי
מ30- בנובמבר עד 12 בדצמבר 2023 ולקראת הדיונים בחוק אקלים שאושר זה מכבר בוועדת
השרים לענייני חקיקה.
מידע נוסף
תחומים הקשורים למדיניות האקלים, לקראת ועידת האקלים 28COP שמתקיימת בדובאי
מ30- בנובמבר עד 12 בדצמבר 2023 ולקראת הדיונים בחוק אקלים שאושר זה מכבר בוועדת
השרים לענייני חקיקה.

תמיכה ממשלתית בתוכניות היערכות לשינוי האקלים ברשויות המקומיות
מסמך זה נכתב לבקשת חבר הכנסת יוראי להב הרצנו, ובו סקירה של התמיכה הממשלתית בתוכניות ההיערכות (אדפטציה) לשינוי האקלים ברשויות המקומיות בישראל.
מידע נוסף

דו״ח ה-OECD: סקירת הביצועים הסביבתיים של ישראל
גירסה מקוצרת: תרגום לעברית של פרסום של ה-OECD
מידע נוסף

אומדן הנזק הכלכלי מהתחממות המרחב הציבורי בעיר תל אביב-יפו
עבודה זו בוחנת את ההשפעות של התחממות המרחב העירוני בתל אביב-יפו על היבטים כלכליים שונים ברווחת ציבור לקוחות העיר (עסקים, תיירים, ותושבים) ובכלכלת העירייה, בשנת 2050.
מידע נוסף

תרחישי ייחוס לאירועי מזג אוויר קיצוניים בישראל (עדכון מרץ 2023)
כדי לאפשר היערכות טובה יותר למצבי מזג אוויר קיצוניים שעלולים להתרחש בעתיד, מתקיים תהליך עבודה משותף של השירות המטאורולוגי (שמ"ט) עם רשות החירום הלאומית (רח"ל) שנועד לגבש תרחישי ייחוס לאירועי מזג אוויר קיצוניים.
בעקבות זאת יצא מסמך המתאר את תרחישי הייחוס, אשר גובשו על-ידי השמ"ט.
המסמך הוכן במקור ב-2015. הוא עודכן לאחרונה במרץ 2023 וכולל גם עדכון לגבי עומס החום.
מידע נוסף
בעקבות זאת יצא מסמך המתאר את תרחישי הייחוס, אשר גובשו על-ידי השמ"ט.
המסמך הוכן במקור ב-2015. הוא עודכן לאחרונה במרץ 2023 וכולל גם עדכון לגבי עומס החום.

על ישראל לעדכן את התחזיות והתרחישים בנוגע לעליית גובה פני הים
הים הוא שחקן מרכזי בתופעת משבר האקלים. הוא קולט פחמן דו חמצני ופולט גזי חממה, אבל גם פולט מחצית מהחמצן שאנחנו נושמים. הים משפיע ישירות על האקלים, והוא מקור פרנסה ומזון למיליארדי בני אדם. בעקבות שינוי האקלים, גובה פני הים עולה, הוא הופך חם יותר וחומצי יותר, המגוון הביולוגי נפגע, קליטת גזי החממה יורדת והפליטה של גזי חממה עולה, בד בבד עם ירידה בפליטת חמצן.
מידע נוסף

דו"ח מצב הטבע 2022 – כרך מגמות ואיומים - פרק ג' - שרפות בשטחים הטבעיים והמיוערים בישראל
דו"ח מצב הטבע מרכז ומציג מידע מרחבי ועיתי על איומים למערכות האקולוגיות ועל תהליכים משמעותיים המשפיעים עליהן ועל המגוון הביולוגי.
פרק ג' - מיפוי וניתוח מרחבי ועיתי של תדירות השרפות בשטחים הטבעיים והמיוערים בישראל בשבע השנים האחרונות
מידע נוסף
פרק ג' - מיפוי וניתוח מרחבי ועיתי של תדירות השרפות בשטחים הטבעיים והמיוערים בישראל בשבע השנים האחרונות

דו"ח מצב הטבע 2022 – כרך מגמות ואיומים - פרק ז' – שינוי אקלים והשפעתו על המגוון הביולוגי
סקירת תופעות שינוי האקלים ונתוני תחזיות בעולם ובארץ, הצגת ההשפעות הנצפות והצפויות על החי והצומח.
מידע נוסף

Agriculture, irrigation and drought induced international migration: Evidence from Mexico
There is now substantial empirical evidence that climatic variability increases international migration, but relatively little is known about the mechanism driving the association and about adaptations that may reduce it. We use detailed data on migrants from Mexico to the U.S. to provide evidence in support of the hypothesis that drought induced migration from Mexico to the U.S. is mediated by agricultural income shocks.
מידע נוסף

Beating the urban heat: Situation, background, impacts and the way forward in China
This paper reviews urban heat (UrHT) challenges following the SBAR (situation, background, assessment and recommendation) framework. The results indicate that heatwaves become more frequent, lasting and intense, especially after 1990s. Above 1960s level, heatwaves across China doubled in both magnitude and frequency by 2018.
מידע נוסף

אוכלוסיות פגיעות ומשבר האקלים – תוכנית המאיץ
מסמך זה הוא פרי שיתוף פעולה של משרד הרווחה והביטחון החברתי (להלן: משרד הרווחה) עם תוכנית המאיץ להיערכות רשויות מקומיות למשבר האקלים של משרד האנרגייה, המשרד להגנת הסביבה ומשרד הפנים – במסגרת מִנהלת ההיערכות לשינויי אקלים.
מידע נוסף

תמותה עודפת בישראל בשל גלי חום – מחקר ראשוני עבור המדענית הראשית של המשרד להגנת הסביבה
גלי חום מתאפיינים בשינויים חדים במזג האוויר, ואלו עלולים להוביל לפגיעה ממשית בבריאות הציבור.
למיטב ידיעתנו, טרם נבדק בישראל הקשר שבין גלי חום לתמותה. ביצענו ניתוח ראשוני לבחינת ההיתכנות
להימצאות של תמותה עודפת בישראל לאחר גלי חום.
מידע נוסף
למיטב ידיעתנו, טרם נבדק בישראל הקשר שבין גלי חום לתמותה. ביצענו ניתוח ראשוני לבחינת ההיתכנות
להימצאות של תמותה עודפת בישראל לאחר גלי חום.

The strengths and weaknesses of future visioning approaches for climate change adaptation: A review
Adaptation to climate change is about planning for the future while responding to current pressures and challenges. Adaptation scientists are increasingly using future visioning exercises embedded in co-production and co-development techniques to assist stakeholders in imagining futures in a changing climate. Even if these exercises are growing in popularity, surprisingly little scrutiny has been placed on understanding the fundamental assumptions and choices in scenario approaches, timeframes,
מידע נוסף

HELP Guiding Principles for Drought Risk Management under a Changing Climate
Disaster risk reduction mainly focused on flood events in the past decades. However, one of the most impactful water-related climate risks to both nature and humanity is considered to be droughts, many regions in the world have already been hit hard by drought events in recent years. Drought impacts are far-reaching and include degraded ecosystems, limited availability of drinking water and loss of food production. To be better prepared for future drought events, the High-level Experts and Leade
מידע נוסף

Who benefits from nature in cities? Social inequalities in access to urban green and blue spaces across Europe
Parks, urban forests, tree-lined streets and riverbanks support urban well-being by providing space for rest, relaxation and exercise, and by keeping temperatures down. However, not everyone across Europe enjoys equal access to green space in cities. This briefing reviews the evidence of socio-economic and demographic inequalities in access to the health benefits derived from urban green and blue spaces across Europe. It showcases examples of green spaces that were designed to meet the needs of
מידע נוסף

The development process and significance of the 3rd National Climate Change Adaptation Plan (2021–2025) of the Republic of Korea
The Republic of Korea has developed its 3rd National Climate Change Adaptation Plan (2021–2025) through joint work between government departments in 2020. This follows the Framework Act on Low Carbon, Green Growth, which was enacted in 2010. In this paper, we presented the development process, main contents, significance, and limitations of the 3rd Adaptation Plan as a helpful case for the international community to consult in formulating their national adaptation plans.
מידע נוסף

Climate change impacts on infrastructure: Flood risk perceptions and evaluations of water systems in coastal urban areas
The importance of public perceptions and their role in climate change adaptation for infrastructure has been highlighted in previous studies. However, public perception of water infrastructure at risk of flooding has not been explicitly addressed. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to investigate flood risk perception, the factors that influence it, and evaluations of water infrastructure systems.
מידע נוסף

Adaptive planting design and management framework for urban climate change adaptation and mitigation
Implementing measures to adapt and mitigate climate change effects in cities has been considered increasingly urgent since the quality of life, health, and well-being of urban residents is threatened by this change. Novel communities of plant species that emerge and thrive in the harsh conditions of cities may represent a promising opportunity to address climate change adaptation and mitigation through the planting design and management of urban green spaces.
מידע נוסף

Climate change increases risk of extreme rainfall following wildfire in the western United States
Post-wildfire extreme rainfall events can have destructive impacts in the western United States. Using two climate model large ensembles, we assess the future risk of extreme fire weather events being followed by extreme rainfall in this region. By mid-21st century, in a high warming scenario (RCP8.5), we report large increases in the number of extreme fire weather events followed within 1 year by at least one extreme rainfall event.
מידע נוסף

GAR Special Report on Drought
The GAR Special Report on Drought 2021 explores the systemic nature of drought and its impacts on achievement of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction, the SDGs and human and ecosystems health and wellbeing. Droughts have deep, widespread and underestimated impacts on societies, ecosystems, and economies.
מידע נוסף

IPCC Sixth Assessment Report - Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change
The IPCC has finalized the third part of the Sixth Assessment Report, Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change, the Working Group III contribution. It was finalized on 4 April during the 14th Session of Working Group III and 56th Session of the IPCC.
מידע נוסף

Impacts of Climate Change on Water Management. Stocktaking, scope for action and strategic fields of action
In December 2020, the German Working Group on Water Issues of the Federal States and the Federal Government (LAWA) prepared a comprehensive report on the concerns, potential responses and strategic fields of action in water resources management, updating the previous work released in 2017.
מידע נוסף

Policy Brief: Gender-Responsive Disaster Risk Reduction
This policy brief explores challenges faced in gender-responsive disaster risk reduction. Gender inequality, coupled with climate and environment crises, is the greatest sustainable development challenge of the present time.
מידע נוסף

Plan of approach for exceptional low water events in the Meuse basin
The Meuse International River Basin District faced several consecutive years of the summer drought between 2017 and 2020. In order to be able to adapt to these events, which are likely to occur more often because of climate change, the International Meuse Commission has drafted a plan of approach to deal with exceptional low water events, published at the end of 2020.
The document aims to answer three questions:
What is an exceptional low-water event in the Meuse basin?
What are their con
מידע נוסף
The document aims to answer three questions:
What is an exceptional low-water event in the Meuse basin?
What are their con

Everyday limits to adaptation
Adaptation to climate change, in terms of both academic and policy debates, has been treated predominantly as a local issue. This scalar focus points towards local agency as well as the contested responsibilization of local actors and potential disconnects with higher-level dynamics. While there are growing calls for individuals to take charge of their own lives against mounting climatic forces, little is known about the day-to-day actions people take, the many hurdles, barriers, and limits they
מידע נוסף

A framework for climate change adaptation indicators for the natural environment
Impacts of climate change on natural and human systems will become increasingly severe as the magnitude of climate change increases. Climate change adaptation interventions to address current and projected impacts are thus paramount. Yet, evidence on their effectiveness remains limited, highlighting the need for appropriate ecological indicators to measure progress of climate change adaptation for the natural environment. We outline conceptual, analytical, and practical challenges in developing
מידע נוסף

מתווה למיפוי סיכוני שינויי אקלים בישראל
שינויי האקלים נותנים את אותותיהם כבר כיום. האקלים בישראל צפוי להיות חם יותר, יבש יותר
וצפויה עלייה נמשכת בפני הים והתגברות השכיחות של אירועי מזג אויר קיצוניים. שינויים אלו
גורמים להתגברות השכיחות והעוצמה של סיכוני אקלים, כלומר נזקים הנגרמים לאדם ולרכוש
כתוצאה מהאקלים, כגון שיטפונות, הצפות, שריפות, בצורות, גלי חום וסערות קשות. סיכוני האקלים
הם בעלי שונות במרחב. היערכות לשינויי אקלים הכרחית בכדי להבטיח חוסן חברתי וכלכלי
בישראל. דרושים אמצעים פיזיים וכלכליים להתמודד עם השפעות האקלים בהווה שיהו
מידע נוסף
וצפויה עלייה נמשכת בפני הים והתגברות השכיחות של אירועי מזג אויר קיצוניים. שינויים אלו
גורמים להתגברות השכיחות והעוצמה של סיכוני אקלים, כלומר נזקים הנגרמים לאדם ולרכוש
כתוצאה מהאקלים, כגון שיטפונות, הצפות, שריפות, בצורות, גלי חום וסערות קשות. סיכוני האקלים
הם בעלי שונות במרחב. היערכות לשינויי אקלים הכרחית בכדי להבטיח חוסן חברתי וכלכלי
בישראל. דרושים אמצעים פיזיים וכלכליים להתמודד עם השפעות האקלים בהווה שיהו

IPCC Sixth Assessment Report - Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability
The IPCC has finalized the second part of the Sixth Assessment Report, Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability, the Working Group II contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report. It was finalized on 27 February 2022 during the 12th Session of Working Group II and 55th Session of the IPCC.
מידע נוסף

Spreading like Wildfire: The Rising Threat of Extraordinary Landscape Fires
Climate change and land-use change are making wildfires worse and anticipates a global increase of extreme fires even in areas previously unaffected. Uncontrollable and extreme wildfires can be devastating to people, biodiversity and ecosystems. They also exacerbate climate change, contributing significant greenhouse gasses to the atmosphere.
מידע נוסף

הערכה אסטרטגית לישראל 2022 - משבר האקלים: אתגר לסולידריות הבינלאומית
שנת 2021, שתחילתה בחילופי הממשל בוושינגטון בינואר וסיומה בוועידת האקלים של האו"ם שנערכה בגלזגו בנובמבר, הייתה "שנת האקלים" בזירה הבינלאומית. למרות אכזבה מהישגי הוועידה, נרשמו במסגרתה הישגים חשובים מבחינת שובה של ארצות הברית להובלה גלובלית, גיבוש שורת אמנות והסכמים בינלאומיים וכן רתימת מדינות רבות ובהן ישראל להגדלת התחייבויותיהן להפחתת פליטות גזי חממה.
מידע נוסף

Building a Resilient Canada
The report examines current practices and emerging actions to reduce vulnerability and exposure to natural hazards through the integration of climate change adaptation and disaster risk reduction. Although the report mainly refers to Canada, it can provide a conceptual framework and examples relevant for governments, businesses, individuals, and other stakeholders of European countries and beyond.
מידע נוסף

Economic losses and fatalities from weather- and climate-related events in Europe
The EU adaptation strategy aims to build resilience and ensure that Europe is well prepared to manage the risks from and adapt to the impacts of climate change, including limiting economic losses and other harm. All regions of Europe face economic losses and fatalities from weather and climate extremes every year. To support policy processes on climate change adaptation, data on these losses must be collected and reported across EEA member countries and in a coherent way over decades.
מידע נוסף

מדריך להכנת תכנית פעולה מקומית להיערכות לשינוי אקלים ואנרגיה מקיימת
תוכנית פעולה מקומית לשינויי אקלים היא מסמך מדיניות המנחה את פעולות הרשות המקומית בתחומי האקלים. רשויות מקומיות ברחבי העולם, החלו להכין תוכניות מקומיות להתמודדות עם משבר האקלים כבר בשנות ה-90 של המאה ה-20 .תוכניות אלו התמקדו בעיקר בצמצום גזי חממה. רק בתחילת שנות ה-2000( אחרי סדרה של אסונות טבע, גל החום באירופה, שיטפונות בקופנהגן, סערות בניו יורק ובניו אורלינס( נכתבו תוכניות הפעולה המקומיות הראשונות להסתגלות והיערכות לשינויי אקלים. כיום מקובל לשלב מהלכים לחוסן אקלימי עם מהלכים לצמצום פליטות כחלק
מידע נוסף

Nature-based solutions and global climate protection: Assessment of their global mitigation potential and recommendations for international climate policy
Nature-based Solutions (NbS) build synergies between biodiversity conservation and societal challenges such as climate change. This paper derives a working definition of NbS based on an evaluation of existing definitions. It assesses the global mitigation and adaptation potential of NbS in relevant studies for forests, croplands, grasslands, terrestrial and coastal wetlands as well as settlements. Recommendations for international climate policy are derived.
מידע נוסף

UK Climate Change Risk Assessment 2022
As required by the Climate Change Act 2008, the UK government has undertaken the third five-year assessment of the risks of climate change on the UK. This is based on the Independent Assessment of UK Climate Risk, the statutory advice provided by the Climate Change Committee (CCC), commissioned by the UK government and devolved administrations.
מידע נוסף

Assessment Frameworks of Nature-based Solutions for Climate Change Adaptation and Disaster Risk Reduction
Nature-based solutions (NBS) play an important and increasing role in both adaptation and disaster risk management. This is also recognized within several global and European agreements and policies (e.g., UN’s SFDRR, EU Green Deal, the EU Adaptation Strategy) which embed NBS as a means to address climate change adaptation (CCA) and disaster risk reduction (DRR) as well as other societal challenges (e.g., biodiversity loss, climate mitigation). This calls for fit-for-purpose assessments, which c
מידע נוסף

Just transition in the context of adaptation to climate change
Climate change impacts affect people in different ways and some members of society will find it more demanding to adapt their living and working conditions and their livelihood to changing climate conditions. Managing climate change adaptation and transition to a climate resilient society in a just and inclusive manner requires awareness about which conditions generate injustice with burdens from climate impacts shared and costs and benefits from adaptation measures distributed in a fair and equ
מידע נוסף

Zero regrets: scaling up action on climate change mitigation and adaptation for health in the WHO European Region.
The Working Group on Health in Climate Change (HIC), established under the European Environment and Health Process, aims to articulate and consolidate an action-oriented position on health and climate change for the WHO European Region.
This HIC paper is aimed at policy-makers, particularly from the health sector, and civil society representatives – with the intent to raise awareness about the links between health and climate change, as well as the policy options that can maximize the benefit
מידע נוסף
This HIC paper is aimed at policy-makers, particularly from the health sector, and civil society representatives – with the intent to raise awareness about the links between health and climate change, as well as the policy options that can maximize the benefit

Adaptation Gap Report 2021: The Gathering Storm
Even as the world looks to step up efforts to cut greenhouse gas emissions, the need to adapt to the impacts of climate change already locked in are just as important. The sixth edition of the UNEP Adaptation Gap Report: The Gathering Storm looks at how the world is doing in adapting to these intensifying impacts.
מידע נוסף

Beating the Heat: A Sustainable Cooling Handbook for Cities
Beating the Heat: A Sustainable Cooling Handbook for Cities, states that by the end of this century, many cities could warm as much as 4 °C if GHG emissions continue at high levels. Even at 1.5°C of warming, 2.3 billion people could be vulnerable to severe heat waves. The new guide offers planners an encyclopedia of proven options to help cool cities.
מידע נוסף

פורום היערכות והתמודדות רשויות השרון עם משבר האקלים-דו"ח מסכם שנת פעילות ראשונה 2020-2021
מידע נוסף
דוח מבקר המדינה 2021: פעולות ממשלת ישראל והיערכותה למשבר האקלים
דוח ביקורת מיוחד זה בנושא פעולות ממשלת ישראל והיערכותה למשבר האקלים מונח על שולחן הכנסת ומובא לפני הציבור לקראת ועידת האקלים העולמית COP26, שעתידה להתכנס בתחילת נובמבר 2021, בעיצומה של תקופה שבה מתקבלות בעולם הכרעות מדיניות אשר ישפיעו על האופן שבו נתמודד עם משבר עולמי זה, שצפוי ללוות אותנו בעשורים הקרובים.
פרק מספר 2 בדוח עוסק באדפטציה - ההעירכות הלאומית להסתגלות לשינויי אקלים
מידע נוסף
פרק מספר 2 בדוח עוסק באדפטציה - ההעירכות הלאומית להסתגלות לשינויי אקלים

Financial Innovation for Climate Adaptation in Africa
Current adaptation finance flows to Africa are insufficient to meet growing adaptation needs on the continent. This report provides an overview of existing adaptation finance flows in Africa and identifies opportunities to increase the volume and efficacy of that finance.
מידע נוסף

מערכות אקולוגיות ורווחת האדם: הערכה לאומית – דו"ח ממצאי מפתח
פרויקט 'מערכות אקולוגיות ורווחת האדם - הערכה לאומית' הוא הפרויקט הראשון שמעריך ומנתח את המגוון הביולוגי ואת המערכות האקולוגיות של ישראל בהיבט של התועלת שלהם לאדם ולחברה. פרויקט זה נערך בהמשך ובמקביל לתהליך עולמי של עיסוק הולך וגובר במצבם של המערכות האקולוגיות ושל המגוון הביולוגי ובאופן שהוא משפיע על היבטים קיומיים ואחרים של החברה האנושית. פרויקט הערכת המילניום בוצע ברמה העולמית בשנים 2000¯2005
ביוזמת הממשלות החברות בארבע אמנות סביבתיות של האו"ם, ומבוצע בשנית על ידי ה"פלטפורמה
מידע נוסף
ביוזמת הממשלות החברות בארבע אמנות סביבתיות של האו"ם, ומבוצע בשנית על ידי ה"פלטפורמה

Israel’s State of Climate Tech 2021
Technological innovations play a crucial role in the global challenge to mitigate and adapt to climate change
Israel is renowned as a global leader of technological innovation and this report sets out to examine, for the first time, Israel’s state of climate tech and the potential of its “problem solving” entrepreneurs to provide solutions for the world’s greatest challenge
מידע נוסף
Israel is renowned as a global leader of technological innovation and this report sets out to examine, for the first time, Israel’s state of climate tech and the potential of its “problem solving” entrepreneurs to provide solutions for the world’s greatest challenge

The way forward: Supporting climate adaptation in coastal towns and small cities
This article summarizes and reflects upon the work presented in ‘The Unusual Suspects in Climate Change Adaptation – Small Coastal Cities and Towns’ special issue. Across the special issue the challenge of adapting coastal towns and small cities to the impacts of climate change was clearly evident. In order to address some of the challenges, an initial way forward is outlined here to act as a pathway for future research. The areas requiring particular focus include: building a network of coastal
מידע נוסף

Infrastructure for Climate Action
By providing quantitative evidence of the influence of infrastructure on sustainable development and climate mitigation and adaptation, Infrastructure for Climate Action highlights the key role that infrastructure plays in fostering climate compatible development.
מידע נוסף

Narratives of ice loss: New approaches to shrinking glaciers and climate change adaptation
This article explores an as-yet overlooked component of glacier melt: how competing narratives of ice loss are embedded in divergent climate change adaptation debates. This analysis of regional narratives of ice loss exposes the contested role of glacial meltwater amongst local residents, framing glaciers not just as physical features but also as nodes of discourse and imagination that influence climate change adaptation. Peru's Cordillera Blanca offers an excellent case study for this new n
מידע נוסף

Interactions between two existential threats: COVID-19 and climate change
The COVID-19 pandemic and climate change are complex existential threats, unpredictable in many ways and unprecedented in modern times. There are parallels between the scale and scope of their impacts and responses. Understanding shared drivers, coupled vulnerabilities, and criteria for effective responses will help societies worldwide prepare for the simultaneous threats of climate change and future pandemics. We summarize some shared characteristics of COVID-19 and climate change impacts and i
מידע נוסף

Long-term sea-level rise necessitates a commitment to adaptation: A first order assessment
Without adaptation, sea-level rise (SLR) will put more people at risk of flooding. This requires a timely and adequate commitment to adaptation. In this paper, we show how adaptation needs to unfold over time to manage climate-induced SLR. We use a novel scenario-neutral approach, applied globally and subsequently combined with SLR and population scenarios, to assess when, where, and how fast to adapt up to 2150.
מידע נוסף

Drivers of and pressures arising from selected key water management challenges — A European overview
This report aims to give a European overview of the main drivers and pressures that are at the core of key water management challenges and which put European water bodies most at risk of not achieving key environmental objectives. Identifying the pressures from and drivers of key water management challenges at the European level can help in prioritising the main issues that should be tackled with measures
מידע נוסף

State of the Climate in 2020
This is the 31st issuance of the annual assessment now known as State of the Climate, published in the Bulletin since 1996. As a supplement to the Bulletin, its foremost function is to document the status and trajectory of many components of the climate system. However, as a series, the report also documents the status and trajectory of our capacity and commitment to observe the climate system.
מידע נוסף

IPCC Sixth Assessment Report - AR6 Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis
The Working Group I contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report addresses the most up-to-date physical understanding of the climate system and climate change, bringing together the latest advances in climate science, and combining multiple lines of evidence from paleoclimate, observations, process understanding, and global and regional climate simulations.
מידע נוסף

A Practical Guide to Climate-resilient Buildings & Communities
This practical guide demonstrates how buildings and community spaces can be constructed to increase their resilience to climate change, especially in developing countries where structures are largely self-built. The publication provides an overview of the fundamental types of interventions at the building scale, including the use of nature-based solutions.
מידע נוסף
Climate change adaptation in fisheries
We conducted a global systematic literature review of climate change adaptation in fisheries. We addressed three specific questions:
(i) What are fisheries adapting to? (ii) How are fisheries adapting? and (iii) What research gaps need to be addressed? We identified, characterized and examined case studies published between 1990 and 2019 that lie at the intersection of the domains of climate change, adaptation and fisheries
מידע נוסף
(i) What are fisheries adapting to? (ii) How are fisheries adapting? and (iii) What research gaps need to be addressed? We identified, characterized and examined case studies published between 1990 and 2019 that lie at the intersection of the domains of climate change, adaptation and fisheries

A Systematic Review of the health co-benefits of urban climate change adaptation
The recent and projected upward trends in the frequency and intensity of climate induced events in cities have enhanced the focus on adaptation. In addition to enhancing the capacity of cities to prepare for and absorb risk, adaptation measures provide multiple co-benefits. However, health co-benefits are among the least explored. These are now seen as increasingly important with the renewed focus on public health since the COVID-19 pandemic. This study reviews literature focused on the health c
מידע נוסף

Defining region-specific heatwave in China based on a novel concept of “avoidable mortality for each temperature unit decrease”
The distribution of temperature and temperature-health association varied largely across different regions in China, a region-specific definition for heatwave was therefore needed. We collected the data on daily mortality, meteorological factors and air pollution in 84 Chinese cities during 2013−2016, which was divided into seven regions. Based on the association between daily maximum temperature and mortality in each city in a threshold distributed lag non-linear model, where the threshold was
מידע נוסף

Rethinking resilient agriculture: From Climate-Smart Agriculture to Vulnerable-Smart Agriculture
Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA) is seeking to overcome the food security problem and develop rural livelihoods while minimizing negative impacts on the environment. However, when such synergies exist, the situation of small-scale farmers is often overlooked, and they are unable to implement new practices and technologies. Therefore, the main aim of this study is to improve CSA by adding the neglected but very important element “small-scale farmer”, and introduce Vulnerable-Smart Agriculture (VSA
מידע נוסף

Index for climate change adaptation in China and its application
With the increasing awareness of the risks and impacts of climate change, scholars tend to pay more attention to the applications of indicators, which access the effectiveness of climate change adaptation. This study aims to evaluate the overall progress of climate change adaptation in China during 2010‒2018 in a quantitative manner. The Index for Climate Change Adaptation in China (ICCAC) has been thus developed by adopting the analytic hierarchy process weighting and expert scoring method. Nam
מידע נוסף

ההיערכות לשיטפונות וההגנה מפניהם - דוח ביקורת מיוחד - משרד מבקר המדינה
בשנים האחרונות מתרבים מקרי השיטפונות וההצפות בישראל כתוצאה מעלייה בתכיפות אירועי
הגשם החריגים ובעוצמתם, בד בבד עם התרחבות ניכרת של השטחים הבנויים והאטומים הפוגעים בכושר החלחול של המים לתוך הקרקע. בחורף 2020 אירעו ברחבי הארץ כמה אירועי גשם חריגים שהובילו לשיטפונות ולהצפות חמורים בעיקר בערי החוף. באירועים אלה קיפחו את חייהם שבעה בני אדם, ונגרמו נזקים לרכוש ולתשתיות בהיקף של עשרות מיליוני שקלים.
הרשות המקומית ממלאת תפקיד חיוני בהיערכותו של העורף האזרחי לאירועי מזג אוויר חריגים, ובמיוחד בכל הקשור
מידע נוסף
הגשם החריגים ובעוצמתם, בד בבד עם התרחבות ניכרת של השטחים הבנויים והאטומים הפוגעים בכושר החלחול של המים לתוך הקרקע. בחורף 2020 אירעו ברחבי הארץ כמה אירועי גשם חריגים שהובילו לשיטפונות ולהצפות חמורים בעיקר בערי החוף. באירועים אלה קיפחו את חייהם שבעה בני אדם, ונגרמו נזקים לרכוש ולתשתיות בהיקף של עשרות מיליוני שקלים.
הרשות המקומית ממלאת תפקיד חיוני בהיערכותו של העורף האזרחי לאירועי מזג אוויר חריגים, ובמיוחד בכל הקשור

Monitoring Report on the German Strategy for Adaptation to Climate Change
Within the framework of the German Strategy for Adaptation to Climate Change (DAS), the Federal Government is now presenting the second monitoring report in 2019. It informs the public and decision-makers in all areas of social life about the observed consequences of climate change. The message of the monitoring report is that the future has already reached us. Germany is in the midst of global warming, with far-reaching consequences for the environment, society and health. Urgent action must be
מידע נוסף

The impact of climate change on mental health and emotional wellbeing: current evidence and implications for policy and practice
Climate change and mental health are two of the most significant and pressing challenges facing societies across the world. Yet, growing awareness of these global issues has not been met with sufficient action to mitigate their impacts. Mental illness – or the disabling effects of distress – already affects around a billion people globally, while the effects of climate change are increasingly apparent. Both of these issues are projected to increase and stand to affect many more people without su
מידע נוסף

Food Systems at Risk: Transformative Adaptation for Long-Term Food Security
his report examines how climate change is impacting agriculture and threatening national and global food systems, particularly in climate hotspots, and how these trends are projected to intensify over the coming decades. The report defines and details transformative adaptation for agriculture and why such longer-term, systemic approaches are needed to protect the lives and livelihoods of millions of small-scale farmers and herders. Transformative adaptation in agriculture promotes long-term resi
מידע נוסף

Introducing the Built Environment in a Changing Climate: Interactions, Challenges, and Perspectives
Planning for climate change adaptation is among the most complex challenges cities are facing today. Worldwide, unprecedented levels of urban overheating have been recently recorded. Hosting more than half of the world population, cities are major receptors and drivers for climate change with disruptive and mutually empowering impacts on both the natural and the socio-economic environment
מידע נוסף

השפעתם של שינויי האקלים על הביטחון הלאומי: היערכות מערכות הביטחון בישראל ובמדינות נבחרות
שינויי האקלים כבר כאן, והם עתידים להתגבר בעשורים הקרובים. השפעתם על הביטחון הלאומי תורגש בשלושה תחומים: החרפת איומים גיאופוליטיים; פגיעה בכשירות המבצעית של כוחות הביטחון; וריבוי אירועי חירום בהם עשויה להידרש מעורבות מערכת הביטחון. בסקירה מתוארים תרחישים אלה, ונסקרת ההיערכות לקראתן במערכת הביטחון של ישראל ובמדינות שונות, ובראשן ארה"ב.
מידע נוסף

Independent Assessment of UK Climate Risk-Advice to Government For the UK's third Climate Change Risk Assessment
The Adaptation Committee’s Independent Assessment of UK Climate Risk sets out the priority climate change risks and opportunities for the UK. The report draws on an extensive programme of analysis, consultation and consideration by the Committee involving over 450 people, 130 organisations and more than 1,500 pages of evidence and analysis
מידע נוסף

Power-sensitive design principles’ for climate change adaptation policy-making in South Asia
Despite the proliferation of power approaches to study climate change, there is little focus on how to deal with the negative effects of power in climate change adaptation (CCA) policy-making. CCA literature provides little insight into understandings of manifestations of power that can create negative effects, especially in the context of South Asia.
מידע נוסף

Cities on the route to 2030
We stand at a major crossroads for city climate action. As we mark a decade of cities disclosing climate data through CDP, there are less than ten years left to halve global emissions. Our new report reveals the huge progress in disclosure and action over the last decade – and where cities must now urgently ramp up their ambition and efforts to secure a resilient, green recovery from COVID-19, and a climate-safe future.
מידע נוסף

אקלים מגדרי: נשים בחזית
הפגיעות העירונית למשבר האקלים נדמית ניטרלית, כזאת שנחלקת באופן שוויוני בין כלל תושבי העיר - אבל מסתבר שנשים פגיעות יותר. מדוע הפגיעות של נשים ייחודית וכיצד ערים צריכות להיערך על מנת לתת לכך מענה ולפתח חוסן עירוני-מגדרי? כתבה נוספת בסדרה "משבר האקלים: הזווית העירונית"
מידע נוסף

Evaluating the impact of nature-based solutions- A handbook for practitioners
The Handbook aims to provide decision-makers with a comprehensive NBS impact assessment framework, and a robust set of indicators and methodologies to assess impacts of nature-based solutions across 12 societal challenge areas
מידע נוסף

היערכות מדינת ישראל לשינוי אקלים - דוח מס' 1
בשנת 2018 אושרה החלטת ממשלה 4079" :היערכות ישראל להסתגלות לשינוי אקלים: יישום ההמלצות
לממשלה לאסטרטגיה ותוכנית פעולה לאומית". בהחלטת הממשלה 4079 נכתב שמדינת ישראל מכירה
בהתרחשות שינויי אקלים עולמיים ובצורך בהיערכות לקראתם, לרבות הקמת מנהלת היערכות לאומית. זאת
בעקבות הסכמה עולמית רחבה והתחזקות הראיות המדעיות כי שינוי האקלים מתרחש, וכן כי כל אחד
כדור הארץ מהעשורים הקודמים, החל בשנת 1850 .משלושת העשורים האחרונים היה חם יותר על פני
הסכנות הנובעות משינוים אלה מגוונות, ובהן עלייה בתכ
מידע נוסף
לממשלה לאסטרטגיה ותוכנית פעולה לאומית". בהחלטת הממשלה 4079 נכתב שמדינת ישראל מכירה
בהתרחשות שינויי אקלים עולמיים ובצורך בהיערכות לקראתם, לרבות הקמת מנהלת היערכות לאומית. זאת
בעקבות הסכמה עולמית רחבה והתחזקות הראיות המדעיות כי שינוי האקלים מתרחש, וכן כי כל אחד
כדור הארץ מהעשורים הקודמים, החל בשנת 1850 .משלושת העשורים האחרונים היה חם יותר על פני
הסכנות הנובעות משינוים אלה מגוונות, ובהן עלייה בתכ

Nature-based solutions in Europe: Policy, knowledge and practice for climate change adaptation and disaster risk reduction
Working with nature and enhancing the role of ecosystems can help reduce the impacts of climate change and increase resilience to climate change. Such an approach can deliver multiple benefits, including lowering pressures on biodiversity, improving human health and well-being, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and building a sustainable economy. This EEA report provides up-to-date information for policymakers on how to apply nature-based solutions for climate change adaptation and disaster risk
מידע נוסף

ניתוח חברתי של משבר האקלים: האם מתבסס אי-צדק אקלימי ברמה המקומית?
גישת אי-צדק אקלימי טוענת להתבססותה של חלוקה לא שווה בקרב מדינות ברחבי העולם בין פליטות גזי החממה והתרומה להתחממות העולמית, לבין רמות הפגיעות ממנה. כהמשך לגישה זו, המאמר מציע מסגרת לניתוח חברתי של משבר האקלים המתמקדת ביחידת ניתוח חברתית, ובאמצעותה נדגים את תהליך התהוותו של אי-צדק אקלימי גם ברמה המקומית.
מידע נוסף

מגמות היסטוריות ומגמות חזויות בדפוסי המשקעים בישראל עד סוף המאה
במרץ 2021 ,הוכנה על-ידי אגף אקלים, בשירות המטאורולוגי, עבודה מקיפה לרשות המים, בנושא
"מגמות היסטוריות ומגמות חזויות בדפוסי המשקעים בישראל עד סוף המאה". בעבודת מחקר זו,
נותחו הן מגמות העבר והן המגמות החזויות בכמות הגשם השנתית, עד שנת 2100 .
מידע נוסף
"מגמות היסטוריות ומגמות חזויות בדפוסי המשקעים בישראל עד סוף המאה". בעבודת מחקר זו,
נותחו הן מגמות העבר והן המגמות החזויות בכמות הגשם השנתית, עד שנת 2100 .

Business-as-usual will lead to super and ultra-extreme heatwaves in the Middle East and North Africa
Global climate projections suggest a significant intensification of summer heat extremes in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA). To assess regional impacts, and underpin mitigation and adaptation measures, robust information is required from climate downscaling studies, which has been lacking for the region. Here, we project future hot spells by using the Heat Wave Magnitude Index and a comprehensive ensemble of regional climate projections for MENA. Our results, for a business-as-usual path
מידע נוסף

Mapping the evolution and current trends in climate change adaptation science
Research on climate change adaptation has increased in number and significance since the 1970s. Yet, the volume of information on adaptation is now difficult to manage given its vast scope and spread across journals, institutions, disciplines and themes. While an increasing number of researchers have used systematic literature reviews to analyse particular themes within this rapidly growing field of research, there is still missing an overall analysis of the current state of climate change adapt
מידע נוסף

The old and the climate adaptation: Climate justice, risks, and urban adaptation plan
With the transition to carbon-free economy, concerns have grown about the “green divide” – the separation of society into different social groups whose socioeconomic status determines one’s well-being from climate change impacts. Studies in environmental justice concur that the adverse effects of urban climate change are disproportionately greater for the demographically vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, the children, and the socially marginalized. Yet, little is known about how these
מידע נוסף

A leverage points analysis of a qualitative system dynamics model for climate change adaptation in agriculture
Participatory modeling approaches provide opportunities for collective action responding to challenges of community resource limitations. In the context of climate change, challenges arise from the potential limitations of water availability and resulting conflicts within the agricultural sector. Northeast Lower Saxony is the region with the highest irrigation intensity in Germany due to the sandy soils with low water holding capacity, the cultivation of crops with high water demand, and a negat
מידע נוסף

Responding to the health risks of climate change in Europe
A new briefing by the Lancet Countdown and the European Environment Agency (EEA), explores the health impacts of climate change in Europe and suggests key opportunities for increased ambition with a focus on adaptation. The briefing highlights key health impacts from climate change including wildfires, heatwaves and extreme temperatures, the spread of infectious diseases and droughts. It outlines the opportunities to reduce climate-related health risks through adaptation policies in Europe
מידע נוסף

Urban planning policy must do more to integrate climate change adaptation and mitigation actions
Well-designed urban planning policy can mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to anticipated climate change impacts. However, there has been limited analysis of the extent to which urban planning policy documents addresses climate change adaptation and or mitigation. There is a need to rapidly reduce greenhouse gas emissions to limit warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels by 2100, and to be well adapted to this change (in line with the Paris Agreement). Achieving this goal will assis
מידע נוסף

Forging a climate-resilient Europe - the new EU Strategy on Adaptation to Climate Change
The European Commission adopted its new EU strategy on adaptation to climate change on 24 February 2021. The new strategy sets out how the European Union can adapt to the unavoidable impacts of climate change and become climate resilient by 2050. The Strategy has four principle objectives: to make adaptation smarter, swifter and more systemic, and to step up international action on adaptation to climate change.
מידע נוסף

Accelerating climate research and action in cities through advanced science-policy-practice partnerships
Cities have become increasingly recognized as key sites for climate research and action. Recently, these efforts have been significantly advanced through science-policy-practice partnerships. The objective of this paper is to assess how these partnerships are structured, the research and action agenda that underpins them, and how this agenda is being articulated and implemented. The assessment also helps to define some of the conceptual and operational gaps faced by the science-policy-practice c
מידע נוסף

Inventories of extreme weather events and impacts: Implications for loss and damage from and adaptation to climate extremes
Extreme and impactful weather events of the recent past provide a vital but under-utilised data source for understanding present and future climate risks. Extreme event attribution (EEA) enables us to quantify the influence of anthropogenic climate change (ACC) on a given event in a way that can be tailored to stakeholder needs, thereby enhancing the potential utility of studying past events. Here we set out a framework for systematically recording key details of high-impact events on a national
מידע נוסף

Study on adaptation modelling
This report proposes recommended approaches to analysis and modelling for better informed decision-making on adaptation at various levels of governance. It also identifies research advancements to foster the development and application of the technical, financial, economic and non-monetary analysis and modelling of climate change hazards, risks, impacts, vulnerability and adaptation.
מידע נוסף

Heat and health in the WHO European Region: updated evidence for effective prevention
The WHO Regional Office for Europe published guidance on heat–health action planning in 2008, and intends to update this to include the latest evidence. An in-depth review was initiated, based on recent epidemiological and environmental research and lessons learned from implementation in practice.
This publication collates and summarizes the most relevant evidence published since 2008, focusing primarily on Member States in the WHO European Region. Findings are organized around the elements the
מידע נוסף
This publication collates and summarizes the most relevant evidence published since 2008, focusing primarily on Member States in the WHO European Region. Findings are organized around the elements the

Changing Lengths of the Four Seasons by Global Warming
How long will the four seasons be by 2100? Increasing evidence suggests that the length of a single season or in regional scales has changed under global warming, but a hemispherical-scale response of the four seasons in the past and future remains unknown. We find that summer in the Northern Hemisphere midlatitudes has lengthened, whereas winter has shortened, owing to shifts in their onsets and withdrawals, accompanied by shorter spring and autumn. Such changes in lengths and onsets can be mai
מידע נוסף

Determinants of flood adaptation: Parametric and semiparametric assessment
Flood adaptation measures are indispensable to offset agricultural losses emanating from the increasing frequency and intensity of floods. Therefore, it is necessary to identify key precursors of adaptation for the success of flood‐related adaptation programs. Using cross‐sectional household survey data from rice farmers of eastern Nepal, this study explores existing adaptation practices along with the factors influencing farmers' adaptation strategies. Both parametric and semiparametric for
מידע נוסף

The burden of heat-related mortality attributable to recent human-induced climate change
Climate change affects human health; however, there have been no large-scale, systematic efforts to quantify the heat-related human health impacts that have already occurred due to climate change. Here, we use empirical data from 732 locations in 43 countries to estimate the mortality burdens associated with the additional heat exposure that has resulted from recent human-induced warming, during the period 1991–2018. Across all study countries, we find that 37.0% (range 20.5–76.3%) of warm-seaso
מידע נוסף

Climate Adaptation Summit 2021 - Delivering an Adaptation Action Agenda
COVID-19 has transformed the landscape of our society and poses both threats and opportunities for the climate adaptation agenda. Climate adaptation is at risk of serious setbacks in the coming years due to shifts in public spending due to immediate relief and the potential fallout of a global recession. Adaptation has also never been more important, climate shocks are happening now, intersecting with and exacerbating impacts of COVID-19 – so building resilience to climate impacts will be critic
מידע נוסף

Toward sustainable climate change adaptation
Industrial ecology (IE) has made great contributions to climate change mitigation research, in terms of its systems thinking and solid methodologies such as life cycle assessment, material flow analysis, and environmentally extended input–output analysis. However, its potential contribution to climate change adaptation is unclear. Adaptation has become increasingly urgent in a continuously changing climate, especially in developing countries, which are projected to bear the brunt of climate‐chan
מידע נוסף

Living with water: climate adaptation in the world’s deltas
Over the centuries, deltas have given rise to some of the world’s greatest cities—and those cities have always been open to the world. They have thrived not only in the trade of goods, but also in the exchange of ideas. Today, as the world faces up to the need to adapt to climate change, it has never been more important for delta countries to learn from one another. That is the thinking behind this ‘lighthouse’ report, which brings together inspiring case studies from around the globe to galvani
מידע נוסף

State and Trends in Adaptation Report 2020
The Global Center on Adaptation presents the first in a series of reports that will assess progress on climate adaptation and provide guidance and recommendations on best practice in adapting to the effects of a changing climate and building resilience to climate shocks
מידע נוסף

Understanding the Links Between Climate Change Risk Perceptions and the Action Response to Inform Climate Services Interventions
Understanding what motivates people to act on climate change provides an opportunity to design more effective interventions, in particular, climate services interventions, by aligning them with factors that strongly influence action. Climate change risk perceptions have been shown to underlie action on climate change. Therefore, this study performs exploratory research to understand how various determinants of risk perceptions contribute and interact to influence climate change risk perceptions
מידע נוסף

The Global Risks Report - 2021
The 16th edition of the World Economic Forum’s Global Risks Report analyses the risks from societal fractures—manifested through persistent and emerging risks to human health, rising unemployment, widening digital divides, youth disillusionment, and geopolitical fragmentation. Businesses risk a disorderly shakeout which can exclude large cohorts of workers and companies from the markets of the future. Environmental degradation—still an existential threat to humanity—risks intersecting with socie
מידע נוסף

Urban adaptation in Europe: how cities and towns respond to climate change
EEA assessment report presenting the status quo of adaptation to climate change at the local government level, with particular focus on cities. The assessment presents the overview of climate risks to cities, types of adaptation responses, extent of adaptation planning and actions at the loal level in Europe and opportunities to scale up and speed up implementation of adaptation to climate change at the local level.
מידע נוסף

Adaptation Gap Report 2020 - UNEP
The UNEP Adaptation Gap Report 2020 finds that while nations have advanced in planning, huge gaps remain in finance for developing countries and bringing adaptation projects to the stage where they bring real protection against climate impacts such as droughts, floods and sea-level rise.
מידע נוסף

Healthy environment, healthy lives: how the environment influences health and well-being in Europe
Nature provides the basis for the good health and well-being of the European population. Cleatreme temperatures, floods an air, water and food are essential for sustaining life; natural environments provide space for recreation, relaxation and social interaction; and raw materials feed into our production systems
to provide the comforts of contemporary life.
Climate change contributes to the burden of disease and premature deaths in Europe. Direct health effects include death, injury and the
מידע נוסף
to provide the comforts of contemporary life.
Climate change contributes to the burden of disease and premature deaths in Europe. Direct health effects include death, injury and the

Climate and Environmental Change in the Mediterranean Basin Current Situation and Risks for the Future - 1st Mediterranean Assessment Report
The First Mediterranean Assessment Report (MAR1) prepared by the independent network of Mediterranean Experts on Climate and environmental Change (MedECC) founded in 2015 is now finished.
MedECC assesses the best available scientific knowledge on climate and environmental change and associated risks in the Mediterranean Basin in order to render it accessible to policymakers, stakeholders and citizens. The report includes a Summary for Policymakers (SPM), which comprises the key messages of the
מידע נוסף
MedECC assesses the best available scientific knowledge on climate and environmental change and associated risks in the Mediterranean Basin in order to render it accessible to policymakers, stakeholders and citizens. The report includes a Summary for Policymakers (SPM), which comprises the key messages of the

Health System Adaptation to Climate Variability and Change
Climate change is already causing avoidable injuries, illnesses, and deaths, and is damaging healthcare and public health facilities. The magnitude and distribution of future climate-sensitive health outcomes and of risks to health systems will depend on the level and timing of investment in adaptation and on the chosen greenhouse gas emission pathway. If no additional actions are taken, then over the coming decades substantial increases in morbidity and mortality are expected, as well as breakd
מידע נוסף

The 2020 report of The Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: responding to converging crises
The Lancet Countdown is an international collaboration established to provide an independent, global monitoring system dedicated to tracking the emerging health profile of the changing climate. The 2020 report presents 43 indicators across five sections: climate change impacts, exposures, and vulnerabilities; adaptation, planning, and resilience for health; mitigation actions and health co-benefits; economics and finance; and public and political engagement. This report represents the findings a
מידע נוסף

1st Mediterranean Assessment Report (MAR1) main results - MedECC
The first report on the environment and climate change produced by the MedECC network was released in November 2020. It is sounding the alarm!
It received the North-South Prize 2020 from the Council of Europe, as a model of collaboration between countries of the North and the South of the Mediterranean.
מידע נוסף
It received the North-South Prize 2020 from the Council of Europe, as a model of collaboration between countries of the North and the South of the Mediterranean.

Risks and Impacts of Environmental Change in the Mediterranean Basin - Infographic
New MedECC infographic on drivers and impacts of climate and environmental change is available
מידע נוסף

שינוי אקלים, תכנון עירוני ובנייה ירוקה
במסמך זה רוכז מידע בנושא תכנון עירוני ובנייה ירוקה בעידן של שינוי אקלים. המידע בנושא שינויי אקלים וההשלכות על התכנון והבנייה הירוקה לקוח מתוך דוחות שהגיש מרכז הידע להיערכות לשינוי אקלים בישראל למשרד להגנת הסביבה.
מידע נוסף

Mapping the effectiveness of nature‐based solutions for climate change adaptation
The paper is the first global systematic review of the effectiveness of nature-based solutions and provides evidence that nature-based solutions play a key role in addressing the impacts of climate change, but also highlights potential trade-offs to be avoided and evidence gaps where further study is needed. The review investigates nearly 400 scientific studies including both real-world cases, and modelled scenarios. Of the real-world cases, most nature-based interventions (59%) were found to re
מידע נוסף

Climate change strategic narratives in the United Kingdom: Emergency, Extinction, Effectiveness
Achieving policy, business and behaviour change necessary to mitigate climate change is one of the most formidable challenges of the twenty-first century. Increasingly, researchers have argued that communicating purposively designed stories – ‘strategic narratives’ – may be effective in building support for the policy measures necessary to limit anthropogenic warming to 2˚C above pre-industrial levels
מידע נוסף

Greening schoolyards - An urban resilience perspective
Greening schoolyards and redesigning them to be better playgrounds delivers multiple benefits
Greening schoolyards is a highly distributed urban intervention that can enhance city resilience as a whole
Integrating resilience into project design and implementation requires a practical resilience framework
מידע נוסף
Greening schoolyards is a highly distributed urban intervention that can enhance city resilience as a whole
Integrating resilience into project design and implementation requires a practical resilience framework

Adaptation to health effects of climate change in Europe
The main impacts on health in Europe are from heat and heat-waves, changing patterns of infectious and vector-borne diseases, and from extreme disasters like floods and fires. This opinion presents the challenges for the health sector caused by the need for adapting to the increased risks from climate change, and provides recommendations aimed to strengthen the resilience of the health sector in Europe in view of climate change impacts.
מידע נוסף

World Cities Report 2020: The Value of Sustainable Urbanization
The World Cities Report 2020 shows that the intrinsic value of sustainable urbanization can and should be harnessed for the wellbeing of all. The Report provides evidence and policy analysis of the value of urbanization from an economic, social and environmental perspective, including the unquantifiable value that gives cities their unique character; and also explores the role of innovation and technology, local governments, targeted investments and the effective implementation of the New Urban
מידע נוסף

Principles, drivers, and policy tools for just climate change adaptation in legacy cities
Climate change adaptation presents an opportunity for legacy cities to address growing social, racial, and economic inequality, or engage in just climate change adaptation. While the importance of just and equitable climate change adaptation is well understood, the policy and politics that underlie such efforts are less well understood. This paper focuses on the development of just climate change adaptation strategies in legacy cities, particularly those in the Great Lakes region of the U.S., wh
מידע נוסף

המשבר הסמוי שמעצב את המזרח התיכון
שיעים נגד סונים, פלסטינים נגד ישראלים, מסורת נגד קידמה - לרשימת הגורמים שהופכים את האזור שלנו לאזור כה נפיץ יש להוסיף כוח אימתני שכבר יוצר שינויים מהותיים בחברה, בכלכלה ובביטחון: משבר האקלים
מידע נוסף

United Nations Climate Change Annual Report 2019
Greater efforts are required to adapt to the impacts of climate change and to
protect people and the planet. The UNFCCC interacts with governments and
partners in searching for ways to increase developing countries’ capacity to adapt.
This year in adaptation was marked by the secretariat’s provision of support to
countries for developing their national adaptation plans, the work of the
Adaptation Committee on climate finance, the enhancement of partnerships
under the Nairobi work programme
מידע נוסף
protect people and the planet. The UNFCCC interacts with governments and
partners in searching for ways to increase developing countries’ capacity to adapt.
This year in adaptation was marked by the secretariat’s provision of support to
countries for developing their national adaptation plans, the work of the
Adaptation Committee on climate finance, the enhancement of partnerships
under the Nairobi work programme

שינוי אקלים ובריאות הציבור - סקירת ספרות, מיפוי מדדי בריאות והמלצות לפעולה
בשנת 2018 ממשלת ישראל קיבלה החלטה להיערכות לאומית להסתגלות לשינוי אקלים ) החלטה מספר 4079.)
לצורך יישום החלטת הממשלה, נקבע כי על כל משרד ממשלתי לפתח תוכנית היערכות ולהשתתף במאמץ הלאומי
להיערכות מיטיבה לשינוי אקלים. מסמך זה צפוי להוות שלב ראשון במאמץ לקראת גיבוש תוכנית עבודה של משרד
הבריאות בנושא
מידע נוסף
לצורך יישום החלטת הממשלה, נקבע כי על כל משרד ממשלתי לפתח תוכנית היערכות ולהשתתף במאמץ הלאומי
להיערכות מיטיבה לשינוי אקלים. מסמך זה צפוי להוות שלב ראשון במאמץ לקראת גיבוש תוכנית עבודה של משרד
הבריאות בנושא

שינוי האקלים וההשפעה על בריאותך- תרשים - הותאם מתוך הדוח: שינוי אקלים ובריאות הציבור
ישראל נמצאת באחד מהאזורים הרגישים ביותר לשינוי האקלים
מתועדת מגמת התחממות הכוללת קיץ ארוך, קיצוני וחם יותר; עלייה בתדירות של גלי חום; הפחתה בכמות המשקעים והקצנה במופעיהם.
משבר האקלים הוא אחד הגורמים המשפיעים ביותר על הבריאות במאה ה–21 ועל מדינת ישראל להיערך למען בריאות הציבור.
מידע נוסף
מתועדת מגמת התחממות הכוללת קיץ ארוך, קיצוני וחם יותר; עלייה בתדירות של גלי חום; הפחתה בכמות המשקעים והקצנה במופעיהם.
משבר האקלים הוא אחד הגורמים המשפיעים ביותר על הבריאות במאה ה–21 ועל מדינת ישראל להיערך למען בריאות הציבור.

Global Biodiversity Outlook 5
Global Biodiversity Outlook (GBO) is the flagship publication of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD). It is a periodic report that summarizes the latest data on the status and trends of biodiversity and draws conclusions relevant to the further implementation of the Convention
מידע נוסף

מגמות השינוי בטמפרטורה בישראל, תחזיות עד 2100
בדו"ח "שינויי אקלים בישראל מגמות עבר ומגמות חזויות במשטר הטמפרטורות והמשקעים"
דו"ח מחקר מס' 0000075-2019-0804-4000 ,נובמבר 2019 ,השירות המטאורולוגי( אותו פרסמנו
בסוף שנה שעברה, מוצגת השתנות הטמפרטורה עבור שני תרחישים, (האחד מתון 5.RCP4 והשני
קיצוני יותר 5.RCP8 )בו האנושות אינה נוקטת בשום פעולה לצמצום גזי החממה. השתנות
הטמפרטורה הוצגה לשני תרחישים אלו עד שנת 2050.
בעבודה הנוכחית אנו מרחיבים את חישוב מגמות השינוי החזויות, לאותם שני תרחישים, עד שנת
2100.
מידע נוסף
דו"ח מחקר מס' 0000075-2019-0804-4000 ,נובמבר 2019 ,השירות המטאורולוגי( אותו פרסמנו
בסוף שנה שעברה, מוצגת השתנות הטמפרטורה עבור שני תרחישים, (האחד מתון 5.RCP4 והשני
קיצוני יותר 5.RCP8 )בו האנושות אינה נוקטת בשום פעולה לצמצום גזי החממה. השתנות
הטמפרטורה הוצגה לשני תרחישים אלו עד שנת 2050.
בעבודה הנוכחית אנו מרחיבים את חישוב מגמות השינוי החזויות, לאותם שני תרחישים, עד שנת
2100.

תכניות היערכות לשינויי אקלים-מבט משווה ראשוני
מסמך זה נכתב לבקשת חה"כ מיקי חיימוביץ', יו"ר ועדת הפנים ואיכות הסביבה לקראת דיון שכותרתו "משבר האקלים - היערכות לשינויי אקלים קיצוניים ברמה המקומית והלאומית". המסמך מהווה סקירה ראשונית של תוכניות פעולה בתחום ההיערכות לשינוי האקלים, בדגש על תוכניות המיושמות במדינות האיחוד האירופי.
מידע נוסף

Accelerating Climate Action in Israel
This report analyses the actions necessary in the near and medium term to reduce Israel’s GHG emissions in three sectors– electricity, residential and transport, for which specific policy recommendations are developed.
The report will serve as input to the roadmap that will be developed to support the country’s long-term low-emission strategy (LT-LEDS)
מידע נוסף
The report will serve as input to the roadmap that will be developed to support the country’s long-term low-emission strategy (LT-LEDS)

תכנית פעולה היערכות לשינויי אקלים - תל אביב יפו - 2020
התכנית ממפה את שינויי האקלים הצפויים ואת השפעתם על העיר, על האוכלוסייה ועל מערך השירותים והסביבה הפיזית.
מתוך ניתוח התחזיות והתרחישים, זיהינו שתי משימות מפתח לעשור הקרוב: קירור העיר וניהול המים.
לצורך מימושן, קבענו מגוון כלים ופעולות, כדי להבטיח את המשך איכות החיים בעיר, למרות שינויי האקלים.
מידע נוסף
מתוך ניתוח התחזיות והתרחישים, זיהינו שתי משימות מפתח לעשור הקרוב: קירור העיר וניהול המים.
לצורך מימושן, קבענו מגוון כלים ופעולות, כדי להבטיח את המשך איכות החיים בעיר, למרות שינויי האקלים.

Nature-based solutions for adapting to water-related climate risks
Healthy ecosystems, and their associated services, can provide effective natural protection against water-related climate risks. Nature-based solutions (NbS) have recently gained momentum in international policy discussions due to their potential to foster synergies between ecosystem health and human wellbeing, while also offering economic benefits. This paper provides an overview of the use of NbS to date in OECD countries and finds that in most cases ambition for NbS does not match practice. F
מידע נוסף

Global hunger and climate change adaptation through international trade
International trade enables us to exploit regional differences in climate change impacts and is increasingly regarded as a potential adaptation mechanism. Here, we focus on hunger reduction through international trade under alternative trade scenarios for a wide range of climate futures. Under the current level of trade integration, climate change would lead to up to 55 million people who are undernourished in 2050. Without adaptation through trade, the impacts of global climate change would inc
מידע נוסף

Care-full and just: Making a difference through climate change adaptation
In the small city of Dunedin, on the south-east coast of Aotearoa New Zealand, sea-level rise and increased flood events are affecting communities. The potential for climate change impacts in South Dunedin to exacerbate existing inequalities is high. Floods in 2015 became a catalyst for a different way of ‘doing’ climate change adaptation suggesting more care-full and just intentions and practices
מידע נוסף

Collaboratively Developing Tools for Climate Change Adaptation-Lessons for Research and Policy
Climate change is causing extreme weather events to increase in frequency and intensity, putting cities, home to most of Europe’s population, at rapidly increasing risk
מידע נוסף

Standardisation in local climate change adaptation: benefits, myths and recommendations
This policy brief provides an outline of the urban standardisation landscape in Europe, covering the benefits of (and barriers to) using standards for local climate change adaptation, outlining existing relevant standards for local governments, busting persistent myths about using them, and concluding with a set of recommendations for local governments and creators of standards.
מידע נוסף

Scaling Local and Community-Based Adaptation
Climate change continues to pose serious threats to inclusive and sustainable development across all scales. The adverse impacts of climate change are manifested largely at the local level. The underlying drivers of vulnerability—including socio-economic, ecological and human resources, institutions, governance and infrastructure—are inherently context-specific and reflected at local scale. Hundreds of millions of people in both developing and developed countries are vulnerable to the direct and
מידע נוסף

How does private adaptation motivation to climate change vary across cultures? Evidence from a meta-analysis
Natural hazards, exacerbated by climate change, increasingly affect societies worldwide. The accelerating risks entail that private adaptation complement more traditional public climate change adaptation measures. Culture plays an important role in framing how individuals experience hazards and behave toward them. Yet, empirical research explicitly measuring whether and how climate change adaptation varies across cultures is lacking. To address this gap, we collect meta-analytic data on factors
מידע נוסף

חוסן עירוני בשגרה ובחירום-אסטרטגיות, פרקטיקות והמלצות לרשויות המקומיות
משבר הקורונה העמיד את הרשויות המקומיות בישראל ובעולם בפני דילמות ואתגרים קריטיים. לצד
המחיר הכבד שהמשבר גבה וממשיך לגבות מהתושבים, מהעסקים ומהרשויות המקומיות עצמן, מבטאת
תקופה זו ביתר שאת את תפקידו המרכזי של השלטון המקומי - לא רק בהוצאה לפועל של מדיניות הממשלה
ובהפעלת מערכי חירום, אלא גם בהובלה של יוזמות ומהלכים מקומיים, המספקים לתושבים מענה משלים
והכרחי, המתבסס על צרכי המקום ונסיבותיו הייחודיות.
מידע נוסף
המחיר הכבד שהמשבר גבה וממשיך לגבות מהתושבים, מהעסקים ומהרשויות המקומיות עצמן, מבטאת
תקופה זו ביתר שאת את תפקידו המרכזי של השלטון המקומי - לא רק בהוצאה לפועל של מדיניות הממשלה
ובהפעלת מערכי חירום, אלא גם בהובלה של יוזמות ומהלכים מקומיים, המספקים לתושבים מענה משלים
והכרחי, המתבסס על צרכי המקום ונסיבותיו הייחודיות.

What is ecosystem-based adaptation
Healthy ecosystems can reduce the negative impacts of climate change. For instance, coastal habitats like mangroves provide natural flood defences, well-protected lakes retain water sources during droughts, and healthy forests reduce the risk of devastating wildfires. Ecosystem-based adaptation (EbA) is an approach that uses these ecosystem services as part of a holistic adaptation strategy. Often through win-win outcomes, EbA protects vulnerable communities from extreme weather while simultaneo
מידע נוסף

A diagnostic tool for supporting policymaking on urban resilience
Urban resilience has become a popular notion among urban policymakers and scientists, as a way to deal with the many complex issues that cities face. While it has positive connotations and resonates with local urban agendas, it is not always clear what it means and what factors contribute to resilience. Additionally, critical literature observes that people's views on what resilience means can differ strongly and the many choices that are made in planning and implementing resilience are ofte
מידע נוסף

Financing Water Supply, Sanitation and Flood Protection
The OECD and the Directorate-General for Environment, the European Commission department responsible for EU policy on the environment, joined forces to examine current and future water-related financing challenges faced by EU member states. These include investments needed to comply with EU regulation for water supply, wastewater collection and treatment, and flood protection. As part of the research, new data was produced on current levels of expenditure for water supply, sanitation and flood p
מידע נוסף

A Method for Enhancing Capacity of Local Governance for Climate Change Adaptation
The lack of capacity for climate change adaptation at the subnational level has been highlighted as a key barrier to implementing the UNFCCC National Adaptation Plans. At the same time, the adaptive capacity of local governance is highly context sensitive, making a “one-size fits all” approach inappropriate. Thus, a versatile methodological approach for application in various local contexts is required. There are several indicator-based local governance assessment methods for evaluating the effe
מידע נוסף

פיתוח חוסן חברתי: מה בין מגפת הקורונה למשבר האקלים?
הזרקור על משבר הקורונה כמגיפה בריאותית והחיפוש אחר פתרונות בריאותיים מידיים בידוד, שמירה
על היגיינה אישית וריחוק חברתי . וארוכי טווח- המרוץ לחיסון , הסיטו מהדיון היבטים חברתיים של
המשבר. כחברה שרוצה לפתח חוסן לאומי וחברתי, עלינו לבחון מי מצליח להתמודד טוב יותר בעתות המשבר ומי פחות? מי יצליח לחזור מהר יותר לשגרה ומי יתקשה?
נתונים ראשוניים בעודנו בעיצומו של המשבר, מלמדים כי הנפגעים העיקריים מגיעים משכבות האוכלוסייה המוחלשות בחברה הישראלית
מידע נוסף
על היגיינה אישית וריחוק חברתי . וארוכי טווח- המרוץ לחיסון , הסיטו מהדיון היבטים חברתיים של
המשבר. כחברה שרוצה לפתח חוסן לאומי וחברתי, עלינו לבחון מי מצליח להתמודד טוב יותר בעתות המשבר ומי פחות? מי יצליח לחזור מהר יותר לשגרה ומי יתקשה?
נתונים ראשוניים בעודנו בעיצומו של המשבר, מלמדים כי הנפגעים העיקריים מגיעים משכבות האוכלוסייה המוחלשות בחברה הישראלית

Exploring potential adaptation options for policy and decision-makers: The Climate-ADAPT Catalogue
Adaptation options are measures and actions that can be implemented to manage climate risks to an acceptable level, taking advantage of any positive opportunities that may arise from climate change. Climate-ADAPT provides a catalogue of potential adaptation options that can be explored by climate impacts and adaptation sectors of interest
מידע נוסף

Green climate change adaptation and the politics of designing ecological infrastructures
There is a distinctive ecological turn within contemporary urban infrastructure design linked to the embrace of green approaches to climate adaptation and new ‘ecological’ and ‘landscape infrastructures’ which combine green and grey features. These promise a wide range of ecological, social and cultural benefits and have been accompanied by distinctive new design visions and imaginaries
מידע נוסף

Multi-Dimensional Data Preparation: A Process to Support Vulnerability Analysis and Climate Change Adaptation
Agriculture is the backbone of a country’s economic system, considering that it not only provides food and raw materials but also employment opportunities for a large percentage of the population. In this way, determining the degree of agricultural vulnerability represents a guide for sustainability and adaptability focused on changing future conditions. In many cases, vulnerability analysis data is restricted to use by authorized personnel only, leaving open data policies aside
מידע נוסף

היערכות ישראל לשינוי אקלים: מיפוי אוכלוסיות פגיעות-סקירת ספרות ומסמכי מדיניות מהעולם
סקירה זו נכתבה לשימוש מינהלת היערכות לשינוי אקלים לצורך העמקת הדיון בנושא פיתוח חוסן חברתי בהיערכות ישראל לשינוי אקלים. זאת מתוך הבנה כי על תוכנית ההיערכות לכלול התייחסות ייחודית לקבוצות חברתיות פגיעות יותר לשינוי אקלים. לצורך הכנת המסמך נערכה סקירה של הספרות האקדמית ושל מסמכי מדיניות מרחבי העולם, מופו הקבוצות החברתיות הפגיעות יותר לשינוי אקלים ונסקרו דרכי ההתמודדות האפשריות ברמה הלאומית והמקומית. כמו
כן, הושם דגש על התאמת הסקירה להיבטים החברתיים והתרבותיים הייחודים של ישראל.
מידע נוסף
כן, הושם דגש על התאמת הסקירה להיבטים החברתיים והתרבותיים הייחודים של ישראל.

What makes climate change adaptation effective? A systematic review of the literature
Increased understanding of global warming and documentation of its observable impacts have led to the development of adaptation responses to climate change around the world. A necessary, but often missing, component of adaptation involves the assessment of outcomes and impact
מידע נוסף

Accelerating invasion potential of disease vector Aedes aegypti under climate change
Vector-borne diseases remain a major contributor to the global burden of disease, while climatechange is expected to exacerbate their risk. Characterising vector development rate and its spatio-temporal variation under climate change is central to assessing the changing basis of human disease risk. We develop a mechanistic phenology model and apply it to Aedes aegypti, an invasive mosquito vector for arboviruses (e.g. dengue, zika and yellow fever).
מידע נוסף

Shifting to climate change aware cities to facilitate the city resilience implementation
Climate change (CC) is one of the most urgent threats to modern societies, having direct and indirect consequences on the rapid growth of urban areas. Cities are attempting to both reduce their impact on the environment and build resilience to be able to face the irreversible effects of CC through plans and strategies
מידע נוסף

The Dasgupta Review – Independent Review on the Economics of Biodiversity- Interim Report
The independent Review will explore the sustainability of our engagements with Nature – what we take from it; how we transform what we take from it and return to it; why we have disrupted Nature’s processes; and what we must urgently do differently to enhance our collective wealth and well-being, and that of our descendants
מידע נוסף

A Snapshot of Global Adaptation Investment and Tracking Methods
The intensity and frequency of extreme weather events and chronic climate-related changes are increasing, globally. With these changes, there is a pressing and clear need for communities worldwide to invest in adapting to climate change. According to the UN Environment Programme, in developing countries alone, adapting to climate change will require USD 280 billion to USD 500 billion per year by 2050 (UNEP 2016). The 46 countries that included adaptation cost estimates in their Nationally Determ
מידע נוסף

-Common Ground Between the Paris Agreement and the Sendai Framework - Climate Change Adaptation and Disaster Risk Reduction
Countries are faced with the growing challenge of managing increasing risks from climate change and climate variability, putting development and the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals at risk. The adoption in 2015 of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction and the Paris Agreement on climate change provides a clear mandate for increased coherence in countries’ approaches to climate and disaster risk reduction
מידע נוסף

Three steps to integrate climate change adaptation and development: Addressing resilience in Danish development policy
The world needs resilient societies. In order to achieve this, adaptation to climate change is key. Denmark’s development cooperation should take a leading role in the integration of climate change adaptation and development.
מידע נוסף

Building resilience against biological hazards and pandemics: COVID-19 and its implications for the Sendai Framework
Year 2020 has become the year of coping with Covid-19
This year was to be the “super year” for sustainability, a year of strengthening global actions to accelerate the transformations required for achieving the 2030 agenda. We argue that 2020 can and must be a year of both. Thus we call for more utilisation of the health-emergency disaster risk management (Health-EDRM) framework to complement current responses to COVID-19 and the patent risk of similar phenomena in the future
מידע נוסף
This year was to be the “super year” for sustainability, a year of strengthening global actions to accelerate the transformations required for achieving the 2030 agenda. We argue that 2020 can and must be a year of both. Thus we call for more utilisation of the health-emergency disaster risk management (Health-EDRM) framework to complement current responses to COVID-19 and the patent risk of similar phenomena in the future

The projected timing of abrupt ecological disruption from climate change
As anthropogenic climate change continues the risks to biodiversity will increase over time, with future projections indicating that a potentially catastrophic loss of global biodiversity is on the horizon1,2,3. However, our understanding of when and how abruptly this climate-driven disruption of biodiversity will occur is limited because biodiversity forecasts typically focus on individual snapshots of the future. Here we use annual projections (from 1850 to 2100) of temperature and precipitati
מידע נוסף

Exposure to air pollution and COVID-19 mortality in the United States
United States government scientists estimate that COVID-19 may kill between 100,000 and 240,000 Americans. The majority of the pre-existing conditions that increase the risk of death for COVID-19 are the same diseases that are affected by long-term exposure to air pollution. We investigate whether long-term average exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) increases the risk of COVID-19 deaths in the United States
מידע נוסף

How our responses to climate change and the coronavirus are linked
The coronavirus pandemic may lead to a deeper understanding of the ties that bind us on a global scale
מידע נוסף

Migration, environment and climate change: Responding via climate change adaptation policy
With the advance of climate change and environmental changes threatening livelihoods, their impacts on migration and displacement are receiving increasing attention in research, politics, and civil society. The issue is complex and multi-dimensional, with environmental changes affecting human mobility in diverse ways. The three reports in this series thus evaluate the evidence base for policymaking, and provide entry points for responses in the field of climate change adaptation
מידע נוסף

UNDRR Annual Report 2019
Annual report for the United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction 2019
מידע נוסף

Floodplains: a natural system to preserve and restore
Floodplains are part of Europe’s natural capital, covering 7 % of the continent's area and up to 30 % of its terrestrial Natura 2000 site area. Studies have shown that 70-90 % of floodplains have been environmentally degraded. The objective of this work is to showcase that natural floodplains support achieving multiple EU policy objectives. More specifically to show that natural and restored floodplains provide an alternative to structural measures for providing flood protection, and at the
מידע נוסף

Global warming to increase violent crime in the United States
Recent studies have revealed large and robust correlations between seasonal climate and violent crime rates at regional scales within the continental United States, begging the question of how future climate change will influence violent crime rates. Here, we combine empirical models from previous studies with 42 state-of-the-art global climate models to make such projections, while accounting for key factors like regionality and seasonality, and appropriately combining multiple of sources of un
מידע נוסף

From incremental to transformative adaptation in individual responses to climate-exacerbated hazards
In this Review of scholarship on behavioural adaptation, we find that most empirical studies focus on the affective and cognitive drivers of behaviours with largely private benefits. Few examine behaviours with collective benefits or explore the moderating role of social factors on affective and cognitive cues
מידע נוסף

The Global Risks Report 2020
The Global Risks Report 2020 presents the major risks the world will be facing in the coming year. The global economy is facing an increased risk of stagnation, climate change is striking harder and more rapidly than expected
מידע נוסף

Economy-wide effects of coastal flooding due to sea level rise: a multi-model simultaneous treatment of mitigation, adaptation, and residual impacts
The article presents a multi-model assessment of the macroeconomic impacts of coastal flooding due to sea level rise and the respective economy-wide implications of adaptation measures for two greenhouse gas (GHG) concentration targets, namely the Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP)2.6 and RCP4.5, and subsequent temperature increases
מידע נוסף

Anomalously warm temperatures are associated with increased injury deaths
Temperatures that deviate from the long-term local norm affect human health, and are projected to become more frequent as the global climate changes. There are limited data on how such anomalies affect deaths from injuries. In the present study, we used data on mortality and temperature over 38 years (1980–2017) in the contiguous USA and formulated a Bayesian spatio-temporal model to quantify how anomalous temperatures, defined as deviations of monthly temperature from the local average monthly
מידע נוסף

Climate risk and response: Physical hazards and socioeconomic impacts
In this report, we look at the physical effects of our changing climate. We explore risks today
and over the next three decades and examine cases to understand the mechanisms through
which physical climate change leads to increased socioeconomic risk
מידע נוסף
and over the next three decades and examine cases to understand the mechanisms through
which physical climate change leads to increased socioeconomic risk
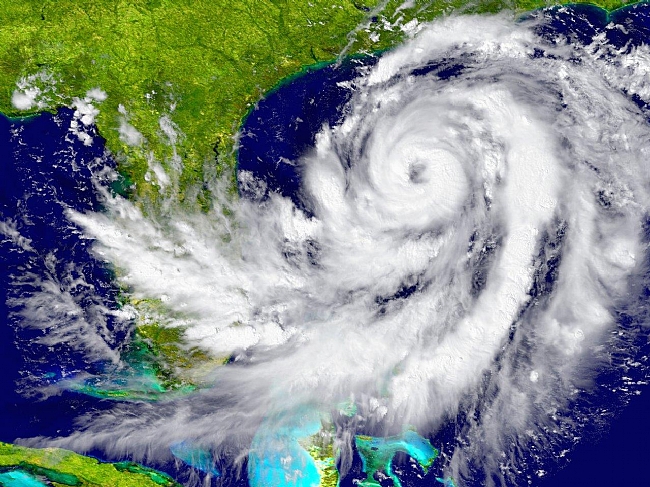

Strengthening Post-Hurricane Supply Chain Resilience - Observations from Hurricanes Harvey, Irma, and Maria
Resilient supply chains are crucial to maintaining the consistent delivery of goods and services to the American people. The modern economy has made supply chains more interconnected than ever, while also expanding both their range and fragility. In the third quarter of 2017, Hurricanes Harvey, Irma and Maria revealed some significant vulnerabilities in the national and regional supply chains of Texas, Florida, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and Puerto Rico
מידע נוסף

2019 Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction
The buildings and construction sector accounted for 36% of final energy use and 39% of energy
and process-related carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions in 2018, 11% of which resulted from
manufacturing building materials and products such as steel, cement and glass. This year’s Global Status Report provides an update on drivers of CO2 emissions and energy demand globally since 2017, along with examples of policies, technologies and investments that support low-carbon building stocks
מידע נוסף
and process-related carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions in 2018, 11% of which resulted from
manufacturing building materials and products such as steel, cement and glass. This year’s Global Status Report provides an update on drivers of CO2 emissions and energy demand globally since 2017, along with examples of policies, technologies and investments that support low-carbon building stocks

Building urban resilience with nature-based solutions: How can urban planning contribute?
Cities face increasing environmental, social and economic challenges that together threaten the resilience of urban areas and the residents who live and work there. These challenges include chronic stresses and acute shocks, amplified by climate change impacts. Nature-based solutions have emerged as a concept for integrating ecosystem-based approaches to address a range of societal challenges
מידע נוסף

Adaptation’s Thirst: Accelerating the Convergence of Water and Climate Action
Water has long been recognized as a central component of climate change impacts as well as a tool to ensure effective adaptation. In the words of Carter Roberts, CEO, WWF-US, at the 15th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP 15) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) in Copenhagen in 2009, “The language of water is the language of climate change.” Nevertheless, miscommunication and misunderstanding remain an issue between the water and climate change commun
מידע נוסף

The Role of Domestic Budgets in Financing Climate Change Adaptation
With climate-induced shocks and stresses threatening fiscal stability and undermining the achievement of broader development goals, governments across the world are recognising the need to mobilise more and smarter investment in climate adaptation. This paper considers the role of domestic budgets as an under-examined but vitally important and sustainable source of adaptation finance at scale. It does so based on the premise that in many developing countries, domestic budgets are already the lar
מידע נוסף

How England’s broken planning system has created (not reduced) the risk of floods
Recent floods in England have been described as unprecedented or even “biblical” events, often with the misguided assumption that they were unavoidable or unpredictable. That is not the case.
מידע נוסף

Climate Finance and Sustainable Cities
The theme of the 2019 SCF Forum was “Climate finance and sustainable cities”. The objective of the Forum was to enhance understanding of how to accelerate the mobilization and delivery of climate finance for the development of sustainable cities
מידע נוסף

2019 National Preparedness Report
The National Preparedness Report evaluates annual preparedness progress and challenges facing the whole community. The 2019 National Preparedness Report highlights the diverse range of preparedness challenges the Nation faces—from terrorism and active shooter incidents, to cyber attacks, to natural disasters, as well as how stakeholders across the Nation are using preparedness grant funding to invest in preparedness improvements
מידע נוסף

Yearbook of global climate Action 2019
The Yearbook identifies opportunities and challenges for mitigation and resilience in the seven thematic areas of the Marrakech Partnership (land use, oceans and coastal zones, water, human settlements, transport, energy and industry) and the cross-cutting area of finance
מידע נוסף

Meeting the looming policy challenge of sea-level change and human migration
Minimizing the adverse consequences of sea-level change presents a key societal challenge. New modelling is necessary to examine the implications of global policy decisions that determine future greenhouse gas emissions and local policies around coastal risk that influence where and how we live
מידע נוסף

Global Climate Report - October 2019
Last October was Earth’s second-hottest October in recorded history, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The agency announced that average global land and ocean surface temperatures in October were 1.76 degrees above the 20th century average.
מידע נוסף

שינוי האקלים בישראל מגמות עבר ומגמות חזויות במשטר הטמפרטורות והמשקעים
בדו"ח זה לראשונה מציג השירות המטאורולוגי ניתוח בהיקף נרחב של מגמות הטמפרטורה
וכמויות המשקעים על בסיס נתוני העבר מכל רחבי הארץ וניתוח תחזיות של מודלים אקלימיים
אזוריים לעשורים הקרובים
מידע נוסף
וכמויות המשקעים על בסיס נתוני העבר מכל רחבי הארץ וניתוח תחזיות של מודלים אקלימיים
אזוריים לעשורים הקרובים

The 2019 report of The Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: ensuring that the health of a child born today is not defined by a changing climate
The Lancet Countdown is an international, multidisciplinary collaboration, dedicated to monitoring the evolving health profile of climate change, and providing an independent assessment of the delivery of commitments made by governments worldwide under the Paris agreement
מידע נוסף

Perspectives of climate change adaptation of building areas against heat waves
This paper makes a contribution to the 11th SDG "Sustainable Cities and Communities" with the target to improve the adaptation to climate change and resilience to disasters in terms of summer heat
מידע נוסף

World Scientists’ Warning of a Climate Emergency
Scientists have a moral obligation to clearly warn humanity of any catastrophic threat and to “tell it like it is”
מידע נוסף

GAR19 - Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction
This fifth edition of the United Nations Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction (GAR) is being issued four years after the adoption of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030 (Sendai Framework).
מידע נוסף

2019 Refinement to the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories
The 2019 Refinement to the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories was adopted and accepted during the 49th Session of the IPCC in May 2019
מידע נוסף

Gender-Transformative Climate Change Adaptation: Advancing Social Equity
Power and gender inequalities can constrain and undermine climate change adaptation. Those who are vulnerable and marginalized, with limited access to resources and assets, are already facing formidable barriers in adapting to climate change. Ignoring this challenge is maladaptive, as it adds to the vulnerabilities of those already burdened disproportionately and encourages new types of exclusions. Meeting the challenge requires that we transform our societies into fairer and more just organizat
מידע נוסף

2019 - IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate
The latest Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Special Report
highlights the urgency of prioritizing timely, ambitious and coordinated action to address
.unprecedented and enduring changes in the ocean and cryosphere
מידע נוסף
highlights the urgency of prioritizing timely, ambitious and coordinated action to address
.unprecedented and enduring changes in the ocean and cryosphere

Quantifying the impact of changing the threshold of New York City heat emergency plan in reducing heat-related illnesses
The adverse health impact of high heat is widely documented and can lead to a substantial public health burden. Although heat-related illness in western countries is largely preventable, extreme heat remains the main weather contributor to the burden of disease in the United States.
מידע נוסף

Risks Associated to Climate and Environmental Changes in the Mediterranean Region
Recent accelerated climate change has exacerbated existing environmental problems in the Mediterranean Basin that are caused by the combination of changes in land use, increasing pollution and declining biodiversity. In most impact domains (such as water, ecosystems, food, health and security), current changes and future scenarios consistently point to significant and increasing risks during the coming decades. Policies for the sustainable development of Mediterranean countries need to mitigate
מידע נוסף

The Role of Green Infrastructures in Urban Planning for Climate Change Adaptation
The population that lives in cities has surpassed the one that lives in the countryside. Cities are recognized as apriority source of pollution. The degradation of air quality and the phenomenon of Urban Heat Island (UHI) are some of the most well-known consequences of urban development. The adaptation of the cities is emerging as one of the greatest challenges that urban planners will face in this century. Urban Green Infrastructures (GIs) could help cities adapt to climate change
מידע נוסף

Peak energy, peak oil, and the rise of renewables: An executive’s guide to the global energy system
In this episode of the McKinsey Podcast, Simon London speaks with senior partners Namit Sharma and Christer Tryggestad about their research in the Global Energy Perspective 2019 and
.where global energy demand is headed in the decades to come
מידע נוסף
.where global energy demand is headed in the decades to come

UN 2019 sixth Global Environment Outlook: GEO-6 - Summary for Policymakers
UN Environment’s sixth Global Environment Outlook (2019) calls on decision makers to take immediate action to address pressing environmental issues to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals as well as other Internationally Agreed Environment Goals, such as the Paris Agreement
מידע נוסף

The case for strategic and managed climate retreat
Faced with global warming, rising sea levels, and the climate-related extremes they intensify, the question is no longer whether some communities will retreat—moving people and assets out of harm's way—but why, where, when, and how they will retreat.
מידע נוסף

Accelerating Climate Action
This report builds on the OECD Well-being Framework and applies a new perspective that analyses synergies and trade-offs between climate change mitigation and broader goals such as health, education, jobs, as well as wider environmental quality and the resources needed to sustain our livelihoods through time
מידע נוסף

Tracking global climate change adaptation among governments
The Paris Agreement and Katowice Climate Package articulate a clear mandate for all parties to undertake and document adaptation progress. Yet persistent challenges have prevented substantive developments in tracking adaptation and the assessment of adaptation actions and their outcomes
מידע נוסף

Building and Measuring Community Resilience: Actions for Communities and the Gulf Research Program
The frequency and severity of disasters over the last few decades have presented unprecedented challenges for communities across the United States. In 2005, Hurricane Katrina exposed the complexity and breadth of a deadly combination of existing community stressors, aging infrastructure, and a powerful natural hazard. In many ways, the devastation of Hurricane Katrina was a turning point for understanding and managing disasters, as well as related plan making and policy formulation. It brought t
מידע נוסף

Business Climate Resilience: Thriving Through the Transformation
WBCSD’s report brings together important global developments and latest thinking on climate adaptation and resilience, with particular focus on private sector climate resilience. It builds on the need for businesses to prepare for both the physical risks that are associated with climate change, as well as the associated transitional risks on the path towards a net-zero economy
מידע נוסף

ערים בעידן של שינוי אקלים — זירות של פגיעוּת והיערכות
ערים נחשבות לפגיעות במיוחד לשינוי אקלים ולאירועי מזג אוויר קיצוניים. לנוכח ההכרה
בפגיעות העירונית ובעקבות שורה של אסונות טבע שהיכו בערים ברחבי העולם, מתחילות ערים
רבות ברחבי העולם להיערך לשינוי האקלים. השיח המרכזי בהיערכות העירונית לשינוי האקלים
נסוב סביב מושג החוסן העירוני, המתואר לרוב כיכולת של עיר נתונה להתמודד בהצלחה עם מגוון
של לחצים ואירועי קיצון. תוכניות להגברת החוסן העירוני מתייחסות לסך הפעולות שיש לבצע
מבעוד מועד כדי להפחית את עוצמת הפגיעה וכן לשפר את היכולת להתאושש לאחריה. המאמר ס
מידע נוסף
בפגיעות העירונית ובעקבות שורה של אסונות טבע שהיכו בערים ברחבי העולם, מתחילות ערים
רבות ברחבי העולם להיערך לשינוי האקלים. השיח המרכזי בהיערכות העירונית לשינוי האקלים
נסוב סביב מושג החוסן העירוני, המתואר לרוב כיכולת של עיר נתונה להתמודד בהצלחה עם מגוון
של לחצים ואירועי קיצון. תוכניות להגברת החוסן העירוני מתייחסות לסך הפעולות שיש לבצע
מבעוד מועד כדי להפחית את עוצמת הפגיעה וכן לשפר את היכולת להתאושש לאחריה. המאמר ס

Adapt Now: A Global Call for Leadership on Climate Resilience - 2019
This report focuses on making the case for climate adaptation, providing specific insights
and recommendations in key sectors: food security, the natural environment, water, cities and
urban areas, infrastructure, disaster risk management, and finance. It is designed to inspire
action among decision-makers
מידע נוסף
and recommendations in key sectors: food security, the natural environment, water, cities and
urban areas, infrastructure, disaster risk management, and finance. It is designed to inspire
action among decision-makers

Challenges to natural and human communities from surprising ocean temperatures
Based on historical and lived experience, people expect certain conditions to prevail in the ecosystems they depend upon. Climate change is now introducing strong trends that push conditions beyond historic levels. Using ocean ecosystems as a case study, we show that the frequency of surprising temperatures is increasing faster than expected. We then use these events as motivation to develop a theory for how temperature trends and events will impact natural and human communities
מידע נוסף

The Global Climate in 2015–2019
Compared to the previous five-year assessment period 2011–2015, the current five-year period 2015–2019 has seen a continued increase in carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions
and an accelerated increase in the atmospheric concentration of major greenhouse
gases (GHGs), with growth rates nearly 20% higher
מידע נוסף
and an accelerated increase in the atmospheric concentration of major greenhouse
gases (GHGs), with growth rates nearly 20% higher

The Global Risks Report 2019
The Global Risks Report 2019 is published against a backdrop of worrying geopolitical and geo-economic tensions. If unresolved, these tensions will hinder the world’s ability to deal with a growing range of collective challenges
מידע נוסף

Tracking the progress of climate change adaptation: An Australian case study
The six adaptation conferences organised by the National Climate Change Adaptation Research Facility between 2010 and 2018 provide a unique and novel opportunity to track adaptation progress in Australia
מידע נוסף

A Land Without Water
Climate change, waves of refugees and poor planning are draining water supplies
in Jordan
מידע נוסף
in Jordan

Climate change adaptation in the agriculture sector in Europe
Climate change affects agriculture in a number of ways. Changes in temperature and precipitation as well as weather and climate extremes are already influencing crop yields and livestock productivity in Europe. Weather and climate conditions also affect the availability of water needed for irrigation, livestock watering practices, processing of agricultural products, and transport and storage conditions
מידע נוסף

Changing climate both increases and decreases European river floods
Climate change has led to concerns about increasing river floods resulting from the greater water-holding capacity of a warmer atmosphere. These concerns are reinforced by evidence of increasing economic losses associated with flooding in many parts of the world, including Europe
מידע נוסף

Monitoring and Evaluating Climate Adaptation Activities: A Reference Guide for City Managers
Cities are leading the way in committing to ambitious climate adaptation goals and implementing strategies to reduce climate risks. However, these commitments to adaptation action often face challenges in documenting changes in resilience of urban systems and populations. To capture these adaptation results, cities will need to develop robust monitoring and reporting frameworks to measure achievement, document outcomes and learn from their adaptation activities
מידע נוסף

Transformative adaptation to climate change for sustainable social-ecological systems
In the face of major shifts in temperature and precipitation, some conventional strategies that help people to cope or incrementally adapt to climate change may become inappropriate in the long-term. Transformative adaptation, i.e. fundamental systems’ changes that address root causes of vulnerability may be needed
מידע נוסף

Managing global catastrophic risks - Part 1 - Understand
Sponsored by the Centre for the Study of Existential Risk (CSER), this report is dedicated to providing options for policy-makers to better understand, mitigate, prepare for, respond to and communicate about global catastrophic risks
מידע נוסף

Valuing the Global Mortality Consequences of Climate Change Accounting for Adaptation Costs and Benefits
We develop empirically-grounded estimates of willingness-to-pay to avoid excess mortality risks caused by climate change. Using 40 countries' subnational data, we estimate a mortality-temperature relationship that enables global extrapolation to countries without data and projection of its future evolution, accounting for adaptation benefits. Further, we develop a revealed preference approach to recover unobserved adaptation costs
מידע נוסף

Tens of thousands additional deaths annually in cities of China between 1.5 °C and 2.0 °C warming
The increase in surface air temperature in China has been faster than the global rate, and more high temperature spells are expected to occur in future. Here we assess the annual heat-related mortality in densely populated cities of China at 1.5 °C and 2.0 °C global warming
מידע נוסף

How does gendered vulnerability shape the adoption and impact of sustainable livelihood interventions in an era of global climate change?
Though many studies have long considered the broad social implications of climate change, researchers have only recently started to consider the gendered unevenness of the global landscape of vulnerability, exposure, and adaptive capacity to environmental stressors and shocks
מידע נוסף

Breathing life into climate change adaptation
The exploration of evolutionary biology and biological adaptation can inform society's adaptation to climate change, particularly the mechanisms that bring about adaptability, such as phenotypic plasticity, epigenetics, and horizontal gene transfer. Learning from unplanned autonomous biological adaptation may be considered undesirable and incompatible with human endeavor. However, it is argued that there is no need for agency, and planned adaptation is not necessarily preferable over autonom
מידע נוסף

Adaptive responses of animals to climate change are most likely insufficient
Biological responses to climate change have been widely documented across taxa and regions, but it remains unclear whether species are maintaining a good match between phenotype and environment, i.e. whether observed trait changes are adaptive. Here we reviewed 10,090 abstracts and extracted data from 71 studies reported in 58 relevant publications, to assess quantitatively whether phenotypic trait changes associated with climate change are adaptive in animals
מידע נוסף

Responsibility for climate change adaptation
As a policy process, climate change adaptation is rapidly advancing. Yet fundamental questions remain unanswered including, who is responsible for planned adaptation and when, who is liable for losses and damages resulting from climate change and how is responsibility distributed in a multilevel governance system? Responsibility can be evaluated in terms of the timing of particular events, the specific societal actors involved and the rules and norms used to attribute responsibility for dealing
מידע נוסף

WMO Statement on the State of the Global Climate in 2018
This publication marks the twenty-fifth anniversary of the WMO Statement on the State of the Global Climate, which was first issued in 1994. The 2019 edition treating data for 2018 marks sustained international efforts dedicated to reporting on, analysing and understanding the year-to-year variations and long-term trends of a changing climate
מידע נוסף

Increased frequency of and population exposure to extreme heat index days in the United States during the 21st century
The National Weather Service of the United States uses the heat index—a combined measure of temperature and relative humidity—to define risk thresholds warranting the issuance of public heat alerts. We use statistically downscaled climate models to project the frequency of and population exposure to days exceeding these thresholds in the contiguous US for the 21st century with two emissions and three population change scenarios
מידע נוסף

The imperative of climate action to protect human health in Europe
The report focuses on the consequences of climate change for human health in Europe and the benefits of acting now to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in order to stabilise the climate
מידע נוסף

Agrivoltaics provide mutual benefits across the food–energy–water nexus in drylands
The vulnerabilities of our food, energy and water systems to projected climatic change make building resilience in renewable energy and food production a fundamental challenge
מידע נוסף

Adaptation challenges and opportunities for the European energy system
This report analyses the needs for climate change adaptation and climate resilience in Europe’s energy system now and in the future. This assessment supports the clean energy transition, which involves a massive expansion of renewable energy sources, many of which are sensitive to climate factors
מידע נוסף

Microbiologists' Warning to Humanity: microorganisms and climate change
This Consensus Statement documents the central role and global importance of microorganisms In climate change biology
מידע נוסף

Deep-ocean climate change impacts on habitat, fish and fisheries
This publication focuses on the impacts of climatic changes on demersal fisheries, and the interactions of these fisheries with other species and vulnerable marine ecosystems. The principal cause of climate change is rising greenhouse gases and other compounds in the atmosphere that trap heat causing global warming, leading to deoxygenation and acidification in the oceans
מידע נוסף

Climate change adaptation at different levels of government: Characteristics and conditions of policy change
Climate change adaptation strategies that aim to minimize harm and maximize benefits related to climate change impacts have mushroomed at all levels of government in recent years. While many studies have explored barriers that stand in the way of their implementation, the factors determining their potential to mainstream adaptation into various sectors are less clear. In the present paper, we aim to address this gap for two international, six national, and six local adaptation strategies.
מידע נוסף

Responding to Rising Seas - OECD Country Approaches to Tackling Coastal Risks
There is an urgent need to ensure that coastal areas are adapting to the impacts of climate change. Risks in these areas are projected to increase because of rising sea levels and development pressures. This report reviews how OECD countries can use their national adaptation planning processes to respond to this challenge
מידע נוסף

Managed retreat as a strategy for climate change adaptation in small communities: public health implications
In coming decades, sea level rise associated with climate change will make some communities uninhabitable. Managed retreat, or planned relocation, is a proactive response prior to catastrophic necessity. Managed retreat has disruptive health, sociocultural, and economic impacts on communities that relocate. Health impacts include mental health, social capital, food security, water supply, sanitation, infectious diseases, injury, and health care access
מידע נוסף

Action Plan on Climate Change Adaptation and Resilience
The accelerating impacts of climate change, and the need to avoid much larger impacts in the future, bring urgency to scaling up action on adaptation and resilience
מידע נוסף

Public Bureaucracy and Climate Change Adaptation
Despite recognizing the importance of public bureaucracies in governing climate change, our knowledge of how their behavioral and structural characteristics influence climate change adaptation policy is limited. This article provides an introduction to a collection of studies that seeks to explore the link between climate change adaptation and public bureaucracies, and to distill lessons for the scholarship on adaptation as well as the persistent debates on the role of administrative traditions
מידע נוסף

Biodiversity and Climate Change Adaptation in Tropical Islands
Biodiversity and Climate Change Adaptation in Tropical Islands provides comprehensive information on climate change, biodiversity, possible impacts, adaptation measures and policy challenges to help users rehabilitate and preserve the natural resources of tropical islands. While biodiversity and climate change of tropical islands has previously received less attention, it is ironically one of the most vulnerable regions in this regard. The core content of the work derives largely from the ideas
מידע נוסף

Climate Change Adaptation - Research, Science and Innovation
The historic Paris Agreement set out the challenging long-term goal of keeping global warming to “well below” 2°C above pre-industrial levels while pursuing efforts to limit it to 1.5°C. At the same time, it called on societies to build up their resilience and ability to adapt to the adverse impacts of climate change
מידע נוסף

Scientists Warn and Call for the Protection of our Planet
We have never been in the history of mankind as a species in such a moment and place. We have
never faced such a challenge during our stay on this planet. Such a great mobilization of scientists from around the world has never happened before
מידע נוסף
never faced such a challenge during our stay on this planet. Such a great mobilization of scientists from around the world has never happened before

Monitoring and Evaluation Indicators for Climate Change-Related Health Impacts, Risks, Adaptation, and Resilience
Climate change poses a range of current and future health risks that health professionals need to understand, track, and manage. However, conventional monitoring and evaluation (M&E) as practiced in the health sector, including the use of indicators, does not adequately serve this purpose. Improved indicators are needed in three broad categories: (1) vulnerability and exposure to climate-related hazards; (2) current impacts and projected risks; and (3) adaptation processes and health system resi
מידע נוסף

Impacts of climate change on transport: A focus on airports, seaports and inland waterways
The report assesses the impacts of climate change on transport for Europe using projections of climate data, coastal inundation, river flooding and river discharge data. Impacts considered include those of sea level rise, storm surges, extreme weather events and floods on airports and seaports, as well as floods and droughts on inland waterways. Main outputs include the identification of transport infrastructure at risk in future time periods and the estimation of economic impacts
מידע נוסף

Climate Change Adaptation for Transportation Systems
Climate Change Adaptation for Transportation Systems examines the international state of knowledge on climate change and weather and their potential impacts on the planning, design and serviceability of transportation networks. The book describes alternative frameworks for adapting to climate change in the planning, provision and management of transportation systems. It discusses methods and models for including climate and weather factors in planning and design for use in transportation asset s
מידע נוסף

A roadmap to effective urban climate change adaptation
This paper outlines a roadmap to effective urban climate change adaptation built from our practical understanding of the evidence and effects of climate change and the preparation of climate change adaptation strategies and plans. This roadmap aims to drive research in achieving fruitful knowledge and solution-based achievable recommendations in adapting to climate change in urban areas with effective and systematic manner
מידע נוסף

The Adaptation Gap Health Report - 2018
The 2018 Adaptation Gap Report has two parts. First, it provides an overview of the status and trends of the adaptation gap in terms of vulnerability to climate change, adaptation costs and finance, and countries’ adaptation commitments and actions. Second, the report undertakes an
in-depth assessment of the adaptation gap in health
מידע נוסף
in-depth assessment of the adaptation gap in health

Port industry survey on climate change impacts and adaptation
Ports are critical infrastructure assets that serve as catalysts of economic growth and development. At the same time, they are also exposed to the risk of the impacts of climate variability and change, particularly in view of their location in coastal zones, low-lying areas and deltas
מידע נוסף

Climate Change, Impacts and Vulnerability in Europe 2016 - An Indicator-based Report
This report is an indicator-based assessment of past and projected climate change and its impacts on ecosystems and society. It also looks at society’s vulnerability to these impacts and at the development of adaptation policies and the underlying knowledge base.
מידע נוסף

Communicating Climate Change Adaptation and Resilience
Communicating the impacts of climate change and possible adaptive responses is a relatively recent branch of the larger endeavor of climate change communication. This recent emergence, in large part, is driven by the fact that the impacts and policy/planning/practice responses have only recently emerged in more widespread public consciousness and discourse, and thus in scholarly treatment
מידע נוסף

Making the Case for Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems as a Nature-Based Solution to Urban Flooding
European cities continue to experience a steady increase in the intensity and frequency of floods, largely due to high urban densities and resultant soil sealing. In the last decade, flooding as a natural hazard has produced the highest economic losses in Europe and storm water management has become a serious urban challenge.
מידע נוסף

WMO Statement on the State of the Global Climate 2017
The global mean temperature in 2017 was approximately 1.1 °C above the pre-industrial
era, more than half way towards the maximum limit of temperature increase of 2 °C sought through the Paris Agreement, which further strives to limit the increase to C 1.5 ° above pre- Industrial levels
מידע נוסף
era, more than half way towards the maximum limit of temperature increase of 2 °C sought through the Paris Agreement, which further strives to limit the increase to C 1.5 ° above pre- Industrial levels

The Adaptation Gap Report
The 2017 Adaptation Gap Report, which is the third global Adaptation Gap Report by UN Environment – prepared in collaboration with the Global Centre of Excellence on Climate Adaptation – focuses on one of the key questions arising in the wake
of the global goal: What are the ways forward to assess progress towards the global goal on
adaptation?
מידע נוסף
of the global goal: What are the ways forward to assess progress towards the global goal on
adaptation?

WMO Statement on the state of the global climate in 2016
This latest report confirms that 2016 was the warmest year on record: a remarkable 1.1 °C above the pre-industrial period, which is 0.06 °C above the previous record set in 2015. This increase in global temperature is consistent with other changes in the climate system.
מידע נוסף

Master ADAPT Project - Climate Change Adaptation Practices Across the EU Countries
Within the EU, southern Europe, and the Mediterranean basin in particular, will be most affected by global climate change. Strategies and plans for adaption to climate change are developed at national and regional level in the EU
מידע נוסף

Advancing climate adaptation practices and solutions: Emerging research priorities
This paper builds on insights from Adaptation Futures 2016: Practices and Solutions – the largest
gathering of adaptation experts to date – to identify research priorities at a time when adaptation
is scaling up and moving from planning to implementation around the world. It traces the
evolution of adaptation research over time, reflects on how it has evolved, maps what it looks
like today, anticipates research directions and gaps, and articulates new research priorities

Climate Change Adaptation in Pacific Countries: Fostering Resilience Through Gender Equality
Women and girls are disproportionately affected by the impacts of climate change in the Pacific due to prevailing gender inequalities. Meanwhile, the participation and leadership of women in climate change adaptation has been identified globally as critical for fostering resilience in families, communities and nations
מידע נוסף

דו"ח הוועדה לקביעת מדדים ודרכי ניהול פעילות שטח בתנאי אקלים חריגים עבור אוכלוסיות משרד החינוך
דו"ח זה מסכם המלצות עדכניות המבוססות על המידע הרפואי / מחקרי הקיים היום, על המידע התפעולי / מחקרי של ניהול מצבי חירום ואסון, על מידע ניהולי וארגוני ועל ידע צבור של ניהול, מניעה ועזרה ראשונה מעשיים בשטח.
בסיכום כל פרק מופיעות המלצות קצרות וברורות אשר יסייעו באיזון גורמי הסיכון ע''מ למנוע פגיעות ותמותה. המסמך סוקר את ההמלצות למענה במניעה ראשונית ובמניעה שניונית של מעטפת ארגונית, עזרים, קריאת מצבים וניהולם.
מידע נוסף
בסיכום כל פרק מופיעות המלצות קצרות וברורות אשר יסייעו באיזון גורמי הסיכון ע''מ למנוע פגיעות ותמותה. המסמך סוקר את ההמלצות למענה במניעה ראשונית ובמניעה שניונית של מעטפת ארגונית, עזרים, קריאת מצבים וניהולם.

Adapting to Climate Change: The Remarkable Decline in the US Temperature-Mortality Relationship over the Twentieth Century
This paper examines the temperature-mortality relationship over the course of the twentieth-century United States both for its own interest and to identify potentially useful adaptations for coming decades. There are three primary findings. First, the mortality impact of days with mean temperature exceeding 80°F declined by 75 percent. Almost the entire decline occurred after 1960. Second, the diffusion of residential air conditioning explains essentially the entire decline in hot day–related fa
מידע נוסף

הצללה במוסדות חינוך ובמגרשי משחקים בגנים ציבוריים
מסמך זה נכתב לבקשת חברת הכנסת ד"ר יפעת שאשא ביטון, יושבת ראש הוועדה לזכויות הילד, לקראת - דיון בוועדה לזכויות הילד בנושא הצללה במוסדות חינוך ובמגרשי משחקים. אמצעי התקשורת מדווחים מזמן לזמן על מקרים של ילדים שנכוו ממתקני משחקים שהפכו ללוהטים בשל חשיפה ממושכת לחום השמש, במגרשים שהצללה בהם לא נכונה או אין בהם הצללה כלל.
מידע נוסף

Periodic Report Summary 1 - DYNAMIC (DYNamic feedbacks of climate impacts on current Adaptation and Mitigation Investment Choice)
The DYNAMIC (DYNamic feedbacks of climate impacts on current Adaptation and Mitigation Investment Choice) project proposes a novel framework to evaluate the economic consequences of climate change impacts and related policy responses.
מידע נוסף

בחינת תרומת קבוצות סוציו אקונומיות בישראל לפליטות גזי חממה מצריכת מזון ביתי
לייצור המזון, במיוחד בחקלאות התעשייתית, נודעת השפעה ממשית על היקף פליטות גזי חממה באופן ישיר או עקיף. גזי חממה אלו נוצרים בכל שלבי מחזור החיים של המזון, החל משלב החקלאות ותשומותיו, דרך הייצור, הפצה, קירור, קמעונאות, הכנת המזון בבית וכלה בסילוק הפסולת.למעשה, בעוד שבמחקרים השונים קיימת הסכמה על כך שפליטות גזי חממה מייצור המזון וצריכתו מהוות חלק משמעותי מפליטות גזי החממה בעולם, המחלוקת המחקרית נסובה סביב הערכת היקף הפליטות. לדוגמא, לפי דוח של האו"ם מ- 2014 14.5% מפליטות גזי החממה כתוצאה מפעילו
מידע נוסף

Climate Adaptation: Seizing the Challenge
The World Economic Forum’s Global Agenda Council on Climate Change’s report, Climate Adaptation: Seizing the Challenge, captures some of the latest thinking in the field of climate adaptation and financing, with the goal of assisting decision-makers in the public and private sectors gain a better understanding of the issue
מידע נוסף

Explaining Extreme Weather Events of 2013 from a Climate Perspective
The annual Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society (BAMS) special issue on the attribution of last year’s extreme weather events is published today. This year’s issue “explaining extreme events of 2013 – from a climate perspective” includes two papers led by researchers from our climateprediction. This is a highly-cited and influential annual publication coined in 2012 asking whether and to what extent anthropogenic climate change altered the risk of major extreme weather events of the p
מידע נוסף

Lima call for climate action- Decision
Climate Action & UNEP delivered their fifth annual Sustainable Innovation Forum on December 9 in Lima. This year’s event brought together close to 500 leaders from key United Nations bodies, governments, international & regional companies and leading non-governmental organisations (NGO's).
מידע נוסף

מדדים לאיכות חיים, לקיימות ולחוסן לאומי
מדידת חוסן: המונח חוסן resilience נעשה רווח בשיח הציבורי בשנים האחרונות. החוסן הפך
עיקרון מנחה בתכנון של מערכות תשתית, בתכנון עירוני, בהיערכות לאירועי משבר סביבתיים,
כלכליים וחברתיים וכן בארכיטקטורה של מערכות מורכבות שונות ברחבי העולם.
מידע נוסף
עיקרון מנחה בתכנון של מערכות תשתית, בתכנון עירוני, בהיערכות לאירועי משבר סביבתיים,
כלכליים וחברתיים וכן בארכיטקטורה של מערכות מורכבות שונות ברחבי העולם.

United Kingdom national adaptation programme: Making the country resilient to a changing climate
This report outlines the steps government, businesses and communities are already taking to address the most severe and urgent threats of climate change, as identified by Defra last year in its Climate Change Risk Assessment
מידע נוסף

Urban Forest Strategy - City of Sydney
In 2012 the City of Sydney (the City) adopted the Greening Sydney Plan. One of the key elements of that Plan is to develop and protect the City’s urban forest. This Urban Forest Strategy outlines the way the City will work to improve the environment, using trees, while managing the associated risks and costs
מידע נוסף

Climate Change Adaptation in Israel
In accordance with a June 2009 decision by the Israel Government, the Ministry of Environmental Protection is preparing a national climate change adaptation program aimed at reducing the adverse effects of global changes on water scarcity, drought and increased frequency of extreme events, among others
מידע נוסף

Climate Change Risk Assessment for the Agriculture Sector
UK agriculture could be significantly affected by climate change Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns, changes in sunshine levels and in concentrations of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2), and increasing frequency of weather events currently considered extreme would all have an impact on operations, productivity and the range of products offered by
the sector
מידע נוסף
the sector

Climate Prediction for Adaptation: Who needs what?
The role of short- and long-term climate predictions in determining the success of adaptation to climate change is investigated. A simple theoretical model that captures the relationship between adaptive performance, decision structure, and prediction accuracy at different temporal scales is developed, and its implications deduced. It is shown that users who face high adjustment costs (i.e. are inflexible) depend more heavily on accurate long-term predictions than those who are able to adjust
מידע נוסף

UK climate change risk assessment: government report
The Government published the UK Climate Change Risk Assessment (CCRA) on 25 January 2012, the first assessment of its kind for the UK and the first in a 5 year cycle. It sets out the main priorities for adaptation in the UK under 5 key themes identified in the CCRA 2012 Evidence Report - Agriculture and Forestry; Business, industries and Services; Health and Wellbeing; Natural Environment and Buildings and Infrastructure - and describes the policy context, and action already in place to tackle
מידע נוסף

Urban Forest Strategy: Making a great city greener 2012-2032
This is the City of Melbourne’s first Urban Forest Strategy. It is the product of a collaborative
process, developed over two years with a large number of stakeholders including local and
the broader community in Melbourne
מידע נוסף
process, developed over two years with a large number of stakeholders including local and
the broader community in Melbourne

2011 Bonn Declaration of Mayors
This declaration is the outcome document of the Mayors Adaptation Forum, which forms the Mayors segment of the Resilient Cities 2011 congress. It highlights the need to build resilience to disasters as a critical issue. It also signals the need to take appropriate action to build local capacities in reducing risk to disasters including those exacerbated by climate change.
The declaration advocates for the implementation of the following: (i) mainstreaming new adaptation and resilience standard
מידע נוסף
The declaration advocates for the implementation of the following: (i) mainstreaming new adaptation and resilience standard

A double-resolution transient RCM climate change
A double-resolution regional experiment on hydrodynamic simulation of climate over the eastern Mediterranean (EM) region was performed using an International Center for Theoretical Physics, Trieste RegCM3 model. The RegCM3 was driven from the lateral boundaries by the data from the ECHAM5/MPI-OM global climate simulation performed at the MPI-M, Hamburg and based on the A1B IPCC scenario of greenhouse gases emission. Two simulation runs for the time period 1960-2060, employing spatial resolutions
מידע נוסף

Climate Change Adaptation and Real Option Evaluation: A Case Study in Campeche, Mexico
This report illustrates the application of a (relatively) new method to guide decision making under high (and unknowable) levels of uncertainty. The approach allows for the identification of robust policy options that are economically beneficial under different scenarios and varying levels uncertainty. Option value techniques are commonly employed in the finance literature to identify investment decisions that are resilient across a spectrum of outcomes. The methods are technically advanced
מידע נוסף

ipcc summary for policymakers
The Working Group III Special Report on Renewa
ble Energy Sources and Climate Change
Mitigation (SRREN) presents an assessment of th
e literature on the scientific, technological,
environmental, economic and social aspects of
the contribution of six renewable energy (RE)
sources to the mitigation of climate change. It is
intended to provide policy relevant information to
governments, intergovernmental processes and ot
her interested parties. This Summary for
Policymakers provides an ov
מידע נוסף
ble Energy Sources and Climate Change
Mitigation (SRREN) presents an assessment of th
e literature on the scientific, technological,
environmental, economic and social aspects of
the contribution of six renewable energy (RE)
sources to the mitigation of climate change. It is
intended to provide policy relevant information to
governments, intergovernmental processes and ot
her interested parties. This Summary for
Policymakers provides an ov
Climate change- vulnerability and adaptation indicators
The purpose of this Technical Paper is to rehearse some fundamental concepts surrounding the
development and delineation of adaptation indicators. It builds upon the outputs of an Expert meeting
on climate change vulnerability and adaptation indicators (Budapest, September 2008) and on the
contents of a Background Paper that was prepared for the meeting.
מידע נוסף
development and delineation of adaptation indicators. It builds upon the outputs of an Expert meeting
on climate change vulnerability and adaptation indicators (Budapest, September 2008) and on the
contents of a Background Paper that was prepared for the meeting.